Battery input – Rockwell Automation 1606-XLS240UPSD Power Supply Reference Manual User Manual
Page 8
All parameters are specified at an input voltage of 24V, 10A output load, 25°C ambient and after a 5 minutes run-in time unless noted otherwise.
It is assumed that the input power source can deliver a sufficient output current.
8
Rockwell Automation Publication 1606-RM017A-EN-P — February 2014
Bulletin 1606 Switched Mode Power Supplies
8. Battery Input
The DC-UPS requires one 12V VRLA battery to buffer the 24V and 12V output.
Battery voltage
nom.
DC 12V
Use one maintenance-free 12V VRLA lead acid battery or
one battery module which is listed in the Accessories
section.
9.0 – 15.0V
Continuously allowed, except deep discharge protection
Battery voltage range
max.
35Vdc
Absolute maximum voltage with no damage to the unit
typ.
7.4V
Above this voltage level battery charging is possible.
Allowed battery sizes
min.
3.9Ah
max. 40Ah
Internal battery resistance
max.
100mOhm
See individual battery datasheets for this value
Battery charging method
CC-CV
Constant current, constant voltage mode
Battery charging current (CC-mode)
nom.
1.5A
Independent from battery size,
max.
1.7A
Corresponding 24V input current see Fig. 8-2
End-of-charge-voltage (CV-mode)
13.4-13.9V
Adjustable, see section 14
Battery charging time
typ.
5h *)
For a 7Ah battery
typ.
17h *)
For a 26Ah battery
typ.
21A
Buffer mode, 240W output, 11.5V on the battery
terminal of the DC-UPS, see
Battery discharging current **)
Fig. 8-1 for other parameters
typ.
0.3A
Buffer mode, 0A output current
max.
50
μ
A
At no input, buffering had switched off, all LEDs are off
typ.
310mA
At no input, buffering had switched off, yellow LED
shows “buffer time expired” (max. 15 minutes)
Deep discharge protection ***)
typ.
10.5V
At 0% output load
typ. 9.0V
At
100%
output
load
*) The charging time depends on the duration and load current of the last buffer event. The numbers in the table represent a
fully discharged battery. A typical figure for a buffer current of 10A at 24V output is 3h 20Min. for a 7Ah battery.
**) The current between the battery and the DC-UPS is more than twice the 24V output current. This is caused by boosting the 12V
battery voltage to a 24V level.
This high current requires large wire gauges and short cable length for the longest possible
buffer time. The higher the resistance of the connection between the battery and the DC-UPS, the lower the voltage on the
battery terminals which increases the discharging current. See also section 24 for additional installation instructions.
***) To ensure longest battery lifetime, the DC-UPS has a battery deep discharge protection feature included. The DC-UPS stops
buffering when the voltage on the battery terminals of the DC-UPS fall below a certain value.
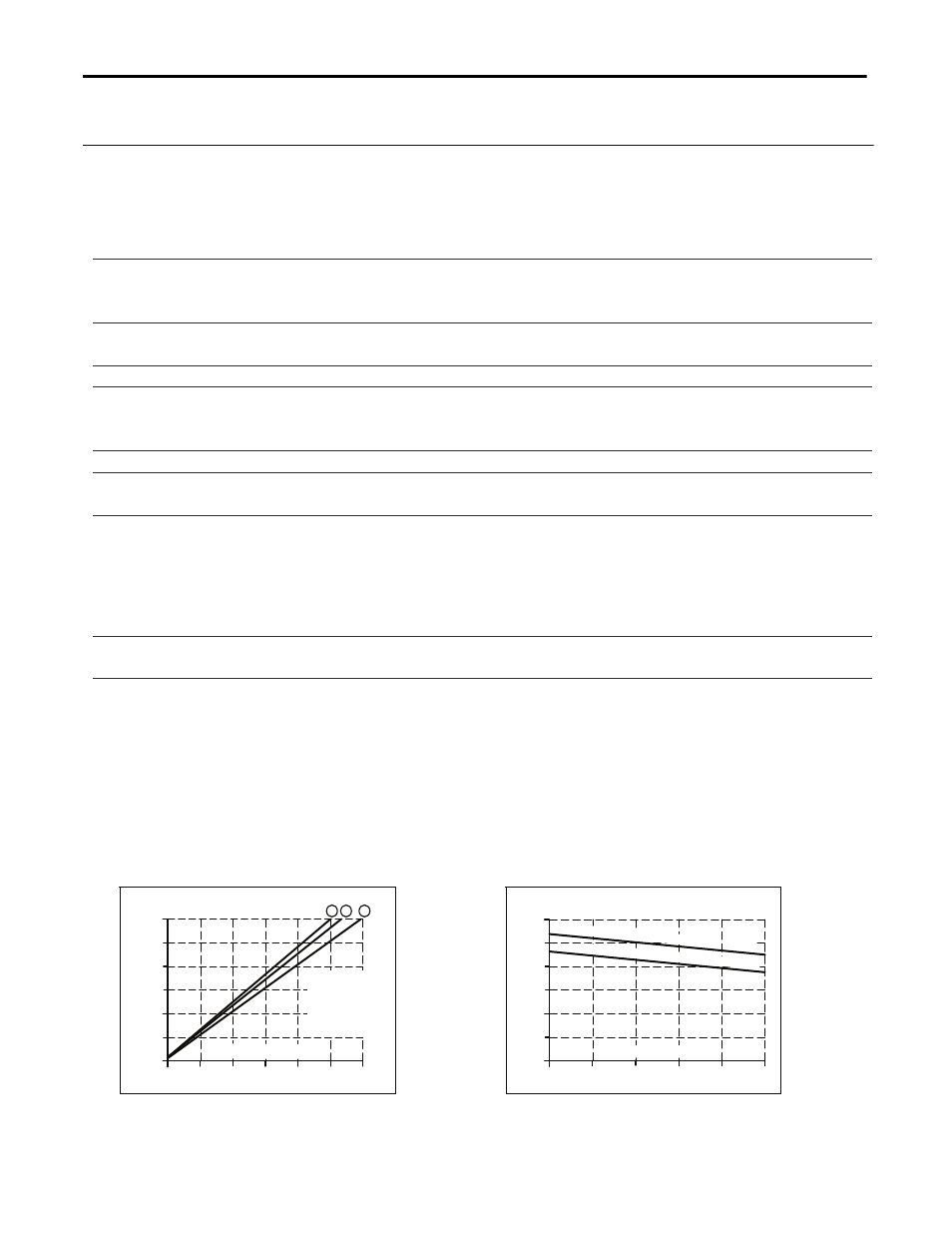
Fig. 8-1 Battery discharging current
vs. 24V output current, typ.
(12V not loaded)
Fig. 8-2 Required input current vs. input
voltage for battery charging
(12V not loaded)
Battery Current
0
0
10
20
5
15
25
30A
2.5
7.5
10
5
.
2
1
A
5
1
5
Output Current
Voltage on
battery terminal
of the DC-UPS:
A: 10.5V
B: 11V
C: 12V
A
B
C
Input Current
0
23
0.5
1.0
0.25
0.75
1.25
1.5A
Input Voltage
24
25
26
28V
max. (battery charging c
urrent 1.7A)
27
typ. (battery charging c
ur rent 1.5A)
