Pppoe – Ubiquiti Networks Rockeac User Manual
Page 24
21
Chapter 4: Network
airOS®7 User Guide
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
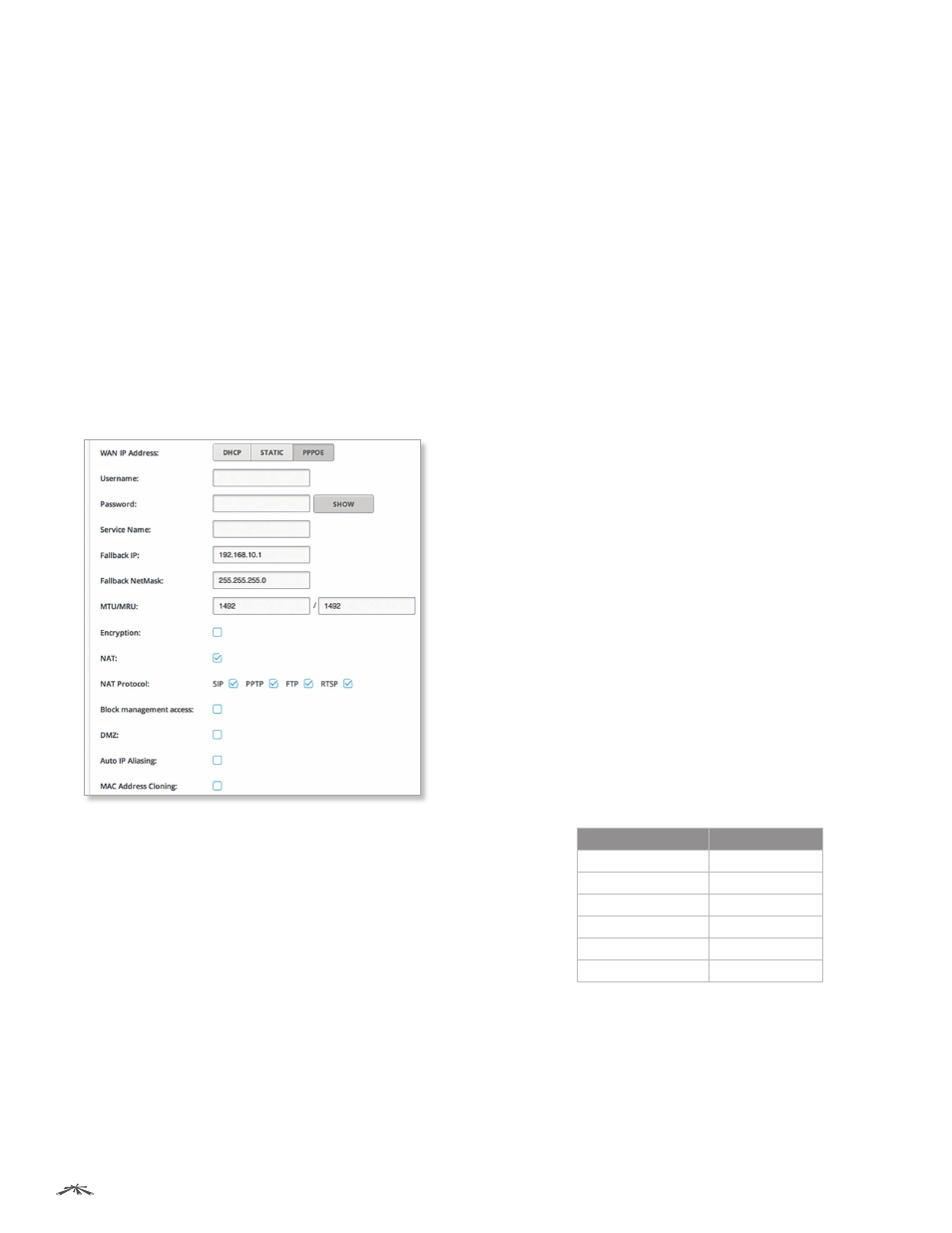
PPPoE
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) is a virtual
private and secure connection between two systems
that enables encapsulated data transport. Subscribers
sometimes use PPPoE to connect to Internet Service
Providers (ISPs), typically DSL providers.
Select PPPoE to configure a PPPoE tunnel. You can
configure only the WAN interface as a PPPoE client because
all the traffic will be sent via this tunnel. After the PPPoE
connection is established, the device will obtain the IP
address, default gateway IP, and DNS server IP address
from the PPPoE server. The broadcast address is used to
discover the PPPoE server and establish the tunnel.
If there is a PPPoE connection established, then the IP
address of the PPP interface will be displayed on the
Main tab next to the PPP interface statistics; otherwise
a Not Connected message and Reconnect button will be
displayed. To re-connect a PPPoE tunnel, click Reconnect.
Username
Enter the username to connect to the PPPoE
server; this must match the username configured on the
PPPoE server.
Password
Enter the password to connect to the PPPoE
server; this must match the password configured on the
PPPoE server.
Show
Click Show if you want to view the characters of the
password.
Service Name
Enter the name of the PPPoE service. This
must match the service name configured on the PPPoE
server.
Fallback IP
Enter the IP address for the device to use if
the PPPoE server does not assign an IP address.
Fallback Netmask
Enter the netmask for the device to
use if the PPPoE server does not assign a netmask.
MTU/MRU
The size (in bytes) of the Maximum
Transmission Unit (MTU) and Maximum Receive Unit
(MRU) used for data encapsulation during transfer through
the PPP tunnel. The default value is 1492.
Encryption
Enables the use of Microsoft Point-to-Point
Encryption (MPPE).
MTU
(Available in Simple view.) The Maximum
Transmission Unit (MTU) is the maximum frame size (in
bytes) that a network interface can transmit or receive. The
default is 1500.
NAT
Network Address Translation (NAT) is an IP
masquerading technique that hides private network IP
address space (on the LAN interface) behind a single
public IP address (on the WAN interface).
NAT is implemented using the masquerade type firewall
rules. NAT firewall entries are stored in the iptables
nat table. Specify static routes to allow packets to pass
through the airOS device if NAT is disabled.
•
NAT Protocol
To disable NAT traversal for the SIP, PPTP,
FTP, or RSTP protocols, uncheck the respective box(es).
Block management access
To block device management
from the WAN interface, check this box. This feature makes
Router mode more secure if the device has a public IP
address.
DMZ
DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) specifically allows one
computer/device behind NAT to become “demilitarized”,
so all ports from the public network are forwarded to the
ports of this private network, similar to a 1:1 NAT.
•
DMZ Management Ports
The airOS device responds to
requests from the external network as if it were the host
device that is specified with the DMZ IP address. DMZ
Management Ports is disabled by default; the device is
accessible from the WAN port. If DMZ Management Ports
is enabled, all management ports will be forwarded to
the device, so you’ll only be able to access the device
from the LAN side.
The default values of the management ports are:
Management Method
Management Port
HTTP/HTTPS
80/443 TCP
SSH
22 TCP
Telnet
23 TCP
SNMP
161 UDP
Discovery
10001 UDP
airView
18888 TCP
•
DMZ IP
Enter the IP address of the local host network
device. The DMZ host device will be completely exposed
to the external network.
