Custom queuing, Congestion management technology comparison – H3C Technologies H3C WX3000E Series Wireless Switches User Manual
Page 48
39
Priority queuing schedules the four queues strictly according to the descending order of priority. It sends
packets in the queue with the highest priority first. When the queue with the highest priority is empty, it
sends packets in the queue with the second highest priority. In this way, you can assign the
mission-critical packets to the high priority queue to make sure that they are always served first. The
common service packets are assigned to the low priority queues and transmitted when the high priority
queues are empty.
The disadvantage of priority queuing is that packets in the lower priority queues cannot be transmitted
if packets exist in the higher queues for a long time when congestion occurs.
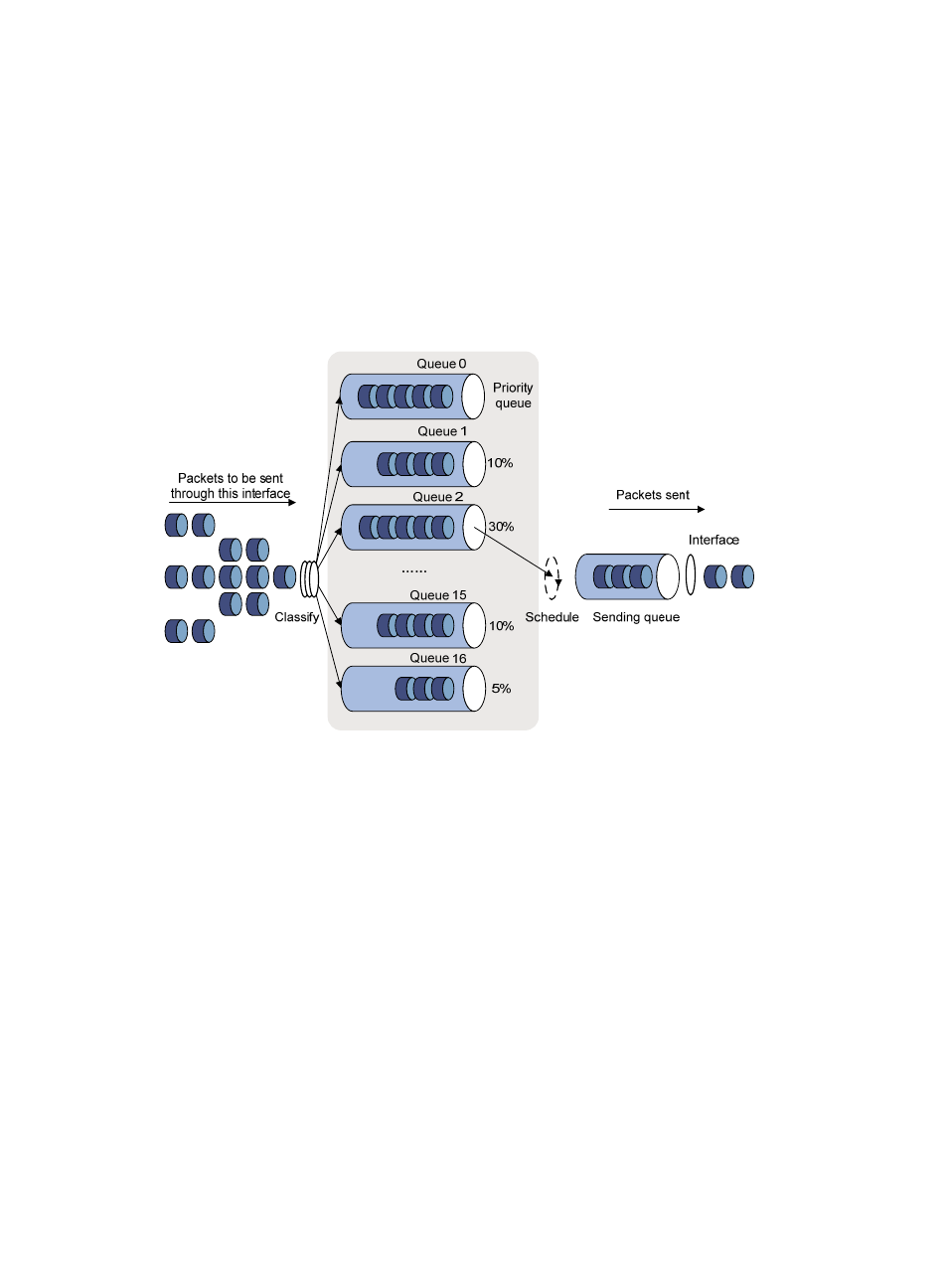
Custom queuing
Figure 13 Custom queuing (CQ)
CQ provides 17 queues, numbered from 0 to 16. Queue 0 is a reserved system queue, and queues 1
through 16 are customer queues, as shown in
. You can define traffic classification rules and
assign a percentage of interface bandwidth for each customer queue. By default, packets are assigned
to queue 1.
During a cycle of queue scheduling, CQ first empties the system queue. Then, it schedules the 16 queues
in a round robin way: it sends a certain number of packets (based on the percentage of interface
bandwidth assigned for each queue) out of each queue in the ascending order of queue 1 to queue 16.
CQ guarantees normal packets a certain amount of bandwidth, and makes sure that mission-critical
packets are assigned more bandwidth.
CQ can assign free bandwidth of idle queues to busy queues. Even though it performs round robin queue
scheduling, CQ does no assign fixed time slots for the queues. If a queue is empty, CQ immediately
moves to the next queue. When a class does not have packets, the bandwidth for other classes increases.
Congestion management technology comparison
Breaking through the single congestion management policy of FIFO for traditional IP devices, the current
device provides all the congestion management technologies above mentioned to offer powerful QoS
capabilities, meeting different QoS requirements of different applications.
- H3C WX5500E Series Access Controllers H3C WX3500E Series Access Controllers H3C WX2500E Series Access Controllers H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers H3C WX5000 Series Access Controllers H3C LSWM1WCM10 Access Controller Module H3C LSUM3WCMD0 Access Controller Module H3C LSUM1WCME0 Access Controller Module H3C LSWM1WCM20 Access Controller Module H3C LSQM1WCMB0 Access Controller Module H3C LSRM1WCM2A1 Access Controller Module H3C LSBM1WCM2A0 Access Controller Module H3C WA3600 Series Access Points H3C WA2600 Series WLAN Access Points
