5 internal requests, 2 unsynchronized transfers, Figure 104. destination-synchronized transfers – Intel 80C188XL User Manual
Page 261
DIRECT MEMORY ACCESS UNIT
10-6
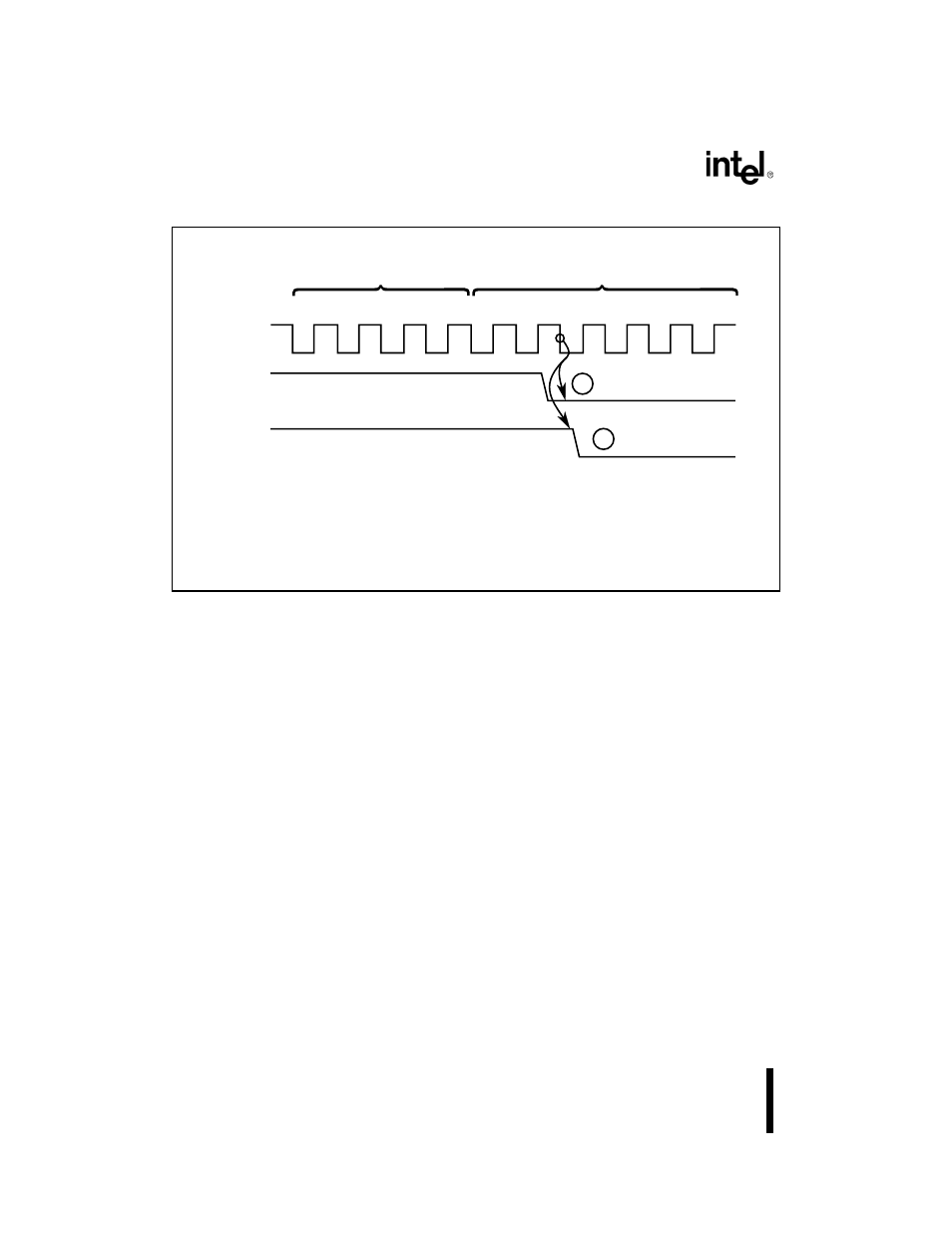
Figure 10-4. Destination-Synchronized Transfers
10.1.5 Internal Requests
Internal DMA requests can come from either Timer 2 or the system software.
10.1.5.1
Timer 2-Initiated Transfers
When programmed for Timer 2-initiated transfers, the DMA channel performs one DMA transfer
every time that Timer 2 reaches its maximum count. Timer-initiated transfers are useful for ser-
vicing time-based peripherals. For example, an A/D converter would require data every 22 mi-
croseconds in order to produce an audio range waveform. In this case, the DMA source would
point to the waveform data, the destination would point to the A/D converter and Timer 2 would
request a transfer every 22 microseconds. (See “Timed DMA Transfers” on page 10-26.)
10.1.5.2
Unsynchronized Transfers
DMA transfers can be initiated directly by the system software by selecting unsynchronized
transfers. Unsynchronized transfers continue, back-to-back, at the full bus bandwidth, until the
channel’s transfer count reaches zero or DMA transfers are suspended by an NMI.
T1
T2
T3
T4
CLKOUT
DRQ
(Case 1)
T1
T2
T3
T4
DRQ
(Case 2)
Fetch Cycle
Deposit Cycle
NOTES:
1. Current destination synchronized transfer will not be immediately
followed by another DMA transfer.
2. Current destination synchronized transfer will be immediately
followed by another DMA transfer.
2
1
TI
TI
A1189-0A
