2 introduction to mib -22, 2 introduction to mib – QTECH QSW-2800 Инструкция по настройке User Manual
Page 36
+7(495) 797-3311 www.qtech.ru
Москва, Новозаводская ул., 18, стр. 1
22
the messages can’t be viewed on transmission. And USM authentication ensures that the
messages can’t be changed on transmission. USM employs DES-CBC cryptography. And
HMAC-MD5 and HMAC-SHA are used for authentication.
VACM is used to classify the users’ access permission. It puts the users with the same access
permission in the same group. Users can’t conduct the operation which is not authorized.
2.4.2 Introduction to MIB
The network management information accessed by NMS is well defined and organized in a
Management Information Base (MIB). MIB is pre-defined information which can be accessed
by network management protocols. It is in layered and structured form. The pre-defined
management information can be obtained from monitored network devices. ISO ASN.1 defines
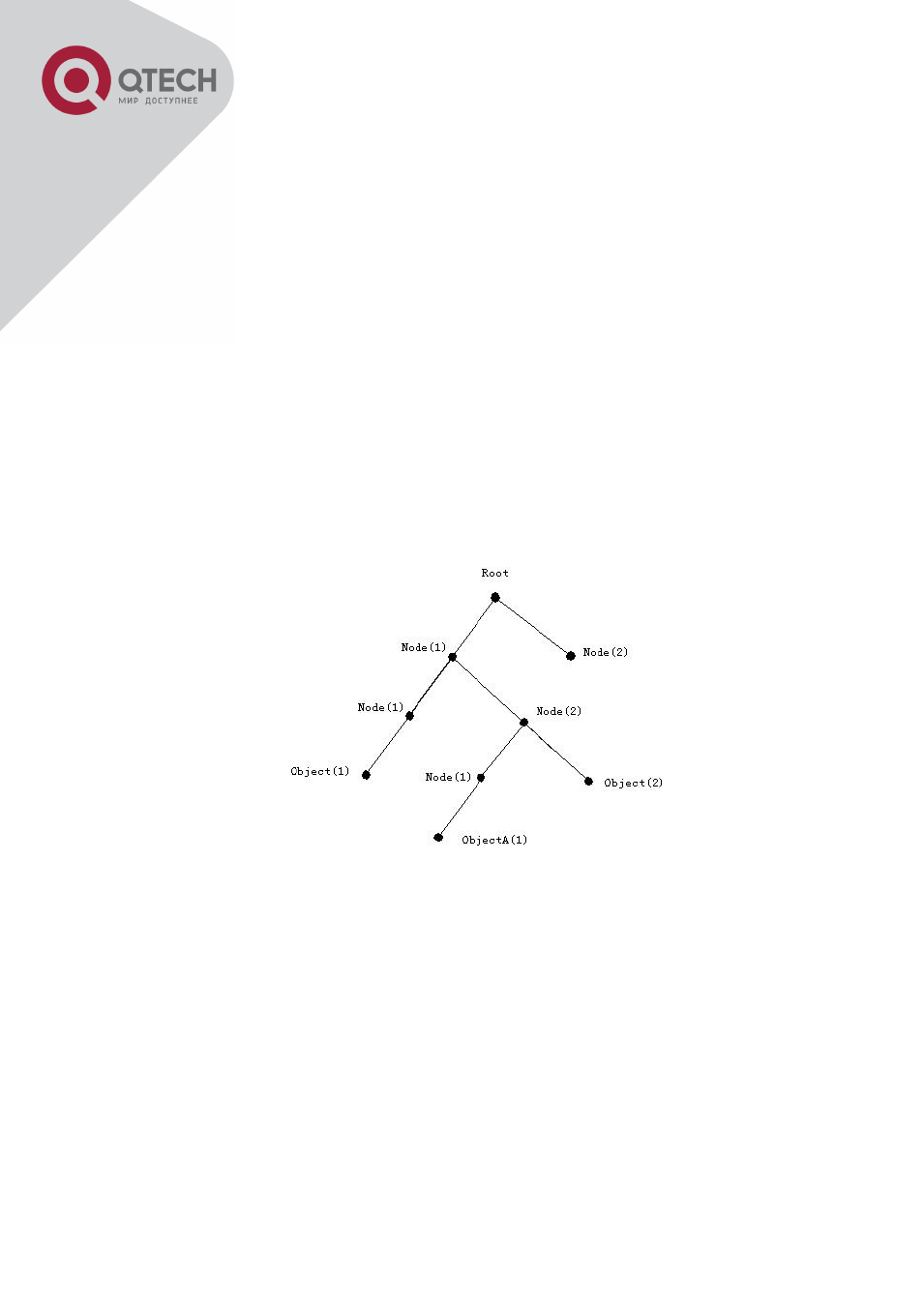
a tree structure for MID. Each MIB organizes all the available information with this tree
structure. And each node on this tree contains an OID (Object Identifier) and a brief description
about the node. OID is a set of integers divided by periods. It identifies the node and can be
used to locate the node in a MID tree structure, shown in the figure below:
ASN.1 Tree Instance
In this figure, the OID of the object A is 1.2.1.1. NMS can locate this object through this unique
OID and gets the standard variables of the object. MIB defines a set of standard variables for
monitored network devices by following this structure.
If the variable information of Agent MIB needs to be browsed, the MIB browse software needs
to be run on the NMS. MIB in the Agent usually consists of public MIB and private MIB. The
public MIB contains public network management information that can be accessed by all NMS;
private MIB contains specific information which can be viewed and controlled by the support of
the manufacturers.
MIB-I [RFC1156] is the first implemented public MIB of SNMP, and is replaced by MIB-II
[RFC1213]. MIB-II expands MIB-I and keeps the OID of MIB tree in MIB-I. MIB-II contains sub-
trees which are called groups. Objects in those groups cover all the functional domains in
