Pr el im in a ry, Fusion, Operation and maintenance, continued – Clarus Environmental Fusion Series Treatment Systems 450/600/800 User Manual
Page 13
13
© Copyright 2012. All rights reserved.
PR
EL
IM
IN
A
RY
RECIRCULATION SYSTEM
1. Measure the recirculation flow
2. Cleaning
BACKWASH SYSTEM
1. Measure the current backwash flow
2. Cleaning
3. Alternating backwash time and frequency
BLOWER AND
CONTROL PANEL
1. Power failure
2. Blower timer setting
3. Noise and vibration
4. Air filter replacement
5. Diaphragm replacement
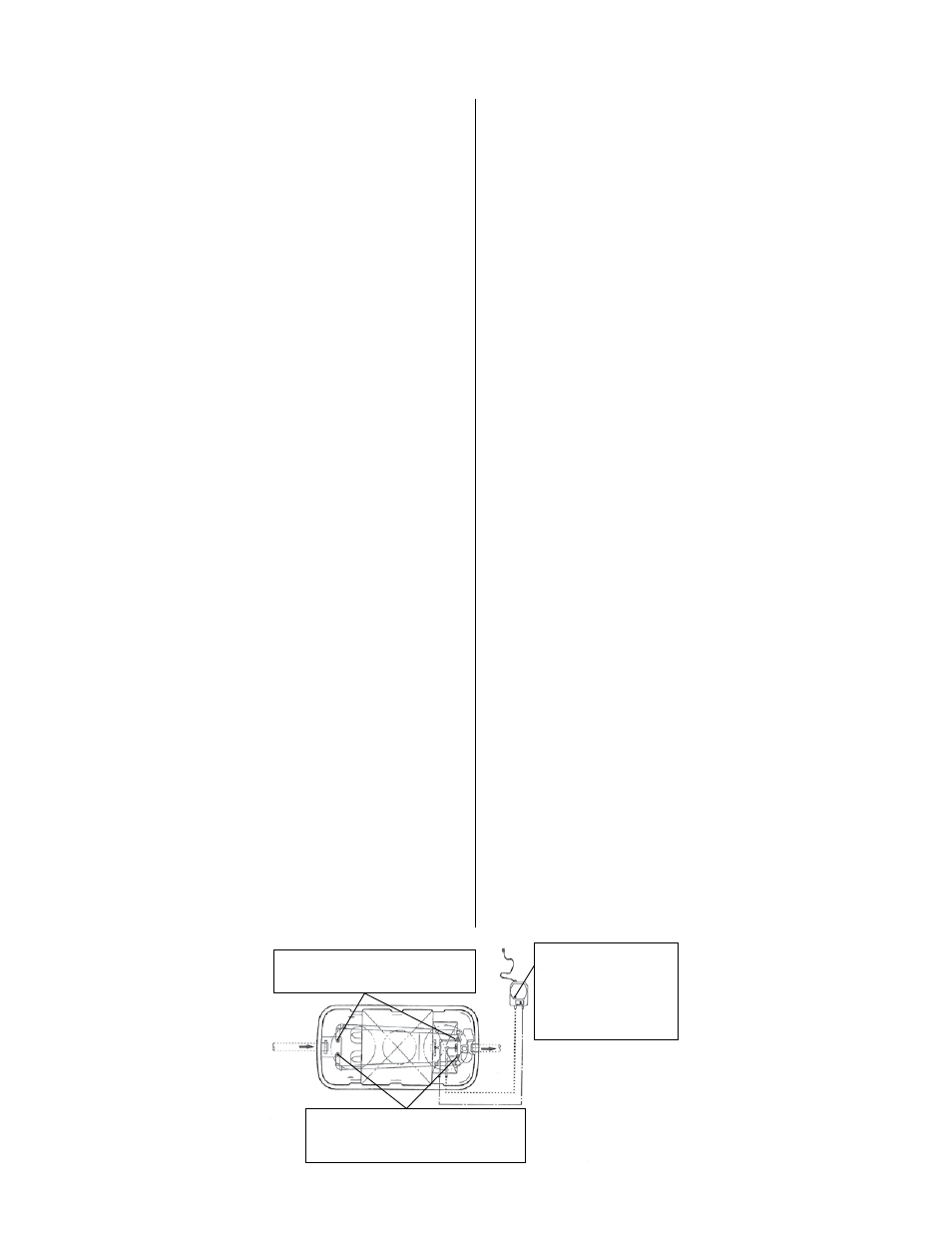
Figure 17 - Inspection details
FUSION
®
OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE, continued
OPTIONAL WATER QUALITY ANALYSES
1. Transparency – A transparency reading more than 20
cm is preferred.
