1 non-maskable interrupts, Figure 226. interrupt sequence – Intel 80C188XL User Manual
Page 71
OVERVIEW OF THE 80C186 FAMILY ARCHITECTURE
2-42
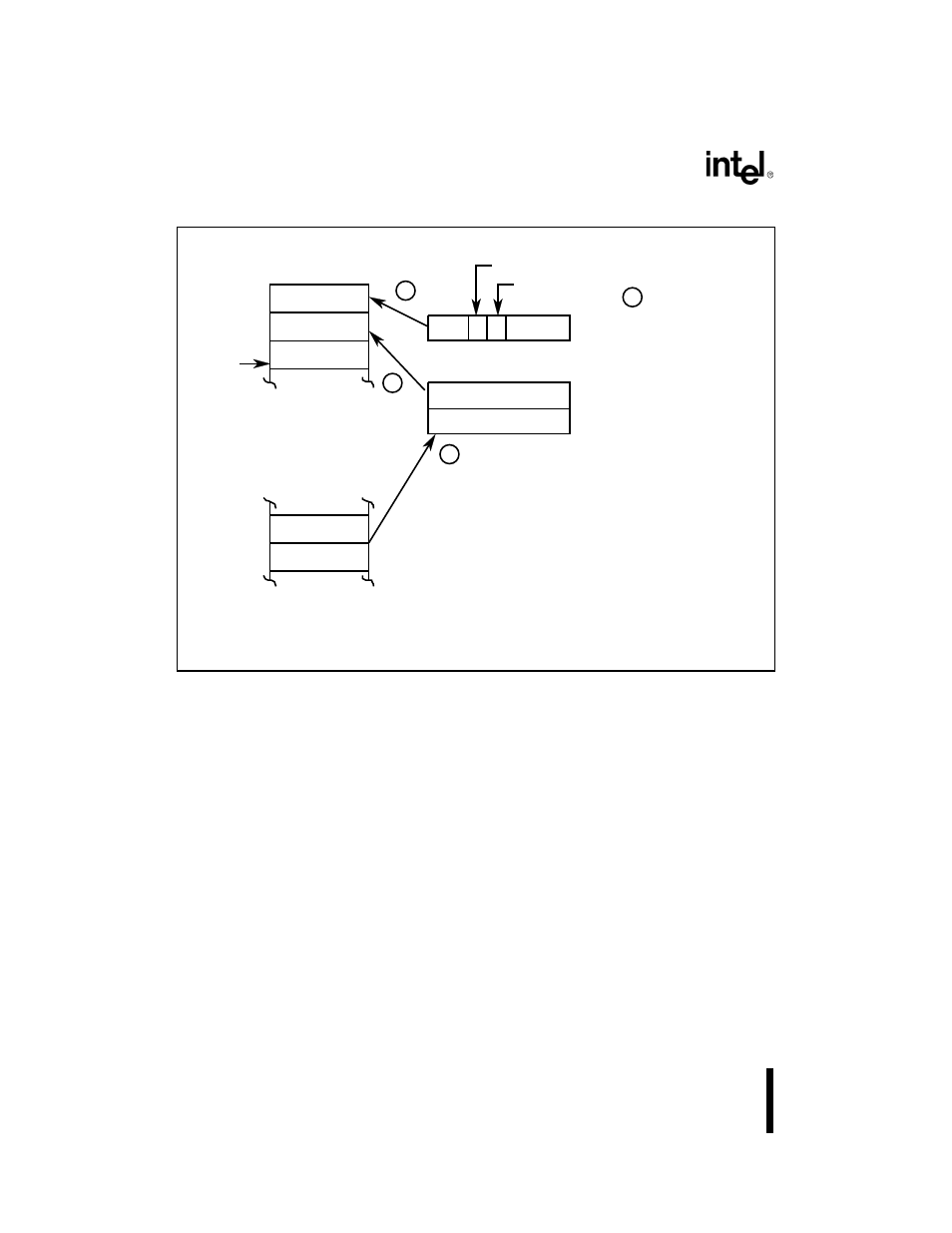
Figure 2-26. Interrupt Sequence
2.3.1.1
Non-Maskable Interrupts
The Non-Maskable Interrupt (NMI) is the highest priority interrupt. It is usually reserved for a
catastrophic event such as impending power failure. An NMI cannot be prevented (or masked)
by software. When the NMI input is asserted, the interrupt processing sequence begins after ex-
ecution of the current instruction completes (see “Interrupt Latency” on page 2-45). The CPU au-
tomatically generates a type 2 interrupt vector.
The NMI input is asynchronous. Setup and hold times are given only to guarantee recognition on
a specific clock edge. To be recognized, NMI must be asserted for at least one CLKOUT period
and meet the correct setup and hold times. NMI is edge-triggered and level-latched. Multiple
NMI requests cause multiple NMI service routines to be executed. NMI can be nested in this man-
ner an infinite number of times.
A1029-0A
Stack
SP
CS
IP
Interrupt Enable Bit
PSW
CS
IP
Trap Flag
Instruction Pointer
Code Segment Register
Processor Status Word
Interrupt
Vector
Table
0 0
2
1
3
4
