Duplicate address detection – H3C Technologies H3C S7500E Series Switches User Manual
Page 127
13-8
Duplicate address detection
After node A acquires an IPv6 address, it will perform duplicate address detection (DAD) to determine
whether the address is being used by any other node (similar to the gratuitous ARP function of IPv4).
DAD is accomplished through NS and NA messages.
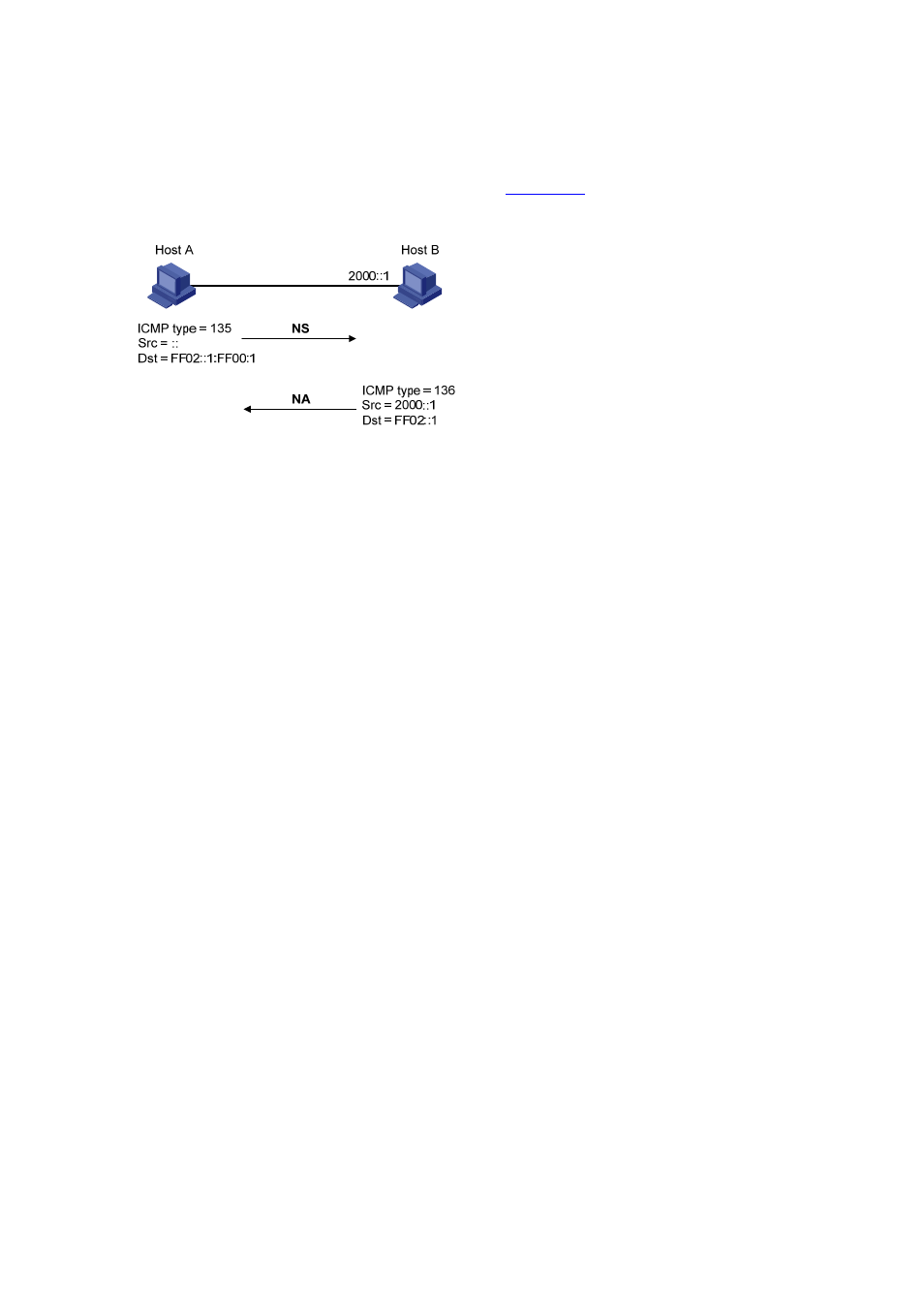
shows the DAD procedure.
Figure 13-4 Duplicate address detection
The DAD procedure is as follows:
1) Node A sends an NS message whose source address is the unassigned address :: and
destination address is the corresponding solicited-node multicast address of the IPv6 address to
be detected. The NS message contains the IPv6 address.
2) If node B uses this IPv6 address, node B returns an NA message. The NA message contains the
IPv6 address of node B.
3) Node A learns that the IPv6 address is being used by node B after receiving the NA message from
node B. Otherwise, the IPv6 address is not in use and node A can use it.
Router/prefix discovery and address autoconfiguration
Router/prefix discovery means that a node locates the neighboring routers, and learns the prefix of the
network where the node is located, and other configuration parameters from the received RA
message.
Stateless address autoconfiguration means that a node automatically generates an IPv6 address
according to the information obtained through router/prefix discovery.
The router/prefix discovery is implemented through RS and RA messages. The router/prefix discovery
procedure is as follows:
1) After started, a node sends an RS message to request the router for the address prefix and other
configuration information for the purpose of autoconfiguration.
2) The router returns an RA message containing information such as prefix information option. (The
router also regularly sends an RA message.)
3) The node automatically generates an IPv6 address and other information for its interface
according to the address prefix and other configuration parameters in the RA message.
