tekmar 665 Snow Detector & Melting Control Installation User Manual
Page 14
14 of 28
©
2012 D
665
-
04/12
tekmarNet
®
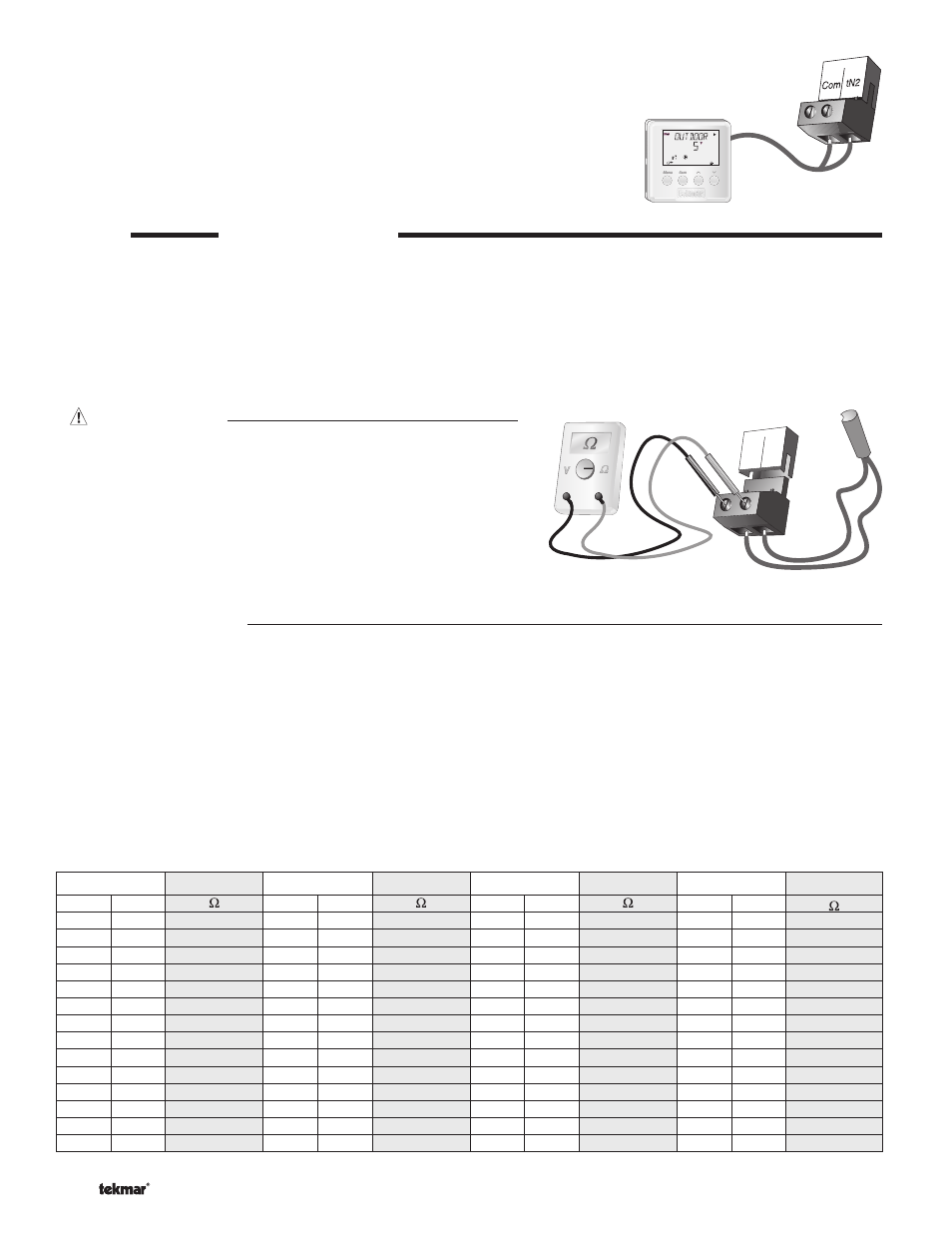
(tN2) Device
A Remote Display Module (RDM) 040 or Remote Start / Stop Module 039 can be
connected to the tekmarNet
®
(tN2) input. Connect the Com terminal from the
appropriate tN2 device to the Com terminal (7) on the 665. Connect the tN2 terminal from
the appropriate tN2 device to the tN2 terminal (8) on the 665.
Note: The wires from the RDM and Remote Start / Stop Module are polarity sensitive.
The tN2 device does not operate correctly if the wires are reversed.
7 8
7
Com
6
Out
STEP SIX
TESTING THE WIRING
Each terminal block must be unplugged from its header on the control before power is applied for testing. To remove the terminal
block, pull straight down from the control.
The following tests are to be performed using standard testing practices and procedures and should only be carried out by properly
trained and experienced persons.
A good quality electrical test meter, capable of reading from at least 0 – 300 V (ac) and at least 0 – 2,000,000 Ω, is essential to
properly test the wiring and sensors.
Test the Sensors
In order to test the sensors, the actual temperature at each sensor
location must be measured. A good quality digital thermometer with
a surface temperature probe is recommended for ease of use and
accuracy. Where a digital thermometer is not available, a spare
sensor can be strapped alongside the one to be tested and the
readings compared.
Temperature
Resistance
Temperature
Resistance
Temperature
Resistance
Temperature
Resistance
°F
°C
°F
°C
°F
°C
°F
°C
-50
-46
490,813
20
-7
46,218
90
32
7,334
160
71
1,689
-45
-43
405,710
25
-4
39,913
95
35
6,532
165
74
1,538
-40
-40
336,606
30
-1
34,558
100
38
5,828
170
77
1,403
-35
-37
280,279
35
2
29,996
105
41
5,210
175
79
1,281
-30
-34
234,196
40
4
26,099
110
43
4,665
180
82
1,172
-25
-32
196,358
45
7
22,763
115
46
4,184
185
85
1,073
-20
-29
165,180
50
10
19,900
120
49
3,760
190
88
983
-15
-26
139,403
55
13
17,436
125
52
3,383
195
91
903
-10
-23
118,018
60
16
15,311
130
54
3,050
200
93
829
-5
-21
100,221
65
18
13,474
135
57
2,754
205
96
763
0
-18
85,362
70
21
11,883
140
60
2,490
210
99
703
5
-15
72,918
75
24
10,501
145
63
2,255
215
102
648
10
-12
62,465
80
27
9,299
150
66
2,045
220
104
598
15
-9
53,658
85
29
8,250
155
68
1,857
225
107
553
A good quality test meter capable of measuring up to 5,000 kΩ (1 kΩ = 1000 Ω) is required to measure the sensor resistance. In
addition to this, the actual temperature must be measured with either a good quality digital thermometer, or if a thermometer is
not available, a second sensor can be placed alongside the one to be tested and the readings compared.
First measure the temperature using the thermometer and then measure the resistance of the sensor at the control. The wires
from the sensor must not be connected to the control while the test is performed. Using the chart below, estimate the temperature
measured by the sensor. The sensor and thermometer readings should be close. If the test meter reads a very high resistance,
there may be a broken wire, a poor wiring connection or a defective sensor. If the resistance is very low, the wiring may be
shorted, there may be moisture in the sensor or the sensor may be defective. To test for a defective sensor, measure the
resistance directly at the sensor location.
Do not apply voltage to a sensor at any time as damage to the sensor may result.
Test the Sensor Wiring
