Configuring ip addresses, Assigning an ip address to an interface – H3C Technologies H3C S7500E Series Switches User Manual
Page 32
3-3
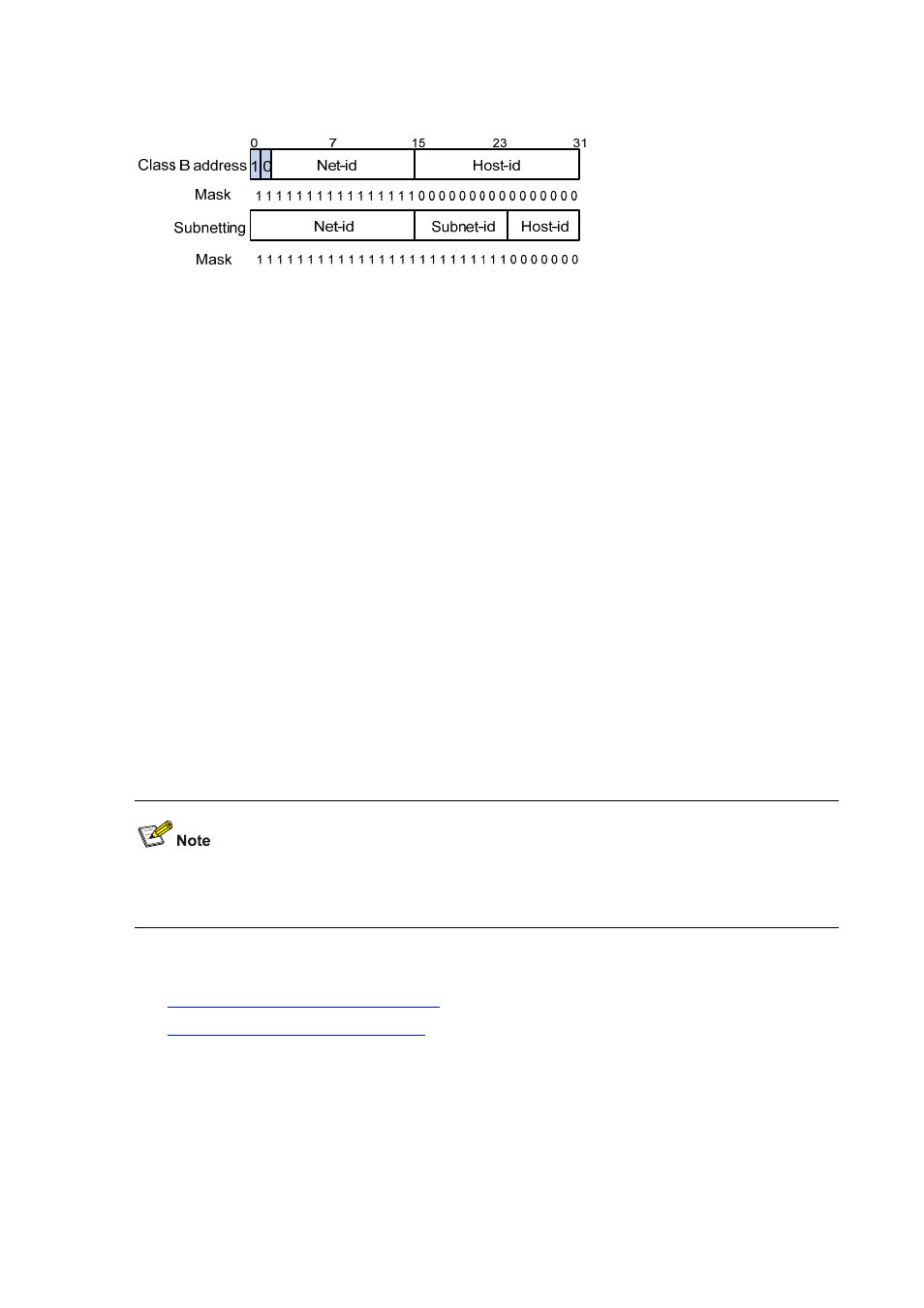
Figure 3-2 Subnet a Class B network
In the absence of subnetting, some special addresses such as the addresses with the net ID of all
zeros and the addresses with the host ID of all ones, are not assignable to hosts. The same is true for
subnetting. When designing your network, you should note that subnetting is somewhat a tradeoff
between subnets and accommodated hosts. For example, a Class B network can accommodate
65,534 (2
16
– 2. Of the two deducted Class B addresses, one with an all-one host ID is the broadcast
address and the other with an all-zero host ID is the network address) hosts before being subnetted.
After you break it down into 512 (2
9
) subnets by using the first 9 bits of the host ID for the subnet, you
have only 7 bits for the host ID and thus have only 126 (2
7
– 2) hosts in each subnet. The maximum
number of hosts is thus 64,512 (512 × 126), 1022 less after the network is subnetted.
Class A, B, and C networks, before being subnetted, use these default masks (also called natural
masks): 255.0.0.0, 255.255.0.0, and 255.255.255.0 respectively.
Configuring IP Addresses
An interface can communicate with other hosts after it obtains an IP address. Besides directly
assigning an IP address to an interface, you may configure the interface to obtain one through DHCP,
address negotiation as alternatives. If you change the way an interface obtains an IP address, from
manual assignment to DHCP for example, the IP address obtained from DHCP will overwrite the old
one manually assigned.
This chapter only covers how to assign an IP address manually. For how to obtain an IP address
through DHCP, refer to DHCP Client Configuration in the Layer 3 - IP Services Configuration Guide.
This section includes:
z
Assigning an IP Address to an Interface
z
IP Addressing Configuration Example
Assigning an IP Address to an Interface
You may assign an interface multiple IP addresses, one primary and multiple secondaries.
Generally, you only need to assign the primary address to an interface. In some cases, you need to
assign secondary IP addresses to the interface. For example, if the interface connects to two subnets,
