Remote voltage programming -47, Remote voltage programming by resistance -47, Remote voltage programming – AMETEK SGI Series User Manual
Page 99
Sorensen SGI Series
Calibration and Verification
M550221-01 Rev AA
3-47
3.11
Remote Voltage Programming
Remote voltage programming is summed with the front panel or digital setting;
see Section 3.9. Remote voltage programming configuration is used for
applications that require the output voltage be programmed (controlled) from a
remote instrument. An external resistance or external voltage source may be
used as a programming device. When using remote voltage programming, a
shielded, twisted-pair cable is recommended to prevent noise interference to
programming signals.
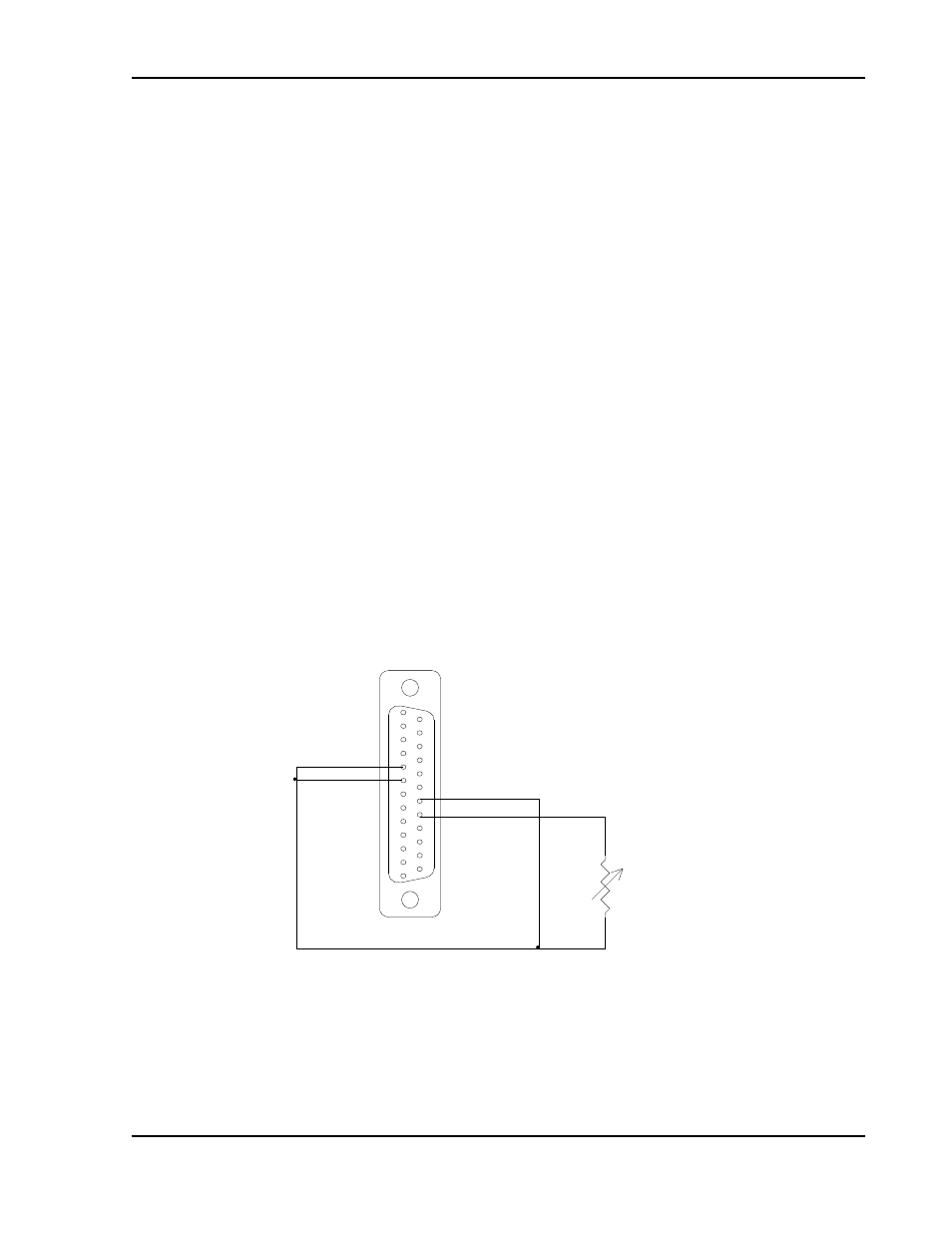
3.11.1 Remote Voltage Programming by Resistance
The resistance-programming coefficient for output voltage is
(100% rated output voltage) /
5 kΩ, with input at Pin J1-21 (VP RES) and
return to Pin J1-20 (VP RTN). An internal current source, factory-set at
1 mA, from Pin J1-21 (VP RES) is utilized to drive the resistance. This
produces a transfer function for output voltage, as follows:
Vout = R * (100% rated output voltage)
/ 5 kΩ), with R in ohms.
Note:
If an external resistance is used for remote programming, the voltage
programming return Pin J1-20 (VP RTN) must be connected directly to, or
within ±3 V, of the circuit common, Pins J1-6 and J1-24. See Figure 3-16 for
connection requirements.
1
13
14
20 VP RTN
21 VP RES
COM 6
0-5 Kohms
PROGRAM
Figure 3-16. Remote Voltage Programming Using Resistance
