Define raid – Syba SB-ATA8212-133R User Manual
Page 13
RAIDExpress 133 RAID USER MANUAL
21
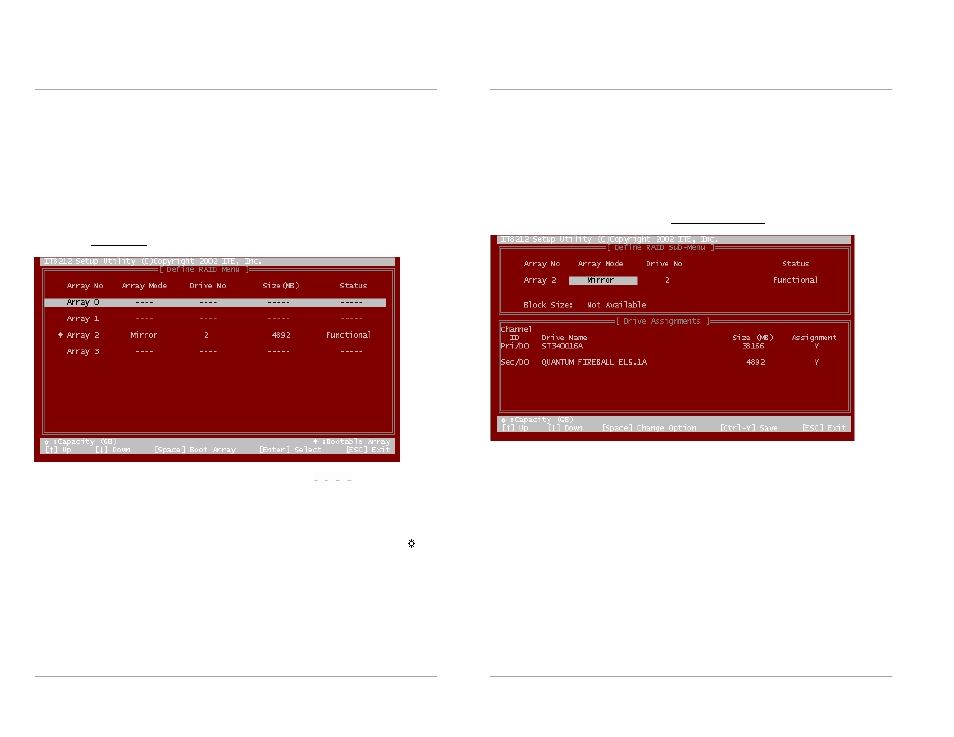
Define RAID
Click
“2” on the Main Menu then you can enter the Define RAID Menu. Please use
arrow keys ↑ and ↓ to highlight the array number you want to define; use the
“space” key to specify the bootable array if you would like to boot your system from
array attached on RAIDExpress 133 controller; and click the
“Enter” key to select it
and enter the Define RAID Sub-Menu to create your array. If you want to quit and go
back to the Main Menu, please click the
“Esc” key.
When an array is not assigned a RAID level, you will see
“
” on the raw.
Column
“Array Mode” shows the RAID level (Stripe, Mirror, Stripe + Mirror or JBOD)
assigned to the array. Column
“Drive No” shows the number of hard drive included in
the array. Column
“Size” shows the array’s total capacity. If there is a symbol
shown in front of
“Size”, the capacity unit is gigabyte. Column “Status” shows array
status. You will see
“Functional” if the array is operational and “Non-Functional” if the
array has lost its functionality.
Please highlight the array number you want to define and click the
“Enter” key, then
the Define RAID Sub-Menu will appear and allow drive assignments to the array.
RAIDExpress 133 RAID USER MANUAL
22
Define RAID Sub-Menu
When you highlight the array you want to define on the Define RAID Menu, click the
“Enter” key then you will enter this Define RAID Sub-Menu. You can use arrow keys
↑ and ↓ to highlight different positions. The
“space” bar key can help you cycle
through the different options.
“Ctrl-Y” keys can save the change and the “Esc” key
can help you quit then go back to the Define RAID Menu on page 21.
Block Size Option
You can select Stripe Block size ranging from 1k to 64k for Stripe (RAID 0) or Stripe +
Mirror (RAID 0+1) array. The selection of block size is related to how your data is sent
and regained from hard drives. You can do some tests to decide which block size is
suitable for your system. Generally, a large block size is suitable to manage large file
transfer such as MPEG files. On the contrary, the small block size is suitable to
manage small files such as e-mail files.
