2 communication, 3 programming, 2 driver overview – KEPCO KLR Series Developers Guide User Manual
Page 12: Communication -2, Programming -2, Driver overview -2, Visa resource string corresponding to interface -2, Ble 1-1 provides the reso, E 1-1) to ad
1-2
KLR-DEV 060713
LabView G driver also uses VISA calls, allowing it to work on all ports of the KLR. The examples
given in Programming, Section 6, PAR. 6.8, all utilize VISA calls so they are universally applied.
1.1.2
COMMUNICATION
Communication between a KLR and a computer system may be via one of three methods: IEEE
488.2, RS 232 and LAN. These three interfaces communicate by sending formatted strings to
the KLR which are then parsed to perform specific actions.
• IEEE 488.2 (GPIB) Interface (see Section 7).
• RS 232 Interface [standard models only] (see Section 8).
• LAN interface [E-Series models only] (see Section 9).
1.1.3
PROGRAMMING
SCPI and IEEE 488 common commands/queries are the building blocks used to control the
KLR power supply. These sections are provided to allow a user to write their own program to
control the KLR power supply or to use the various interactive tools provided by Measurement
Computing, National Instruments, Agilent Technologies and Microsoft to send strings to a
device over the RS 232, GPIB or LAN interfaces. SCPI commands and queries are supported
by all three interfaces.
• Description of SCPI Syntax (see Section 6).
• IEEE 488 Common commands supported (see Appendix A).
• Listing of SCPI commands supported (see Appendix B).
1.2
DRIVER OVERVIEW
The three drivers for KLR all have common functional groups Each group contains similar func-
tions which work together. The four different environments, IVI-COM, LabView G, VXI
Plug&Play and Programming all have common functionality.
The KLR power supply, like most instrument power supplies, has four subsystems: output, trig-
ger, status and measurement. In additional to these subsystems, the KLR has a storage system
and a list system. The commands to use these subsystems have been grouped by function as
detailed in the following paragraphs. These functional groupings are also used in the examples
that are presented in Sections 3 (IVI-COM Driver), 4 (LabView G Driver), and 5 (VXI plug&play
Driver).
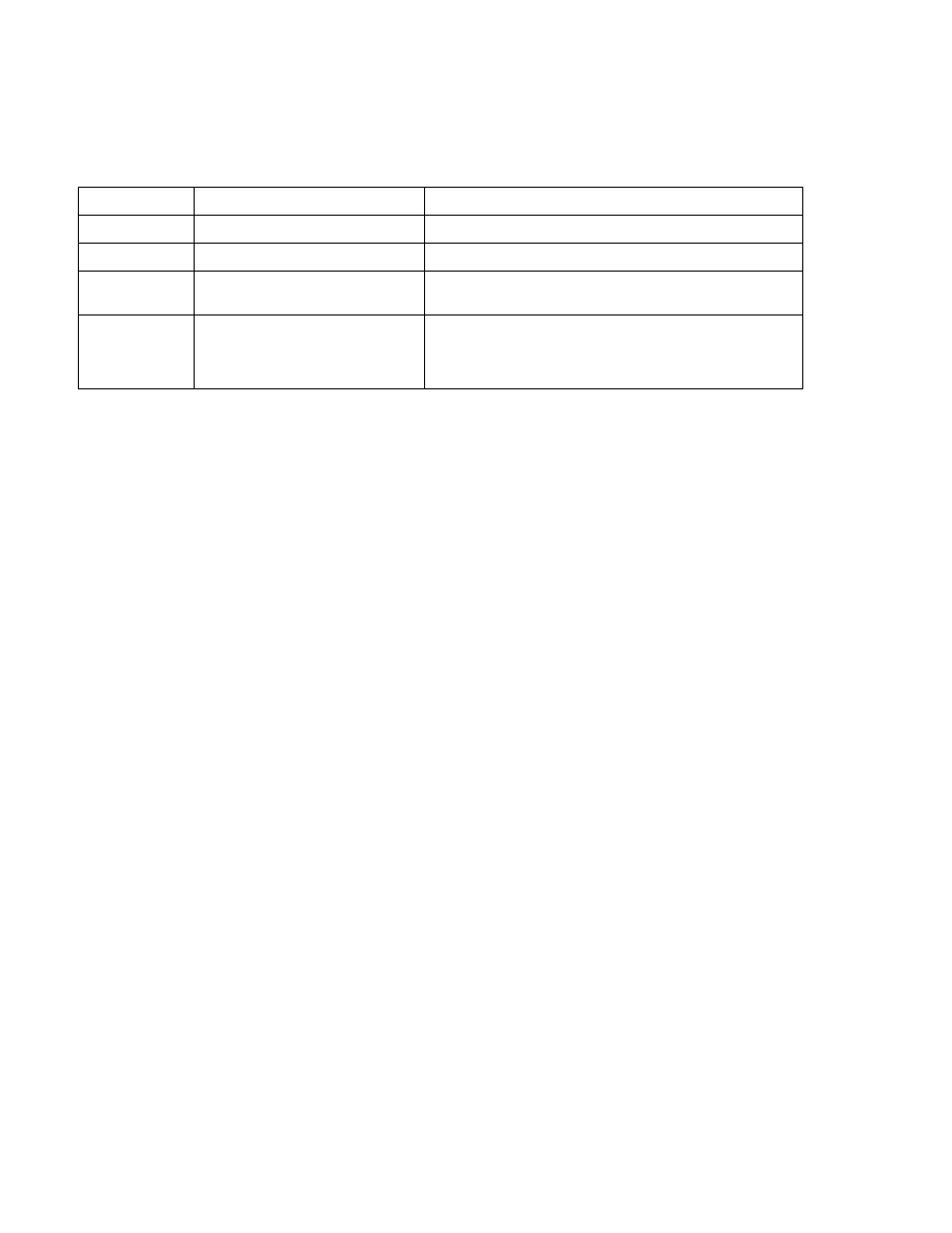
TABLE 1-1. VISA RESOURCE STRING CORRESPONDING TO INTERFACE
INTERFACE
VISA RESOURCE STRING
COMMENT
GPIB
GPIB::xx::INSTR
The GPIB address replaces xx.
SERIAL
ASRLy::INSTR
The com port number replaces y.
LAN-SCPI-RAW
TCIP::192.168.0.100::5025::SOCKET
This is the fastest LAN interface, similar to the serial port with
automatic XON XOFF protocol support.
LAN-VXI-11
TCIP::192.168.0.100::INSTR
This LAN interface requires a more complex handshake for data
and is inherently slower than a socket interface. It is similar to the
GPIB interface where you tell the device when to take data and
when it is acceptable to receive data.
