If p3ot ials i.® d.o not, Isio – Carrier 48KH User Manual
Page 15
Attention! The text in this document has been recognized automatically. To view the original document, you can use the "Original mode".
#
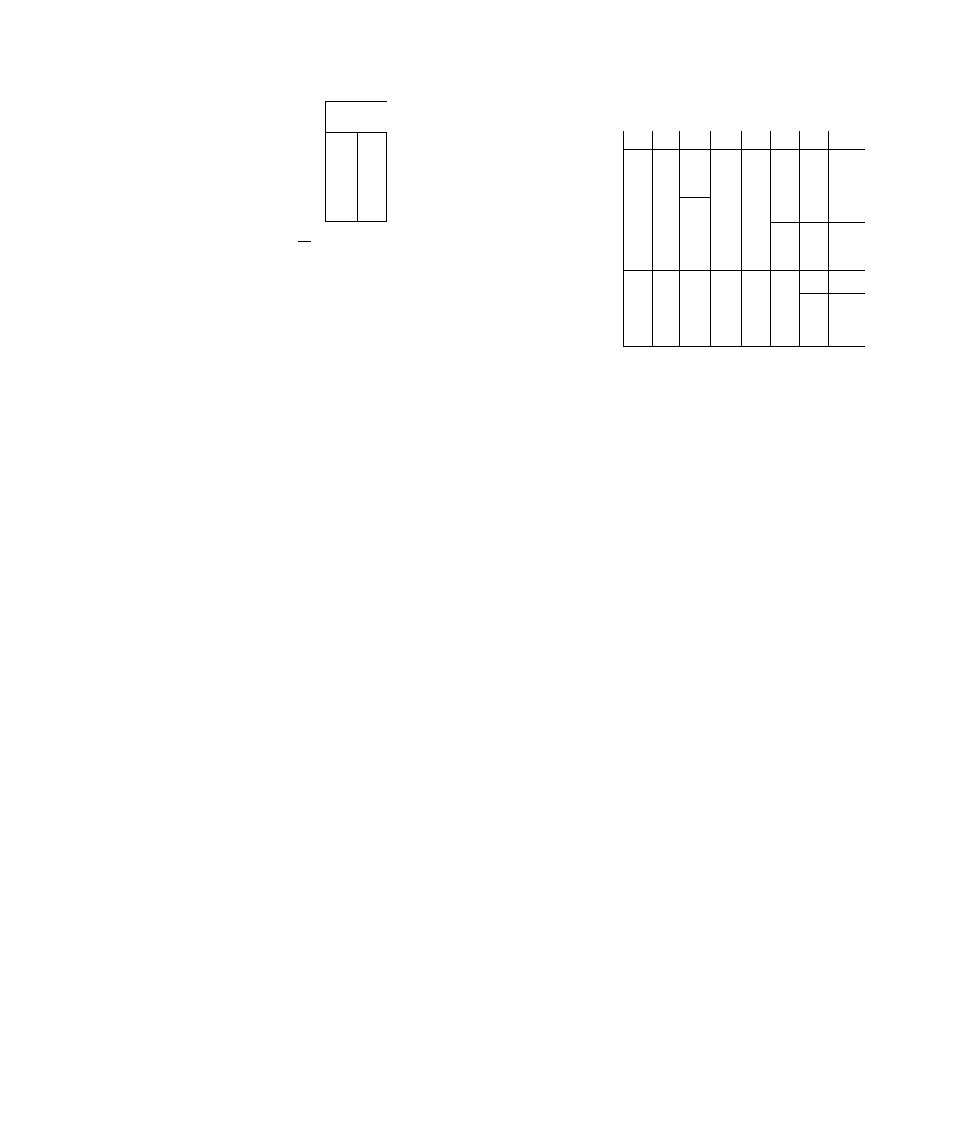
Table 6 — Model 48KH,KL Air Delivery (cfm)*
at Indicated External Static Pressure and Voltage (Cont)
MODEL
48-
UNIT
VOLTS-
PHASE (60 Hz)
208/
230—3
BLOWER
MOTOR
SPEED
Low
Med
High
Low
High
Low
Med
High
COILt
Heat
Cool_
Heat
Cooli
Heat
Cool
Heati
Cool
Heat
Coolt
Heat
Cool
HeatJ
Cool
Heat
Cooli
- -
—
0 0
0 1
1440
1435
1435
1430
1755
1740
1745
1730
1950
1920
1925
1890
EXTERNAL STATIC PRESSURE (in wg)
208V
1425
1420
1725
1710
1880
1850
1415
M10
1700
1680
1840
1810
1400
1395
1665
1645
1795^
1765
1385
1380
1625
1600
1750
1715
•Air delivery values are without air filter Deduct field-supplied air filter pressure drop to
obtain external static pressure available for ducting
tHeating airflow values are with a dry coil Cooling airflow values are with a wet coil
iThese airflow values are at the factory heating and cooling blower motor speed setting
A dash {—) indicates portions of the table that are beyond the blower motor capability or
that are not applicable
1365
1355
1580
1550
1700*
1665
1340
1330
1530
1500
1645
1615
0
8
1305
1290
147(T
1440
1590
1560
230V or 460V
1730
1725
1970
1950
2175*
2130
Î585
1585
2375
2270
Isio
1875
2130
2075
2345
2255
0
1
0
2
0 3
0 4
0 5
0
6
0 7
0
8
1720
1700
1675
1645
1610
1560
1520
1470
1710
1685
1660
1625
1585
1545
1495
1445
1945
1910
1875
1825
1775
1720
1660
1600
1920
1880
1840
1790
1735
1685
1625
1570
2130
2085
2030
1970
1905
1840
1765
1695
2085
2035
1980
1920
1855
1790
1720
1650
1585
1580
1560
1530
1495
-
—
—
1585
1575
1550
1515
1475
—
—
—
2280
2185
2095
2000
1905
—
—
___
2185
2100
2015
1930
1840
-
-
—
1875
1860
1825
1770
1700
—
—
_
1865
1840
1790
1725
1650
—
-
—
2075
2015
1955
1890
1810
_
_
___
2025
1965
1900
1835
1760
—
—
—
2260
2180
2095
2010
1930
_
_
___
2175
21002020
1945
1865
-
-
—
NOTE: Do not operate the unit at a cooling airflow that is less than 350 fpm per each
1 2,000 Btuh of rated cooling capacity Indoor coil icing may occur at airflows below this
point
thermostat
simultaneously
energizes
pilot
valve
(part of gas valve) and pilot igniter. Energized pilot
gas valve permits gas to flow to pilot.
NOTE: Pilot gas valve is a solenoid consisting of a
PICK and a HOLD coil. Both coils must be ener
gized to open pilot gas valve, but only HOLD coil
must be energized to keep valve open.
Energized pilot igniter sends a high-voltage charge
to pilot electrode (part of pilot). Pilot electrode pro
duces a spark that ignites pilot. Elame-sensing
monometal switch in pilot proves presence of pilot
flame. Approximately 40 to 60 seconds after pilot
