PASCO CI-6729 (1X) CONDUCTIVITY SENSOR User Manual
Page 17
13
012–06485B
Conductivity Sensor
Experiment 3: Temperature Dependence of Conductivity in
Dilute Aqueous Solutions
Purpose
The purpose of this experiment is to explore the relationship between temperature and conductivity
in aqueous solutions.
Materials and Equipment Needed
• Conductivity Sensor
• sodium chloride (NaCl)
• Temperature Sensor
• 200 ml 0.005 M sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
• Temperature Sensor Teflon FEP cover
• 400 ml distilled or deionized H
2
O
• Science Workshop version 2.2.5 or higher
• 250 ml Erlenmeyer flask or beaker (5)
• PASCO computer interface
• hot plate with magnetic stirrer
• computer
• base and support rod
• Conductivity Sensor manual
• mass balance
• graduated cylinder
• buret clamps (2)
• apron, gloves, and goggles
Procedure
1. Soak the Conductivity Electrode in distilled or deionized H
2
O for 5–10 minutes.
2. Prepare a 0.1% NaCl solution by dissolving 200 mg of NaCl in 200 ml of distilled or deionized
H
2
O. Prepare a 0.4% NaCl solution by dissolving 800
mg of NaCl in 200 ml of distilled or deionized H
2
O.
Prepare a 0.005 M NaOH solution by dissolving 200
mg of NaOH in 1000 ml of distilled or deionized H
2
O.
A graduated cylinder should be used to measure 200
ml of H
2
O. Pour 150–200 ml of the solution into the
250 ml flask or beaker and place it on the hot plate.
The distilled H
2
O for the samples should be at room
temperature or below.
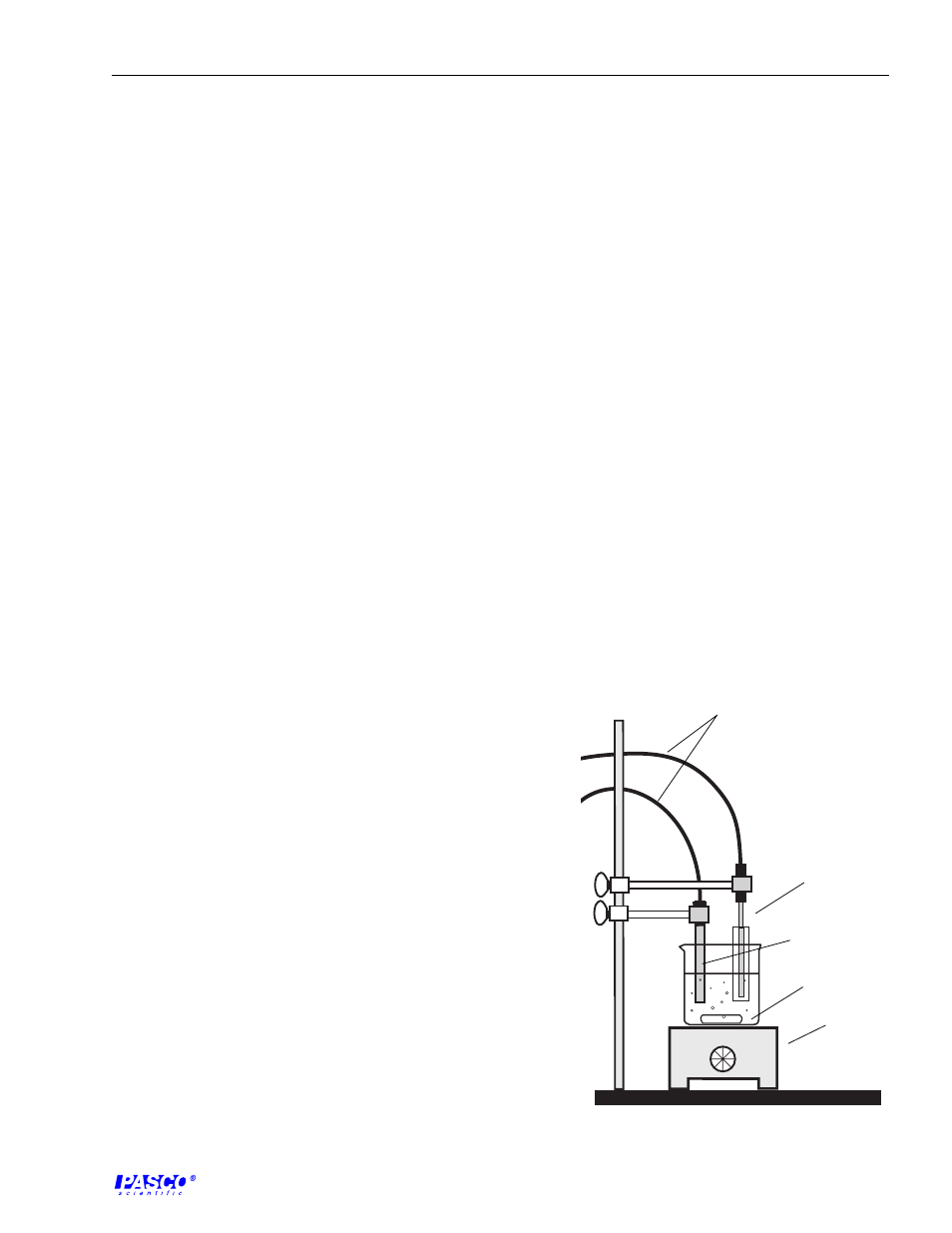
3. Insert the Temperature Sensor into the Teflon FEP
cover to isolate the grounded tip of the Temperature
Sensor from the conductive solution. Place the
Conductivity Electrode and Temperature Sensor into
the flask or beaker. Both electrodes should be supported
with buret clamps that are mounted on base and
support rods (see Figure 3.1).
Figure 3.1
Experiment Setup
Temperature
Sensor and
Teflon cover
conductivity
electrode
beaker &
spin bar
magnetic
stir-hot
plate
to computer
interface
