Locations and functions of controls, Location and functions of controls – Sears 113.19771 User Manual
Page 21
Attention! The text in this document has been recognized automatically. To view the original document, you can use the "Original mode".
locations and functions of controls
1. Depth of Cut ^Elevation)
d.
The diagram shows the elevation crank which is
used to raise and lower the saw blade,
b.
Clockwise rotation raises the blade .
. .
counterclockwise
rotation
lowers
it.
One
complete
turn of the handle will raise or lower the saw blade
1/1 6-inch.
2.
Angle of Cut (Miter)
Proper
Indexing
Method
—
Experienced
operators
of
woodworking equipment, such as this Craftsman Radial
Saw,
acquire
the
habit
of
indexing
in
one
direction
only, whenever a new setting is made in preparation for
a different operation.
Exampie:
When moving the arm to a miter index
position move it slightly past the desired index position,
then return to the index position carefully to index and
lock.
Yoke
indexing
and
bevel
indexing
can
be
accomplished
in
a
similar
manner.
This
indexing
technique
tends
to
neutralize
any
stresses
impaired
upon
saw
components
and
contributes
to
the
high
degree of accuracy the saw is capable of producing
when operated expertly.
a.
The arm control lever locks, unlocks and indexes
the arm for Lett and Right Miter cuts.
h.
The radial arm has positive index positions at 0“
and 4E° Left and Right. The arm is rotated by
pulling arm control lever to index release position.
With
arm
control
lever
released
the
arm
will
automatically index at 0° and 45° Left or Right.
After
positioning
arm
to
the
desired
miter
angle,
push arm control lever to locked position.
LOCK
UNLOCK
i n d e x
r e l e a s e
3.
Yoke Pivot (Ripping)
a.
Two controls are used m this operation. They are:
the
swivel
latch-pin
lever
and
the
yoke
clamp
handle.
b.
A swivel latch lever automatically indexes the yoke
at each 90° position. Pull the spring-loaded swivel
latch-iever forward to release this pin.
c.
The yoke clamp handle locks the yoke
To
the
carriage in any position. Pull the handle forward to
release the yoke; push the handle rearward
to
secure
the yoke.
4.
Carriage Lock
a.
The carriage lock knob is rotated clockwise to lock
the carriage on the radial arm, and counterclockwise
to release it.
b.
When
performing
crosscutting
operations
the
carriage
lock
knob
must
be
rotated
counterclockwise until the carriage is free to travel
along the arm. This knob should be tightened until
the
operator
is
ready
to
grasp
the
bevel
index
handle and make a cut.
5.
Blade Angle (Bevel)
a. The two controls used in angular positioning and
indexing
of
the
motor,
to
provide
the
desired
saw-blade (bevel) angfe, are: bevel lock lever and
bevel-index lever.
b.
The bevel-index scale indicates the angular position
of the motor with respect to horiiontal, from 0° to
90° in either vertical position.
c.
The
bevel
index
lever
automatically
indexes
the
motor at 0°, 45° and 90°. Move bevel index lever
to the left while positioning the blade, then release
it. At any other position it does not engage.
d.
The bevel lock lever locks The motor to the yoke
when the motor is in any position. Pull lever to
release and push to lock.
