Vrrp group, Vrrp standard mode – H3C Technologies H3C MSR 50 User Manual
Page 63
55
•
Load balancing mode—Extends the standard mode and realizes load balancing. For more
information, see "VRRP load balancing mode."
VRRP standard mode
VRRP group
VRRP combines a group of routers (including a master and multiple backups) on a LAN into a virtual
router called VRRP group.
A VRRP group has the following features:
•
A virtual router has a virtual IP address. A host on the LAN only needs to know the IP address of the
virtual router and uses the IP address as the next hop of the default route.
•
Every host on the LAN communicates with external networks through the virtual router.
•
Routers in the VRRP group elect a master that acts as the gateway according to their priorities. The
other routers function as the backups. When the master fails, to make sure that the hosts in the
network segment can communicate without interruption with the external networks, the backups in
the VRRP group elect a new gateway to take the responsibility for the failed master.
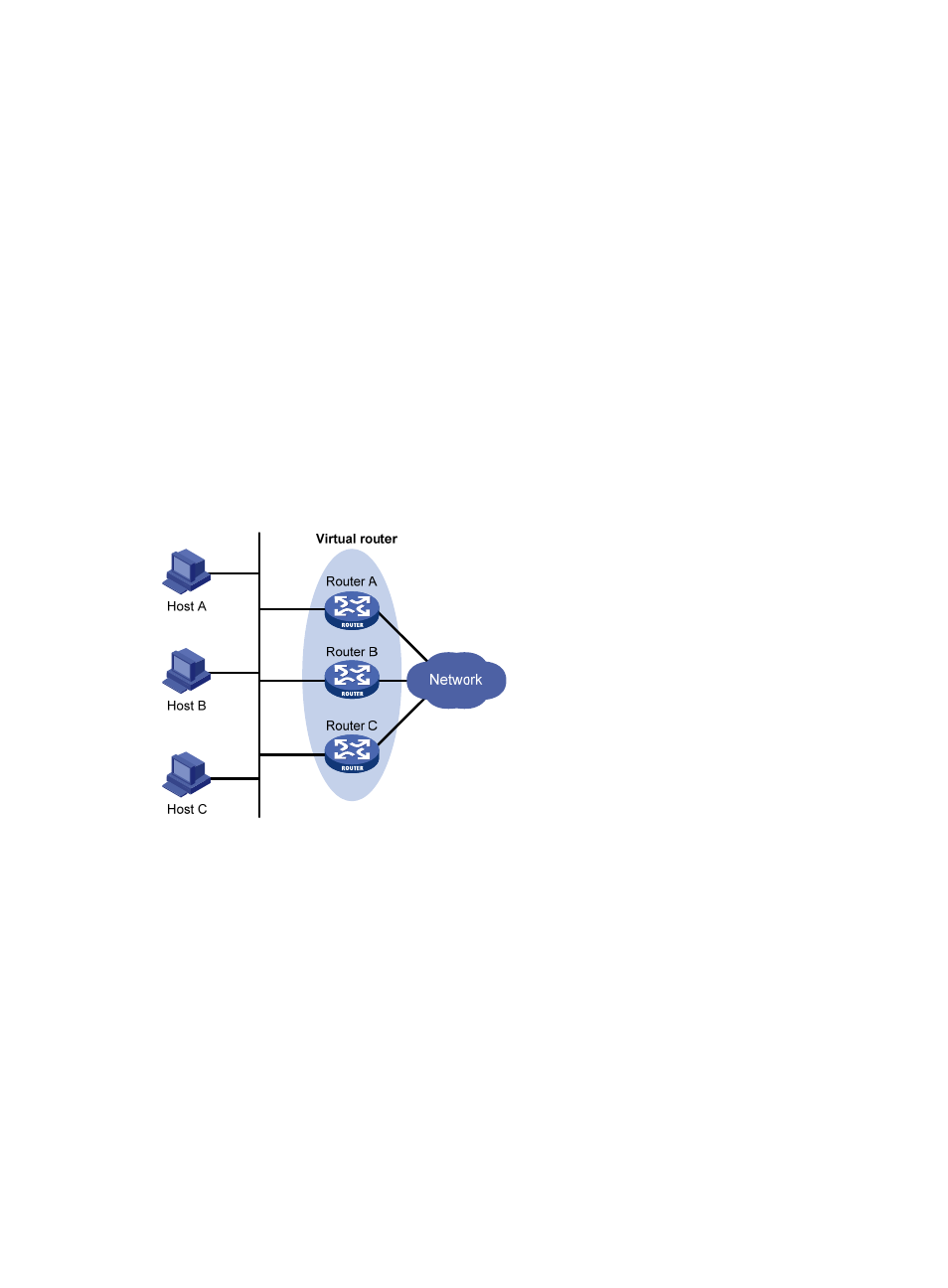
Figure 18 Network diagram
As shown in
, Router A, Router B, and Router C form a virtual router, which has its own IP
address. Hosts on the Ethernet use the virtual router as the default gateway.
The router with the highest priority among the three routers is elected as the master to act as the gateway,
and the other two are backups.
The IP address of the virtual router can be either an unused IP address on the segment where the VRRP
group resides or the IP address of an interface on a router in the VRRP group. In the latter case, the router
is called the IP address owner.
Only one IP address owner can be configured for a VRRP group.
Statuses of a router in a VRRP group include master, backup, and initialize.
1.
VRRP priority
VRRP determines the role (master or backup) of each router in a VRRP group by priority. A router
with a higher priority is more likely to become the master.