flame is established, normally closed contacts of
pilot open and normally open contacts close.
Switching of pilot contacts de-energizes pilot igniter
and PICK coil of pilot solenoid. HOLD coil of
pilot solenoid is still energized; therefore, pilot gas
valve remains open and pilot remains lit.
if p3ot ialS i.®
d.o not
a sjafcli or ofeW soarco of
i
Switching of pilot contacts also completes low-
voltage circuit to time-delay heat relay, and terminal
no. 1 of gas valve. After approximately 10 seconds,
heat-motor-operated gas valve opens and permits
gas to flow to burners where gas is ignited by pilot.
Ignited burners heat the heat exchanger.
After built-in time delay, normally open relay
contacts of energized heat relay close, and circuit to
blower motor is completed. Blower motor starts.
Heating cycle remains on until room temperature
rises to a point that is slightly above heating control
setting of room thermostat. At this point, thermostat
heating bulb tilts and breaks circuit between thermo
stat terminals R and W. Gas flow thru gas valve
stops and burner flames go out. Gas flow thru pilot
gas valve also stops and pilot flame goes out.
Time-delay heat relay de-energizes; however, there
is a built-in delay before heat relay contacts open, and
blower continues to move air across heat exchanger
to help optimize heating efficiency. When heat relay
contacts open, circuit to blower motor breaks and
motor stops.
Unit is in a standby condition, waiting for next
call for heat from thermostat.
LIMIT AND PRESSURE SWITCHES — Eurnace
limit switch (see Eig. 10) closes gas valve if leaving-
air temperature exceeds 175 E.
Normally closed limit switch completes control
circuit thru pigtail lead W to gas valve 5 F. See
Fig. 10. Should leaving-air temperature rise to 175 F,
switch opens and W control circuit breaks. Any
interruption in W control circuit instantly closes gas
valve and stops gas flow to burners and pilot. Blower
motor continues to run until time-delay sequence of
heat relay is completed.
When air temperature at limit switch drops to the
low-temperature setting of limit switch, switch
closes and completes W control circuit. Electric-
spark ignition system cycles and unit returns to
normal heating operation.
Pressure switch (see Fig. 10) is required only when
unit operates on LP (propane) gas.
BLOWER
SAFETY
SWITCH
Blower
safety
switch is a temperature-actuated switch connected
parallel with contacts of heat relay. Function of
switch is to activate blower should gas valve fail to
close when thermostat is satisfied. Safety switch is
mounted on blower divider panel. When tempera
ture at safety switch reaches approximately 175 F,
switch closes to start blower. Switch opens when
temperature at switch drops to approximately 116 F.
1 5
