Irf domain id – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F5020 User Manual
Page 15
6
For more information about physical interfaces that can be used for IRF links, see "
."
For more information about physical interfaces that can be used for IRF links, see the following sections:
•
IRF physical interface requirements
(centralized IRF devices).
•
IRF physical interface requirements
(distributed devices).
MAD
An IRF link failure causes an IRF fabric to split in two IRF fabrics operating with the same Layer 3
configurations, including the same IP address. To avoid IP address collision and network problems, IRF
uses multi-active detection (MAD) mechanisms to detect the presence of multiple identical IRF fabrics,
handle collisions, and recover from faults.
IRF domain ID
One IRF fabric is one IRF domain. IRF uses IRF domain IDs to uniquely identify IRF fabrics and prevent IRF
fabrics from interfering with one another.
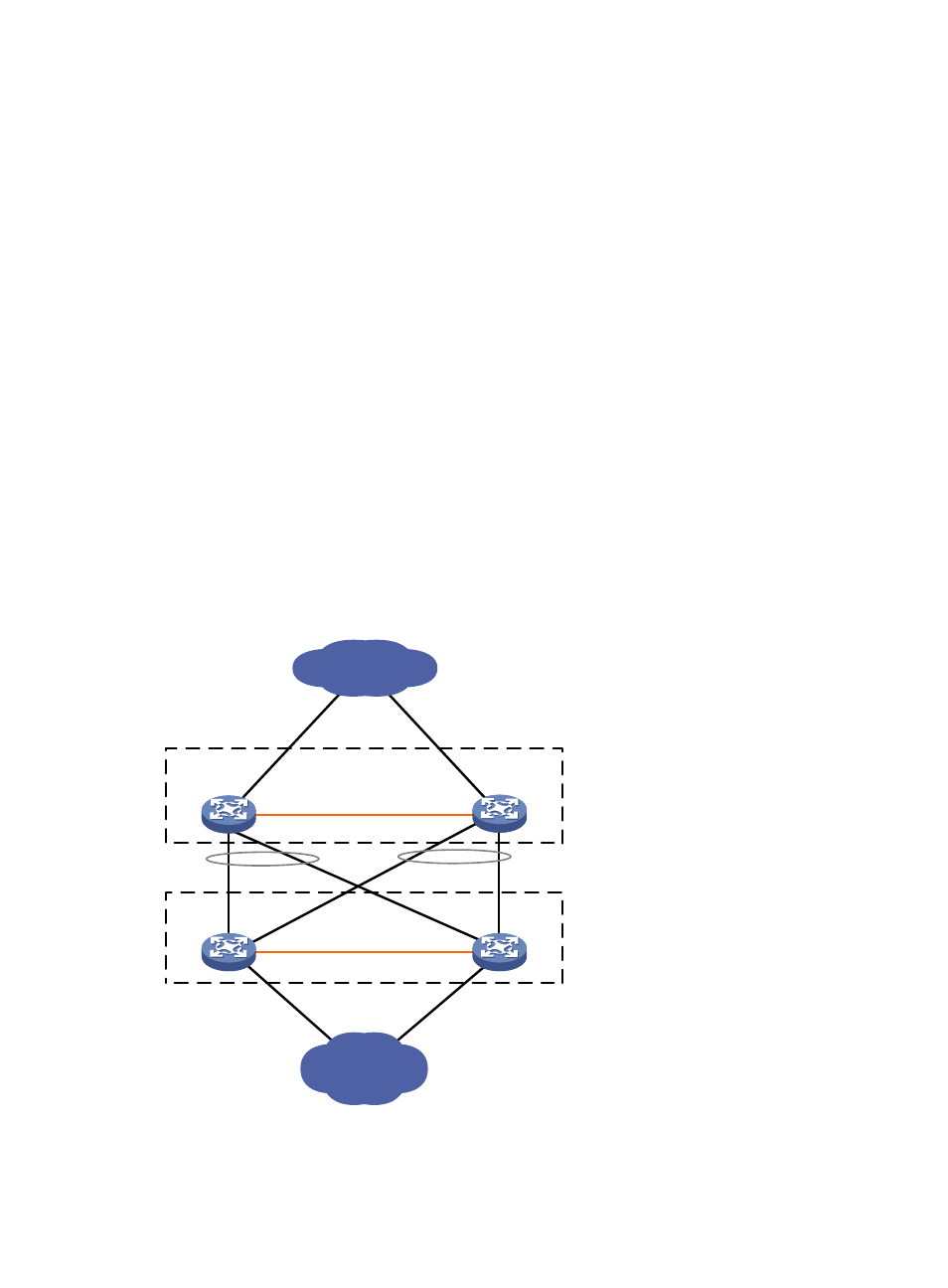
As shown in
, IRF fabric 1 contains Device A and Device B, and IRF fabric 2 contains Device C
and Device D. Both fabrics can use the aggregate links between them for MAD. When a member device
receives a packet for MAD, it checks the domain ID to see whether the packet is from the local IRF fabric.
Then, the device can handle the packet correctly.
Figure 3 A network that contains two IRF domains
Device A
Device B
IRF 1 (domain 10)
IRF link
Core network
IRF 2 (domain 20)
IRF link
Device C
Device D
Access network
