Chapter 4: network, Network role, Chapter 4 – Ubiquiti Networks Rockeac User Manual
Page 19: Network
16
Chapter 4: Network
airOS®7 User Guide
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
Chapter 4: Network
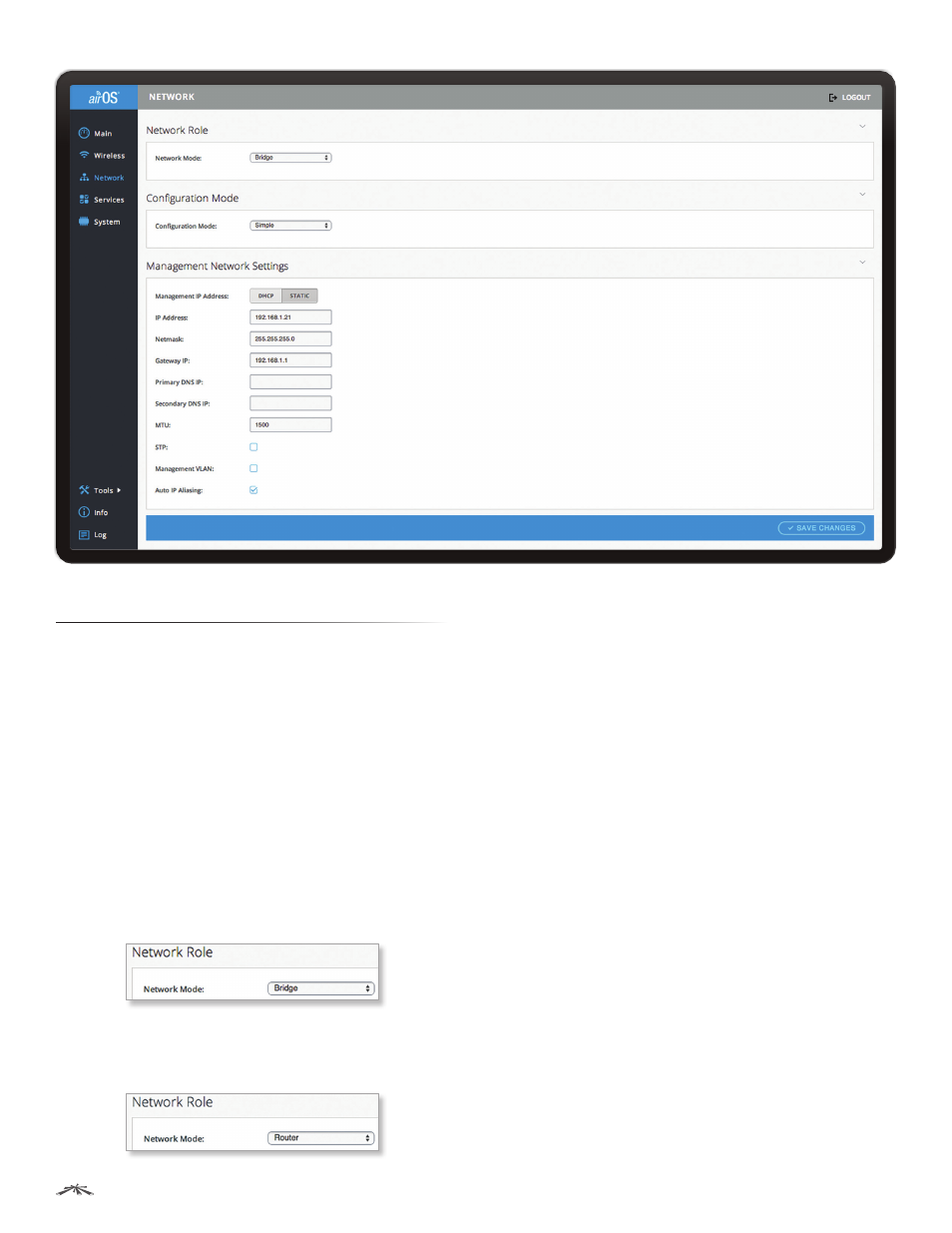
The Network page allows you to configure bridge or
routing functionality and IP settings.
Network Role
airOS v7.1 supports Bridge and Router modes.
Network Mode
Select the Network Mode of the device
(the mode depends on network topology requirements).
Bridge mode is adequate for very small networks. Larger
networks have significantly more traffic and need to be
managed by a device in Router mode to keep broadcast
traffic within its respective broadcast domain and prevent
it from overloading the overall traffic in the network.
•
Bridge
The device acts as a transparent bridge, operates
in Layer 2 (like a managed switch), and usually has only
one IP address (for management purposes only).
•
Router
The device contains two networks or subnets:
a Wide Area Network (WAN) and a LAN. Each wired or
wireless interface on the WAN or LAN has an IP address.
The following summarizes the differences between Bridge
and Router modes:
Bridge mode:
• The device forwards all network management and
data packets from one network interface to the other
without any intelligent routing. For simple applications,
this provides an efficient and fully transparent network
solution.
• There is no network segmentation, and the broadcast
domain is the same. Bridge mode does not block
any broadcast or multicast traffic. You can configure
additional firewall settings for Layer 2 packet filtering
and access control.
• WLAN and LAN interfaces belong to the same network
segment and share the same IP address space. They
form the virtual bridge interface while acting as bridge
ports. The device features IP settings for management
purposes.
Router mode:
• The device operates in Layer 3 to perform routing and
enable network segmentation – wireless clients and
the WAN interface are on a different IP subnet. Router
mode blocks broadcasts and can pass through multicast
packet traffic. You can configure additional firewall
settings for Layer 3 packet filtering and access control.
• The device can act as a DHCP server and use Network
Address Translation (Masquerading), which is widely
used by APs. NAT acts as the firewall between the LAN
and WAN.
