ProSoft Technology 5201-DFNT-DNPM User Manual
Page 23
DNPM Protocol Configuration
DNPM ♦ ProLinx Gateway
Driver Manual
DNP 3.0 Master
ProSoft Technology, Inc.
Page 23 of 56
September 30, 2009
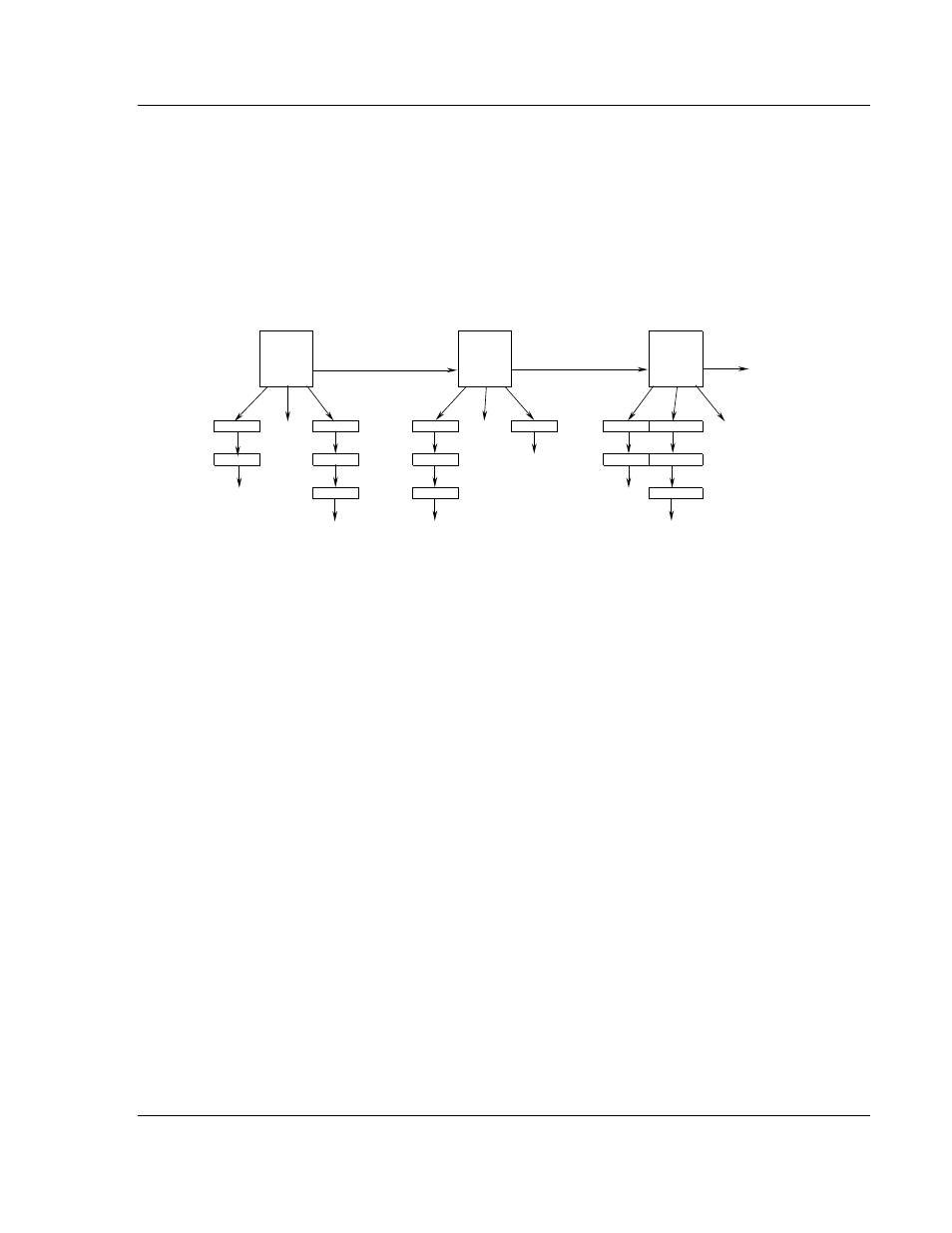
Besides issuing commands to slave devices, the command list is also used to
map data received in event messages to the proper database locations. For
example, Slave 1 and Slave 1 both possess binary point 0. When an event from
each slave is received, the data entered into the command list is utilized to place
the data for the two events in the correct database location. When the command
list is read by the module is forms lists for each slave relating the address in the
device to that in internal database of the module. The following illustration shows
how the module stores this data:
SLAVE LIST
Address
Address
Address
DNP Data
DNP Data
DNP Data
Comm Data
Comm Data
Comm Data
Next Ptr
Next Ptr
Next Ptr
Null
DI | AI | C
DI | AI | C
DI | AI | C
DI Pnts
Null
Cntr Pnts
DI Pnts
Null
Cntr Pnts
DI Pnts
AI Pnts
Null
DI Pnts
Cntr Pnts
DI Pnts
Null
DI Pnts
AI Pnts
Null
Cntr Pnts
DI Pnts
Null
AI Pnts
Null
Null
Null
DI Pnts are generated for each command with an object type of 1.
AI Pnts are generated for each command with an object type of 30.
Cntr Pnts are generated for each command with an object type of 20 or 21.
The point lists are used by the module to determine the destination of all data
read by the module from the IED's. When the master receives a poll response or
an unsolicited response message, the points in the message are mapped to the
IED database using the point lists. For example, when the master receives a
value for binary input point 10 from slave unit 14, the following steps are
performed by the module:
1 First the module searches the slave list to make sure slave 14 is valid for the
module. If the slave not found the message is ignored. If the slave is found,
the module saves the pointer to the binary input point list.
2 Point number 10 is searched for in the binary input point list. If the point is
found in the DNP point list, the new value is stored at the correct offset in the
BI database. If the point is found in the IED point list, the new value is stored
at the correct offset in the IED database. If the point is not found in either
point list, it is ignored.
Each node in the point lists contain the start-stop IED point ranges and the IED
database offset values. These values are read by the module from the command
list each time the module performs the restart operation. If the database address
value is set to -1, the database is not used for the specified point range.
When the lists are formed by the module, the enable/flag field is ignored.
Therefore, you can place commands that will not be executed in the command
list and are only used for data mapping.