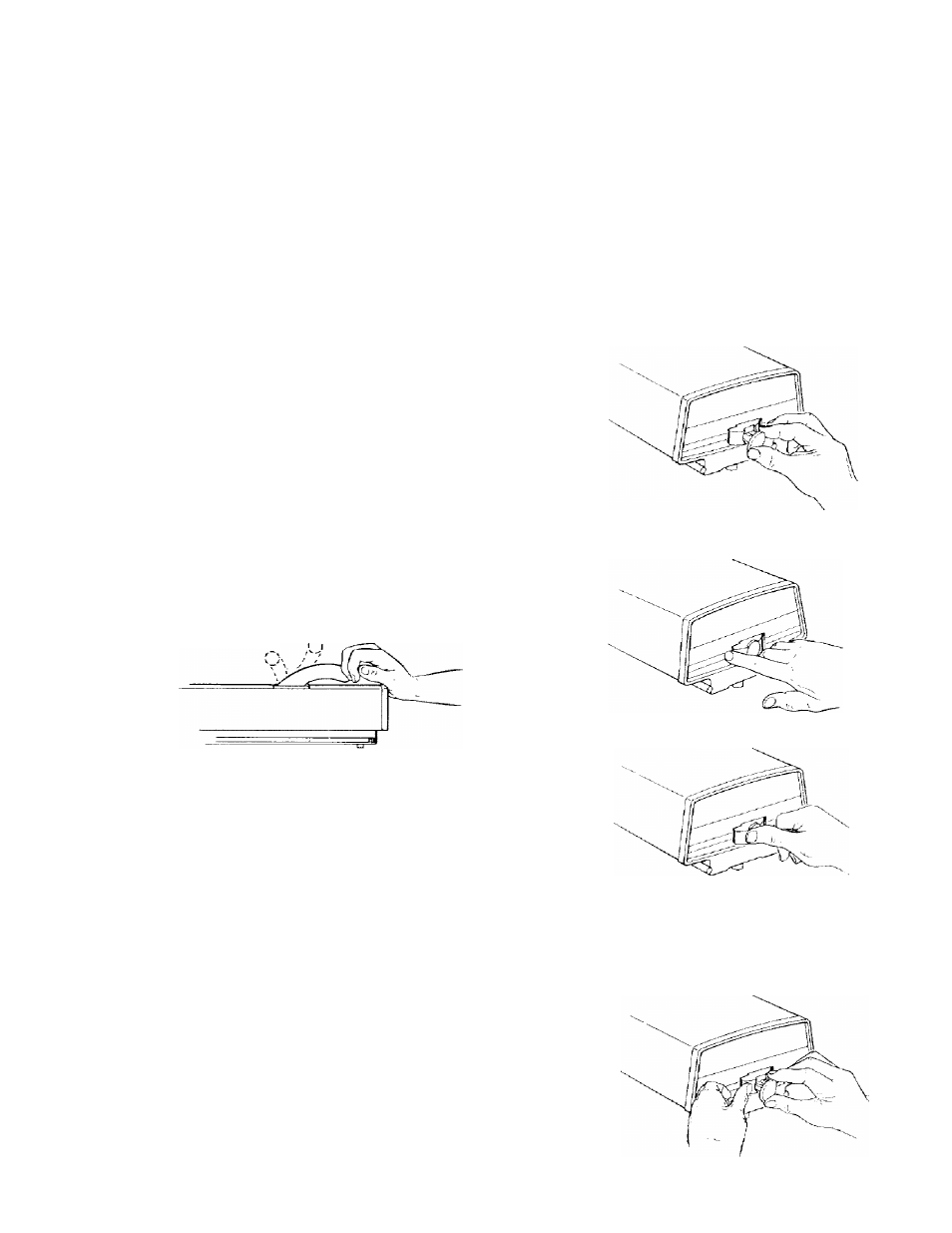
6. Power Switch and Key
a. Insert key into switch lock.
b. Insert finger under end of switch lever and pull end
out, to turn switch on.
c.
Push lever in to turn switch off.
W A R N I N G :
T H I S LOCKING FEATURE IS
P R O V I D E D
TO
PREVENT
UNAUTHORIZED
USE
OF
YOUR
SAW.
ALWAYS
REMOVE
THE
KEY
AND
KEEP
IT
IN
A
SAFE
PLACE.
TO
REMOVE
K E Y ,
HOLD
THUMB
ON
END
OF
LEVER
TO
KEEP
SWITCH
IN
"OFF"
POSITION
AND PULL KEY STRAIGHT OUT.
2 1
