Using a heat sink – Altera PowerPlay Early Power Estimator User Manual
Page 59
Altera Corporation
3–41
January 2007
PowerPlay Early Power Estimator For Stratix II, Stratix II GX & HardCopy II
Using the PowerPlay Early Power Estimator
Using a Heat Sink
When a heat sink is used the major paths of power dissipation are from
the device through the case, thermal interface material, and heat sink.
There is also a path of power dissipation through the board. The path
through the board has much less impact than the path to air.
shows the thermal representation with a heat sink.
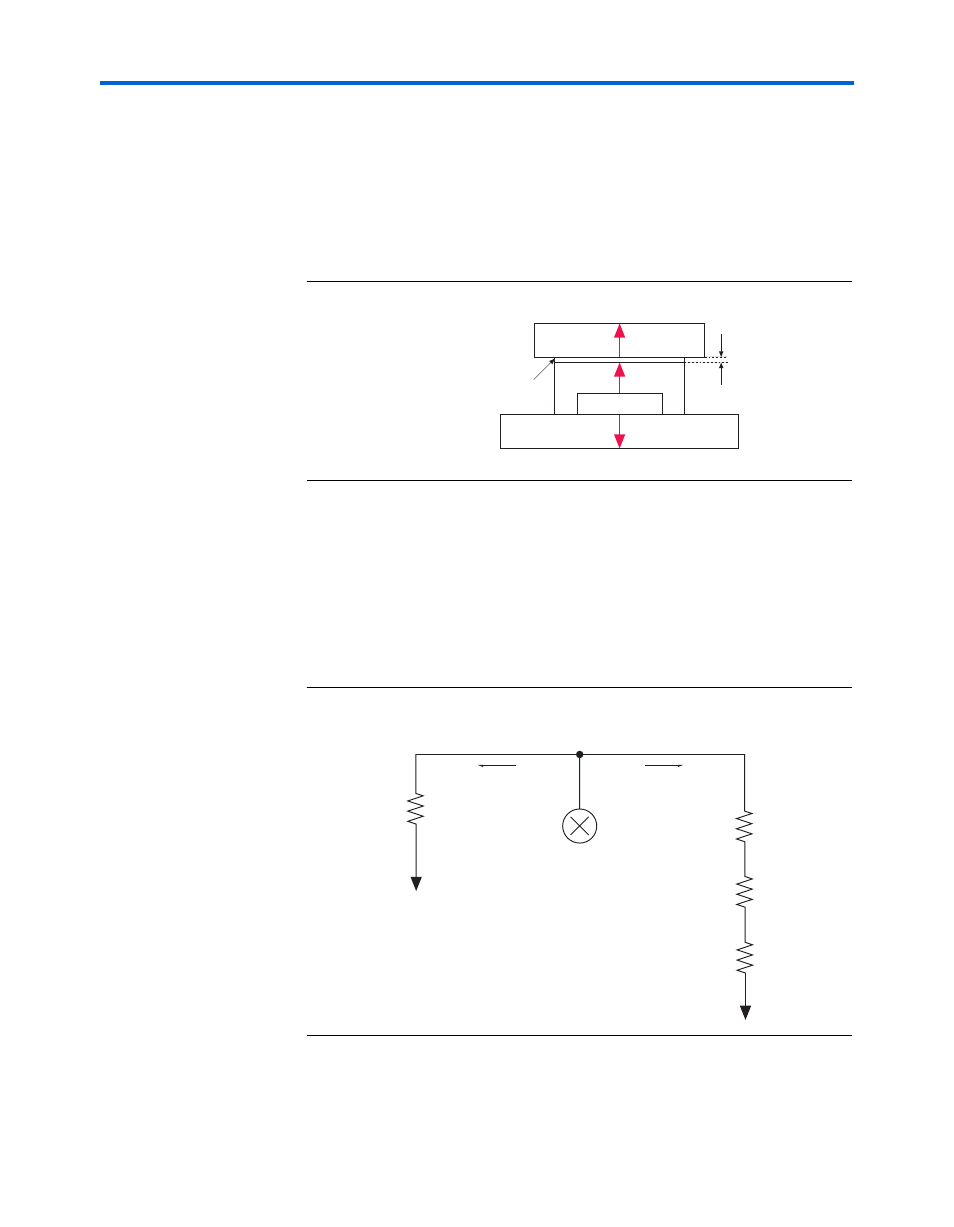
Figure 3–28. Thermal Representation with Heat Sink
In the model used in the PowerPlay Early Power Estimator, power can be
dissipated through the board or through the case and heat sink. The
thermal resistance of the path through the board is referred to as the
junction-to-board thermal resistance (
θ
JA
). The thermal resistance of the
path through the case, thermal interface material and heat sink is referred
to as the junction-to-ambient thermal resistance (
θ
JA
).
Figure 3–29
shows
the thermal model for the PowerPlay Early Power Estimator.
Figure 3–29. Thermal Model for the PowerPlay Early Power Estimator with a
Heat Sink
Heat Sink
Case
Device
Board
Thermal Interface Material
θ
JB
θ
JC
θ
SA
Thermal Representation with Heat Sink
θ
CS
θ
JC
θ
CS
θ
SA
θ
JB
T
J
T
B
T
J
T
C
T
S
T
A
Power (P)
Power (P)
Heat Source
