Siemens 4100 Series User Manual
Page 51
Router User’s Guide
Monitoring Network Health
9. If you selected This IP Address, enter an IP address in the IP Address field. And do one of the
following:
• Enter a netmask in the Netmask field.
• Or, select or Host to use your Router netmask as the source netmask.
10. Under the Destination heading, select a network connection from the Network Interface drop-down
menu.
11. Select one of the following options:
• Any IP Address
Select this option if this rule applies to any IP address of the destination.
• This IP Address
Select this option if a rule applies to a specific IP address of the destination.
12. If you selected This IP Address, enter an IP address in the IP Address field. And do one of the
following:
• Enter a netmask in the Netmask field.
• Or, select or Host to use your Router netmask as the destination netmask.
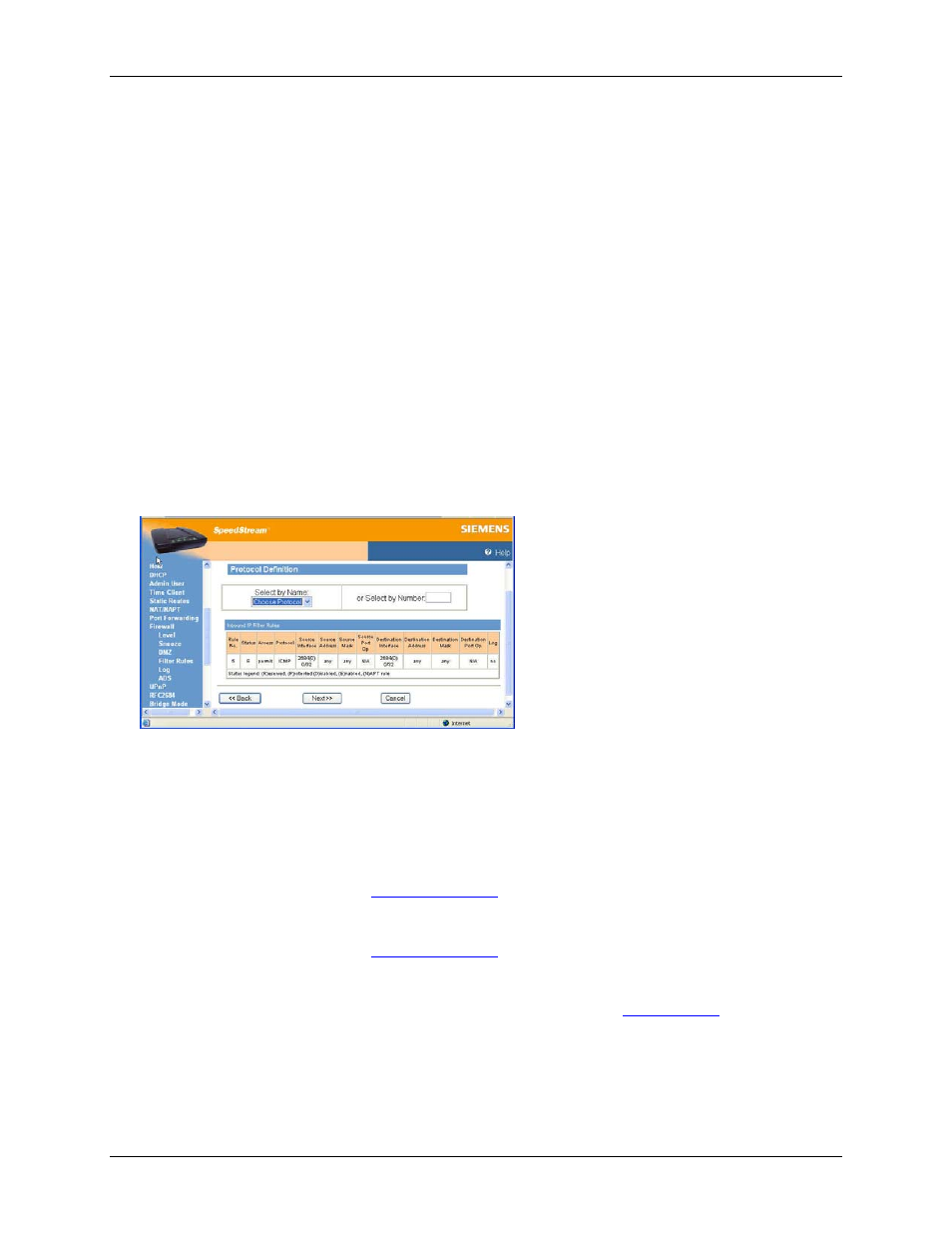
13. Click Next. This displays the “Protocol Definition” window.
14. Do one of the following:
• Select one of the following protocol options from the Select by Name drop-down menu. This
defines the types of packets filtered.
− Any Protocol
− TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
Provides reliable, sequenced, and unduplicated delivery of bytes to remote or local users.
Click Next to display the “
” window.
− UDP (User Datagram Protocol)
Provides for the exchange of datagrams without acknowledgement or guaranteed delivery.
Click Next to display the “
” window.
− ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol)
A mechanism that provides for peer communication. The most commonly used application for
this protocol is the PING command. Click Next to display the “
” window.
− GRE (Generic Routing Encapsulation):
A tunneling protocol that is used primarily for VPN (Virtual Private Networks).
• Type a protocol number in the Select by Number field.
15. Click Finish.
48