2. Scum – Should not be present unless recirculation
and/or backwash rate is too high or daily flow exceeds
design capacity. To correct, reduce the recirculation and
or backwash rate.
3. Sludge – A range of 0” to 15” (0-38 cm) is preferred.
Typically brown and settled, becomes gray to black
as depth and digestion increases. More than 15” (38
cm) may require a reduction in recirculation rate. A
sludge accumulation of greater than 24” (61 cm) in the
sedimentation and 15” (38 cm) in the anaerobic chamber
requires pumping.
PART C: Sedimentation Chamber – collect samples
from the outlet baffle of the sedimentation chamber for the
following analyses:
1. Scum – 0” to 12” (0-30.5 cm) is common, so long as it
is not rising above the partition wall. If so, punch down
using ladle.
2. Sludge – A range of 0” to 24” (0-61 cm) is common.
Typically brown and settled, becomes gray or black as
depth and digestion increases. A sludge accumulation
of > 24” (61 cm) in the sedimentation chamber and 15”
(38 cm) in the anaerobic chamber requires pumping.
PART D: Clean Water Storage Chamber – samples should
be collected as previously described.
1. NO
3
-
N – Determined with the use of the nitrate test strips
included in the Fusion Maintenance Kit. Dip a test strip
into the water sample for 1 second, remove, allow to
react for 60 seconds, and read by comparing to the color
chart provided on the container. Nitrate-nitrogen is the
final step in the oxidation of ammonia. The test strips
provided range from 0-50 mg/L. Average is 7.0mg/L. No
or low nitrate concentrations are common in systems
where nitrifying microbes are absent. To correct high
nitrate concentrations in established systems increase the
recirculation rate.
2. NH
3
-
N – Determined with the use of the ammonia test
strips included in the Fusion Maintenance Kit. Dip a test
strip into the water sample and move up and down for 30
seconds, remove, allow excess water to drain, allow to react
for 30 seconds, and read by comparing to the color chart
provided on the container. Ammonia-nitrogen is measured
using low range test strips, 0-6 mg/L. Average is 3.0
mg/L. Low ammonia readings are desirable and require no
changes. To correct high ammonia readings decrease the
recirculation rate.
3. Dissolved oxygen – Follow the instructions included
with the dissolved oxygen meter. D.O. should be measured 25
inches (635 mm) below the water level. Average is 2.0 mg/L.
4. Temperature – Most dissolved oxygen meters include
a built-in thermometer which can be used to measure
temperature. Varies with system location.
PART E: Anaerobic Chamber – samples should be
collected and analyses performed as previously described
1. pH – The range suitable for biological activity is 6.5
to 7.5. Recurring results outside this range should be
investigated – water source for the home or business,
chemical use, etc.
2. NO
2
-
N – < 3.0 mg/L is common for this chamber.
Adjustments should be based on water quality in the
clean water storage chamber.
3. NO
3
-
N – < 2.0 mg/L is common for this chamber.
Adjustments should be based on water quality in the
clean water storage chamber.
4. NH
3
-
N – Ammonia-nitrogen in this chamber is typically <
20.0 mg/L. If this test is desired, it should be conducted
with test strips suitable for the expected concentration.
Adjustments should be based on water quality in the
clean water storage chamber.
5. Dissolved oxygen – Typically < 0.5 mg/L.
6. Temperature – varies with system location.
PART F: Sedimentation Chamber - samples should be
collected and analyses performed as previously described.
1. pH – The range suitable for biological activity is 6.5
to 7.5. Recurring results outside this range should be
investigated – water source for the home or business,
chemical use, etc.
2. NO
2
-
N – < 2.0 mg/L is common for this chamber.
Adjustments should be based on water quality in the
clean water storage chamber.
3. NO
3
-
N – < 2.0 mg/L is common for this chamber.
Adjustments should be based on water quality in the
clean water storage chamber.
4. NH
3
-
N – Ammonia-nitrogen in this chamber is
typically < 30 mg/L. If this test is desired, it should be
conducted with test strips suitable for the expected
concentration. Adjustments should be based on
water quality in the clean water storage chamber.
5. Transparency – Typically < 15 cm. Adjustments should
be based on water quality in the clean water storage
chamber.
6. Dissolved Oxygen – Typically < 0.5 mg/L
7. Temperature – Varies with system location
