Configuration procedure – H3C Technologies H3C MSR 50 User Manual
Page 95
87
•
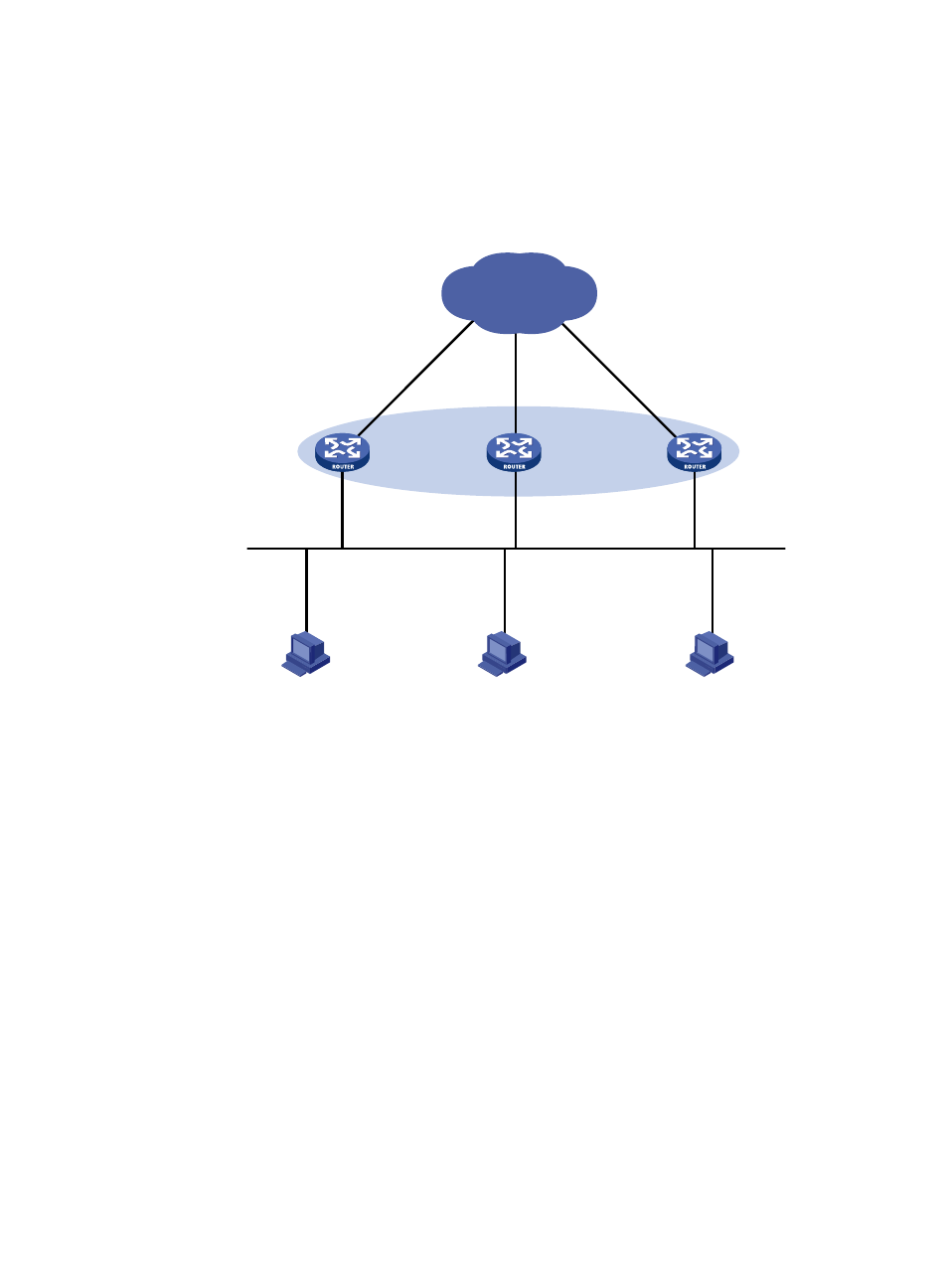
Configure a track entry on Router A, Router B, and Router C to monitor their own Ethernet 1/2.
When the interface on Router A, Router B, or Router C fails, the weight of the corresponding router
decreases so that another router with a higher weight can take over.
•
Configure track entries on Router C to monitor Router A and Router B. When Router A or Router B
fails, Router C immediately takes over the AVF on Router A or Router B.
Figure 31 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
1.
Configure Router A:
# Configure VRRP to operate in load balancing mode.
[RouterA] vrrp mode load-balance
# Create VRRP group 1 and configure its virtual IP address as 10.1.1.1.
[RouterA] interface ethernet 1/1
[RouterA-Ethernet1/1] ip address 10.1.1.2 24
[RouterA-Ethernet1/1] vrrp vrid 1 virtual-ip 10.1.1.1
# Set the priority of Router A in VRRP group 1 to 120, which is higher than that of Router B (110)
and that of Router C (100), so that Router A can become the master.
[RouterA-Ethernet1/1] vrrp vrid 1 priority 120
# Configure Router A to operate in preemptive mode so that it can become the master whenever
it works correctly. Configure the preemption delay as 5 seconds to avoid frequent status
switchover.
[RouterA-Ethernet1/1] vrrp vrid 1 preempt-mode timer delay 5
[RouterA-Ethernet1/1] quit
# Create track entry 1 to associate with the physical status of Ethernet 1/2 on Router A. When the
track entry becomes negative, it means that the interface fails.
Host A
Host B
Host C
Router A
Router B
Router C
Eth1/1
IP: 10.1.1.2/24
VIP: 10.1.1.1/24
Network
Eth1/1
IP: 10.1.1.3/24
VIP: 10.1.1.1/24
Eth1/1
IP: 10.1.1.4/24
VIP: 10.1.1.1/24
Master
AVF 1
Backup
AVF 2
Backup
AVF 3
IP: 10.1.1.5/24
Gateway IP: 10.1.1.1/24
IP: 10.1.1.6/24
Gateway IP: 10.1.1.1/24
IP: 10.1.1.7/24
Gateway IP: 10.1.1.1/24
Eth1/2
Eth1/2
Eth1/2
