Rockwell Automation 1768-CNxxx ControlNet Communication Modules User Manual
Page 34
34
Rockwell Automation Publication CNET-IN005C-EN-P - July 2014
Chapter 3
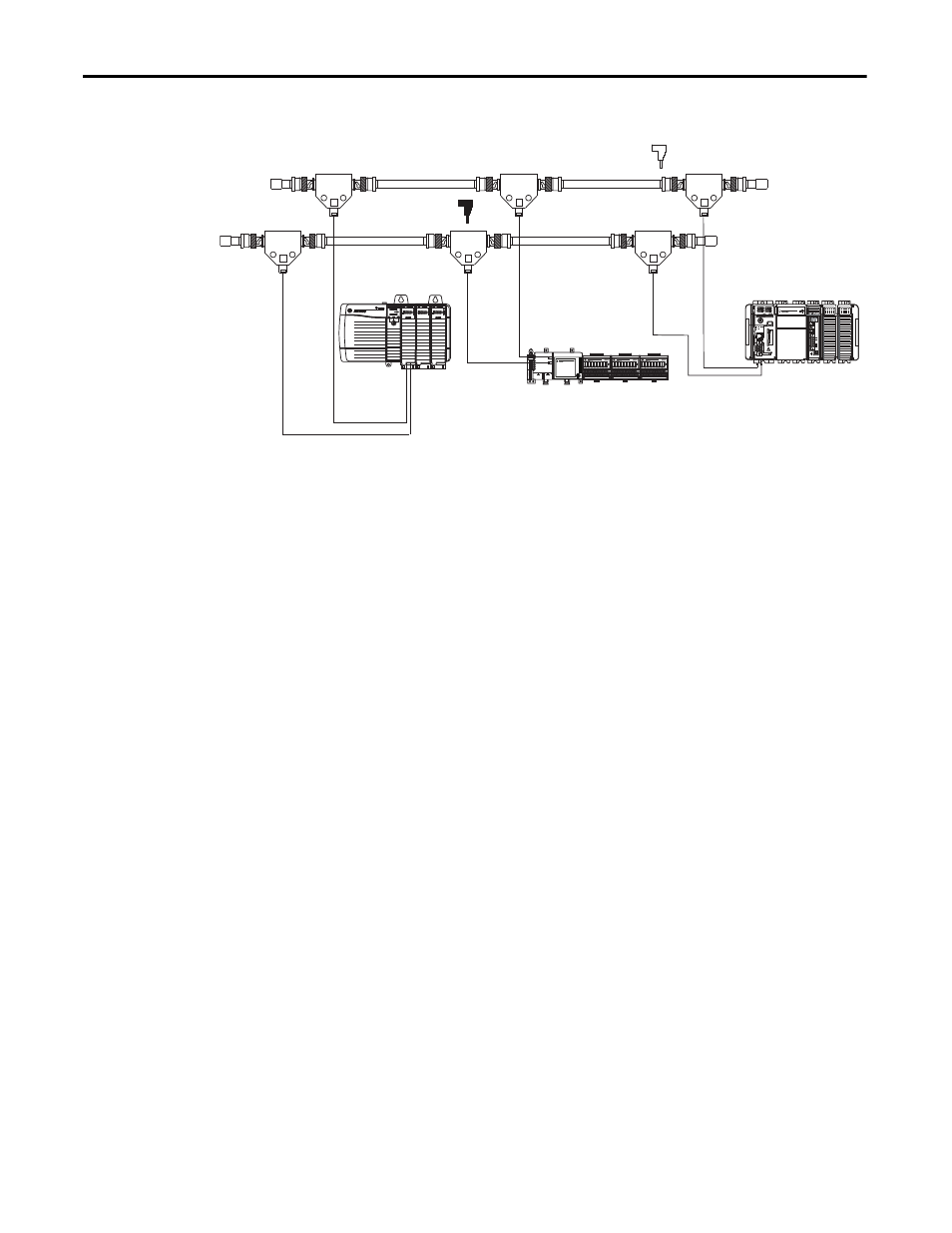
Redundant Media
Figure 1 - Redundant Media Example
Observe these guidelines when planning a redundant media system in a
hazardous area:
• Route trunk cables A and B differently to reduce the chance of both cables
being damaged simultaneously.
– Trunk cables A and B may contain different lengths of cable if you are
using 1786-RPA/B repeater adapters. However, the difference in length
must not exceed 800 m (2640 ft).
– Trunk cables A and B must have identical configurations. Each segment
must contain the same number of taps, nodes, and repeaters. Connect
nodes and repeaters in the same relative sequence on both trunk cables.
• Each node on a redundant-cable link must support redundant coax
connections and be connected to both trunk cables at all times. Any nodes
connected to only one side of a redundant-cable link will result in media
errors on the unconnected trunk cable.
• Install the cable system so that the trunk cables at any physical device
location can be easily identified and labeled with the appropriate icon or
letter. Each redundant ControlNet device is labeled so you can connect it
to the corresponding trunk cable.
Node
Trunk Cable A
Trunk Cable B
Node
Node
To use redundant media, all nodes must support redundant media.
