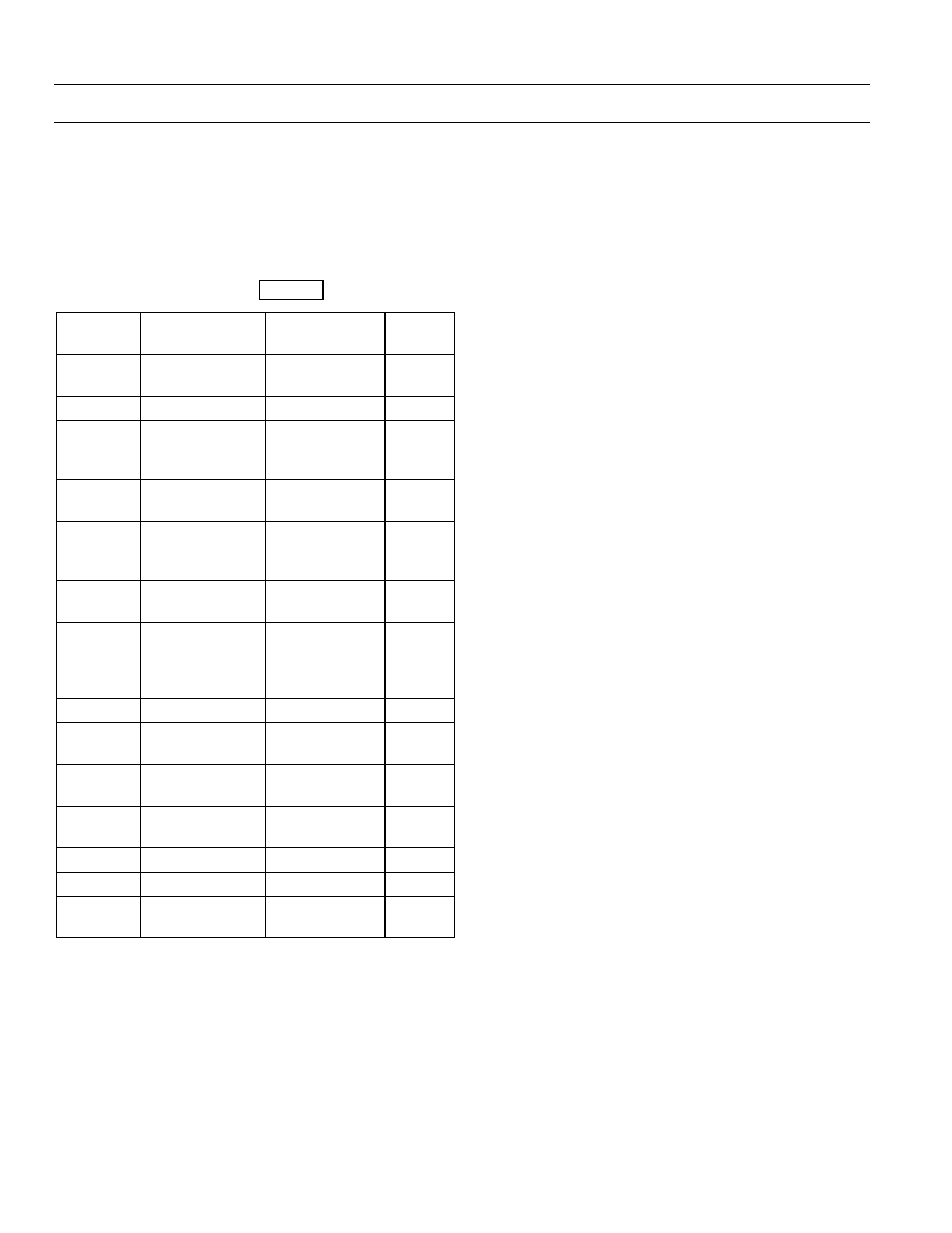
Table 12. ied addresses for case five – GE Industrial Solutions POWER LEADER PMCS Network Architecture Guide User Manual
Page 44
Power Management Control System
Chapter 2 – Network Design
34
met, Bill selects Modbus addresses for the IEDs. He checks
Section 2-7 and sees that he can assign the Modbus IEDs
on each network any Modbus address between 1 and 247
(except for the Modbus Concentrator, which must have an
address between 1 and 32). The commnet IEDs must have
Modbus-equivalent addresses between 33 and 247. He
selects addresses and records them for future reference.
The address chart is shown in Table 12.
RS-485
Network #
IED Type
Physical
Location
Modbus
Address
1
Multilin 565
Power intake
area
01
2
Multilin 269+
Assembly line
01
3
SR469 Motor
Management
Relay
Assembly line
01
3
Modbus Monitor
#1, RS-485 Port A
Lathe area
02
3
Multilin 239
Motor Protection
Relay
Machining area
03
3
Modbus Monitor
#2, RS-485 Port A
Machining
04
4
Multilin SR750
Feeder
Management
Relay
Milling area
01
4
EPM 3720
Milling area
02
4
Modbus Monitor
#1, RS-485 Port B
Lathe area
03
4
Modbus Monitor
#2, RS-485 Port B
Machining area
04
4
Modbus
Concentrator
Machining area
05
4
EMVT-C trip unit
Machining area
33
4
Spectra ECM
Machining area
34
4
POWER
LEADER EPM
Machining area
35
Table 12. IED Addresses for Case Five.
Chapter 3 provides Bill with physical wiring requirements
and rules. He’ll use Belden 3074F cable, readily available.
He also locates the correct terminating resistors at both
ends of each RS-485 network.
He installs the IEDs according to the instructions in each
IED’s user manual. He then makes connections to the RS-
485 communications cable in daisy-chain fashion, one IED
to the next, terminated at both ends of each RS-485
network, double-checking his wiring against the example
provided in Section 2–4. Since several of his Multilin IEDs
have two ports, he is careful to connect only one RS-485
port per IED. The Modbus Monitors are also RS-485 dual-
port, but Bill carefully follows the wiring instructions to
correctly connect them to the RS-485 networks. The A port
of each Monitor is connected to one RS-485 network and
the B port of each is connected to another network.
He must also bear in mind proper shield-grounding
considerations: each RS-485 IED grounded at only one
point and no two IEDs’ grounds connected (Rule 4,
Section 2-4). The Multilin 565 special grounding
considerations are also taken into account (see Chapters 2
and 3).
Bill assigns a Modbus address to each IED. He then sets
communication speeds and functional and protective
parameters according to the instructions in each user
manual.
Bill installs the PMCS software at the host PC and
configures IED addresses at the host to match the
addresses assigned to each IED on the network.
Configuration files for the Modbus Monitors are
downloaded to the units or created using the Monitor’s
“Create from PMCS” feature (see DEH-027 for details).
When all connections have been made and the IEDs and
software are appropriately configured, Bill applies power
to the system and runs tests to assure that everything is
functioning properly.
If any difficulties are encountered, Bill refers to the
trouble-shooting guide in Chapter 4.
