Dnp master driver data flow, 3 dnp master driver data flow – ProSoft Technology 5201-DFNT-DNPM User Manual
Page 9
Functional Overview
DNPM ♦ ProLinx Gateway
Driver Manual
DNP 3.0 Master
ProSoft Technology, Inc.
Page 9 of 56
September 30, 2009
Note that the order of the data types is fixed by the driver. In order to access the
binary input data read from a slave device, registers 0 to 1 are used. To set
analog output data to pass to the driver for remote slaves, registers 74 to 113 are
used. Register 74 contains the value for analog output point 0, and register 113
contains the value for analog output point 39.
The other protocol on the ProLinx module should place data in the binary and
analog output data areas. Values set will be passed by the master driver to slave
units on the network.
The other protocol on the ProLinx module should retrieve the data for the binary
and analog inputs and counters as these are obtained by the master driver from
slave units. This monitored data area should not be altered by the other protocol
on the module.
1.3
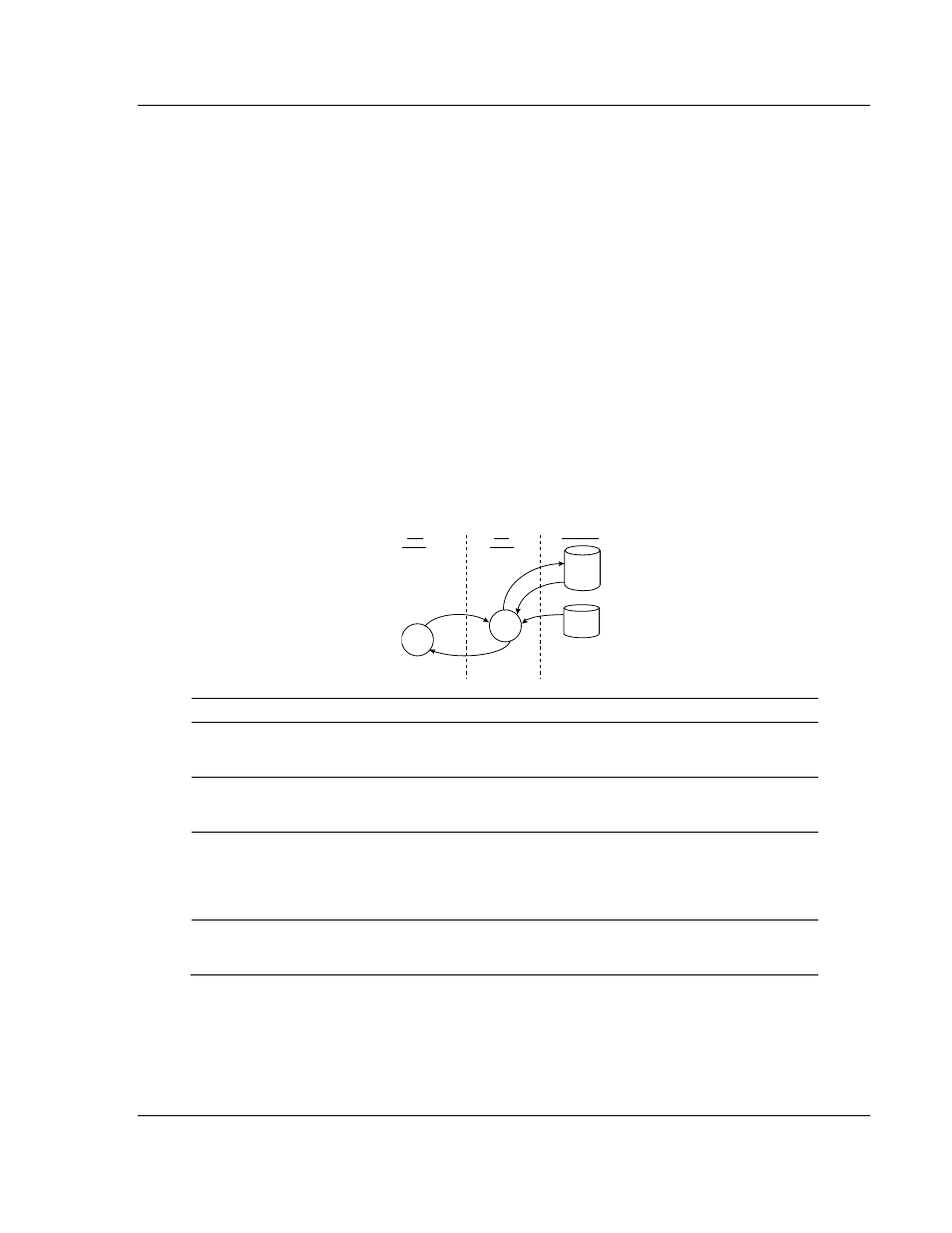
DNP Master Driver Data Flow
The DNP Master Driver allows the module to generate read and write commands
issued to slave units on the DNP network. The following flow chart and
associated table describe the flow of data into and out of the module.
Virtual
Database
Command
List
Master
Driver
Slave
Device
Databases
DNP
Master
DNP
Slaves
Request
Unsolicited
Messages or
Responses
Read for DNP
Write Function
W rite for DNP Read
Function
Read
Step Description
1
The DNP Master driver receives the configuration information from the Flash memory in
the module. This information configures the serial port and define the Master node
characteristics.
2
The Master Driver issues a read or write command to the DNP Slave’s node address.
The Slave device qualifies the message then issues a response containing the
information requested by the master..
3
After the module accepts the response, the data is immediately transferred to or from the
internal database in the module. If the command is a read command (binary input,
analog input, counter, event, and so on), the data is written to the module database. If
the command is a write command (binary output or analog output), the data is read
directly from the database.
4
Error/Status data are available in a Status Block that can be placed anywhere in the
module’s database. This area can be accessed by the other protocol on the module
using the correct database offset.
