Module operation - devicenet example – Rockwell Automation 1790P-4R0 CompactBlock LDX I/O RTD/Resistance Input Module User Manual
Page 11
Publication 1790-UM002A-EN-P
Overview 1-5
Once a channel is properly configured and enabled, the module
continuously converts the RTD or resistance input to a value within the
range selected for that channel.
Each time the module reads an input channel, it tests the data for a fault
(over- or under-range or open-circuit condition). If it detects a fault, the
module sets a unique bit in the channel status word. See Input Data File
on page 3-2. The module sends two’s compliment binary converted RTD/
resistance data out over the network. See Appendix B for a description of
two’s compliment binary numbers.
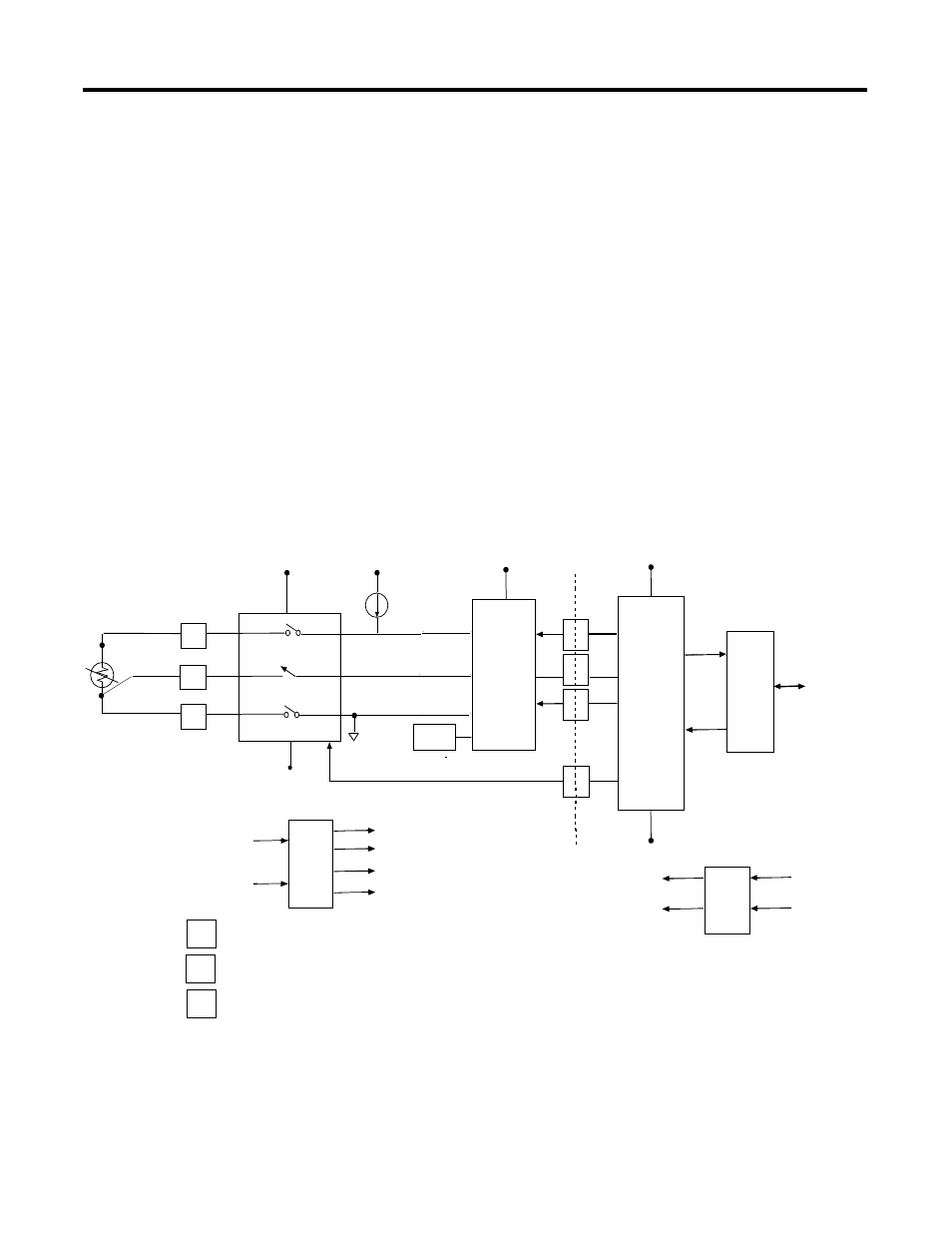
Module Operation - DeviceNet Example
As shown in the block diagram below, each input channel of the module
consists of an RTD/resistance connection that accepts excitation current; a
sense connection that detects lead wire resistance; and a return
connection. The signals are multiplexed to an A/D converter that reads
the RTD or resistance value and the lead wire resistance.
From the readings taken by the converter, the module sends RTD or
resistance data through the microcontroller to the DeviceNet network.
The PROFIBUS block diagram is similar.
Input
EXC0
SENSE0
RTN0
CH0
Multiplexer
VA2
A/D
VREF
Vref
Channel Select
Channels 1 through 3 same as
channel 0 above.
43224
A
B
COM
VA1
VA1
EXC
Current
Vcc
Optical
Isolation
AIN-
AIN+2
AIN+1
VA3
A-GND
Micro-
Controller
Transmit
Receive
GND
Network
Power
Supply
Analog
Power
Supply
DeviceNet
24Vdc
Power
Vcc
GND
VA1
VA2
VA3
A-GND
VDC
GND
1
2
3
Auxiliary
24Vdc
Power
