7 performing a multiplexed access without has, Section 3.7 – Texas Instruments TMS320C6457 User Manual
Page 20
Data 2
Data 1
HCS
HSTRB
HR/W
HCNTL[1:0]
HD[15:0]
HRDY
A
HHWIL
Internal
HPI latches
control information
Host latches
data
HPI latches
control information
Host latches
data
HPI Operation
www.ti.com
3.7
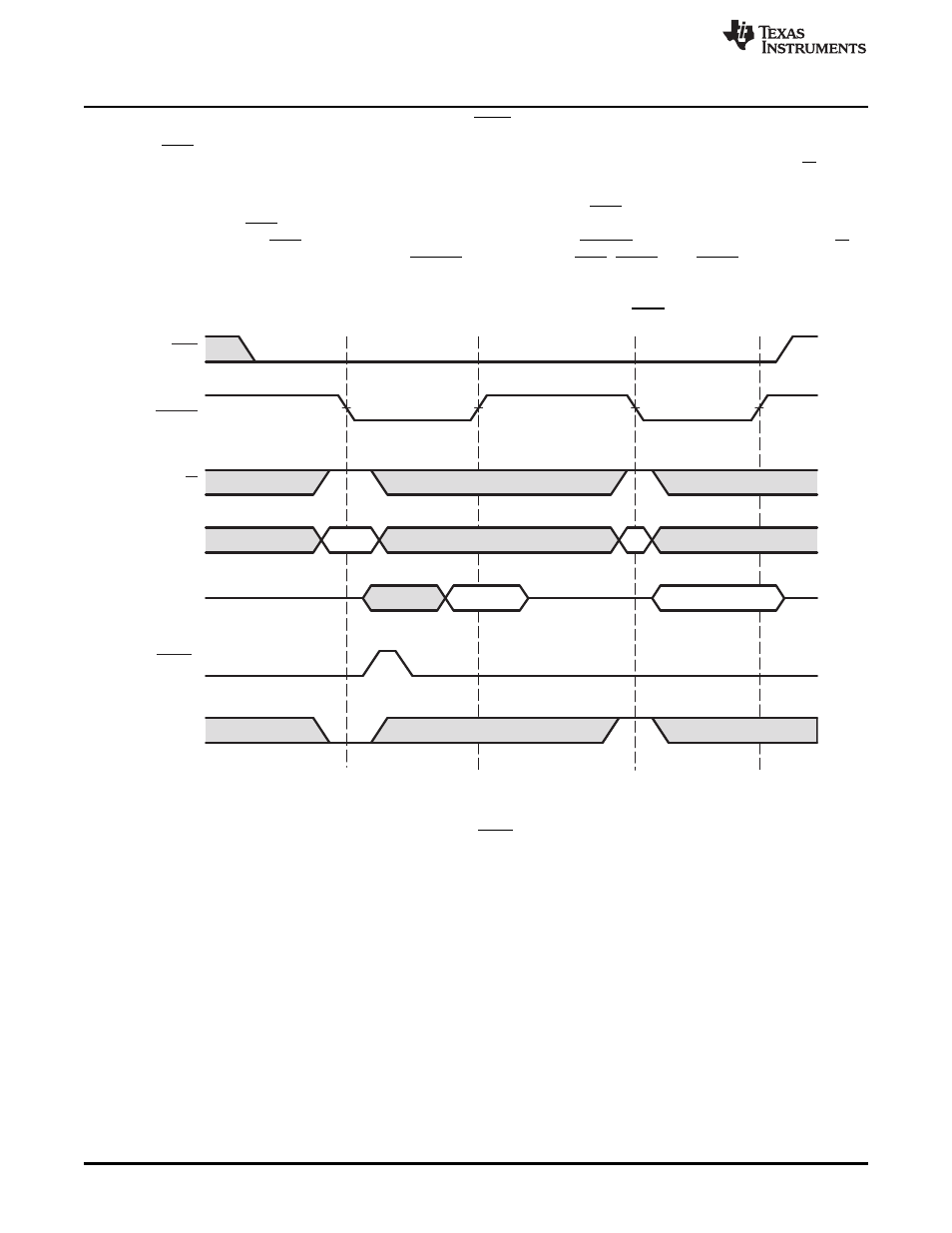
Performing a Multiplexed Access Without HAS
The HAS signal is not required when the host processor has dedicated signals (address lines or bit I/O)
capable of driving the control lines. Dedicated pins can be directly connected to HCNTL[1:0], HR/W, and
HHWIL.
and
show examples of signal connections when HAS is not used for multiplexed
transfers. When HAS is not used, it must be tied high (inactive).
and
show typical HPI
signal activity when HAS is tied high. The falling edge of internal HSTRB latches the HCNTL[1:0], HR/W,
and HHWIL states into the HPI. Internal HSTRB is derived from HCS, HDS1, and HDS2, as described in
.
Figure 9. 16-Bit Multiplexed Mode Host Read Cycle With HAS Tied High
A
Depending on the type of write operation (HPID without autoincrementing, HPIA, HPIC, or HPID with
autoincrementing) and the state of the FIFO, transitions on HRDY may or may not occur. For more information, see
.
20
Host Port Interface (HPI)
SPRUGK7A – March 2009 – Revised July 2010
Copyright © 2009–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
