Concentrators with dual-homing – Sun Microsystems 1.0 User Manual
Page 100
74
SunFDDI/P 1.0 Adapter User’s Guide—May 1997
7
Concentrators with Dual-Homing
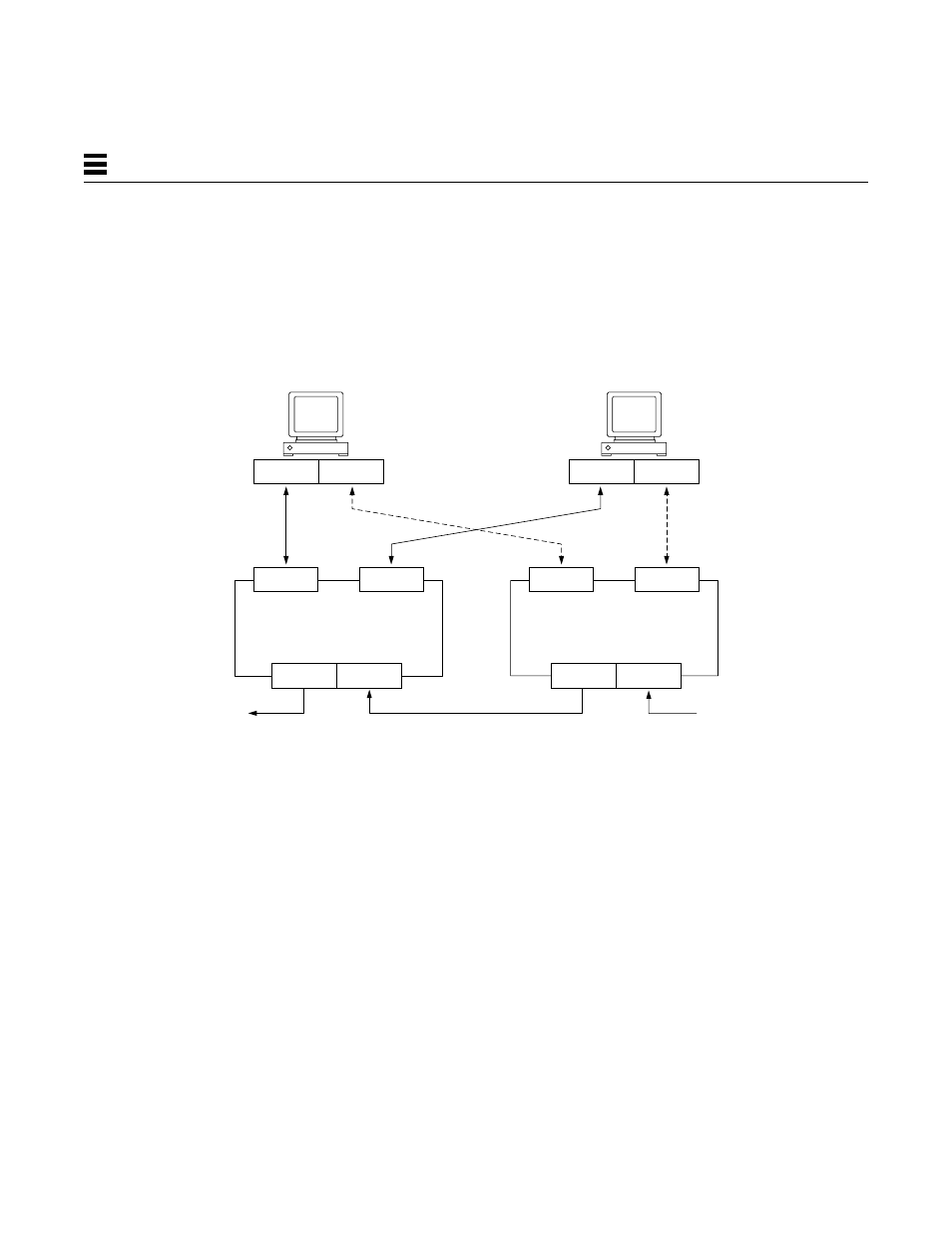
Figure 7-3 shows two dual-attached stations connected to two dual-attached
concentrators in a dual-homing configuration. In this case, each dual-attached
station is connected to both DACs. This topology is typically used for
connecting critical systems such as file and name servers.
Figure 7-4
Standalone Concentrator With Dual-Homing
Dual-homing provides two independent data paths for each dual-attached
station. Under normal conditions, the station communicates on its primary
path through the B-port. In the event of a cable or concentrator failure, the
station switches to the secondary path connected through the A-port.
Dual-homing is equivalent to the redundant single-attached station (RSAS)
configuration, which was supported by SunFDDI 2.0. In the RSAS
configuration, two single-attached interfaces are used to emulate a
dual-attached interface connected in a dual-homing configuration. RSAS is
not supported by SunFDDI/P 1.0.
FDDI DAS
FDDI DAS
B-port
B-port
B-port
B-port
A-port
A-port
A-port
A-port
M-port
M-port
M-port
M-port
Dual-attached concentrator
Dual-attached concentrator
(primary)
(secondary)
