An372 – Cirrus Logic AN372 User Manual
Page 10
AN372
10
AN372REV1
Step 2) Select a Value for Boost Output Voltage
The value of the boost output voltage, V
BST
, must be greater than the maximum input AC line voltage peak.
The maximum V
BST
voltage, V
BST(max)
, should be kept as low as possible to help maintain the FET breakdown
requirement within economical constraints.
V
BST
is determined by an internal parameter and changes slightly depending on the type of dimmer detected.
With sense resistors R7, R8, R14, and R15 set to 1.5M
, the resulting V
BST
is approximately 405V for a 230V
system. For a 120V system, sense resistors R7, R8, R14, and R15 are set to 750k
each, and the resulting
V
BST
is approximately 200V. V
BST
is regulated by charging the boost output capacitor to its nominal value
each half line-cycle. V
BST
droops to its lowest value towards the end of each half line-cycle until the boosting
process starts again in the next half line-cycle.
Step 3) Select an Appropriate FET
Determine the FET breakdown voltage, V
Breakdown
, and reflected voltage, V
Reflected
. The FET maximum drain
voltage, V
Drain(max)
, is calculated using Equation 1.
The ringing associated with the inductor leakage, L
K
, usually does not have enough energy to cause a
destructive avalanche breakdown. Voltages closely approaching the FET breakdown voltage are acceptable.
Ideally, V
Reflected
should have nearly the same value as V
BST
because operating the tapped buck inductor at
near 50% duty cycle optimizes efficiency. Alternatively, V
CLAMP
should be much greater than V
Reflected
to
rapidly discharge the energy stored in the inductor leakage, L
K
.
The FET breakdown voltage is constrained by cost and performance. A compromise must be reached in
partitioning voltage between V
BST
, V
CLAMP
, and V
Margin
. A second compromise will then determine how to
divide V
CLAMP
into V
Reflected
and a reasonable overshoot voltage portion, V
Overshoot
.
The losses caused by the leakage inductance are inversely proportional to V
Overshoot
, which is determined by
V
Drain max
V
BST max
V
CLAMP max
+
=
[Eq. 1]
V
Overshoot
V
CLAMP
V
Reflecteed
–
=
[Eq. 2]
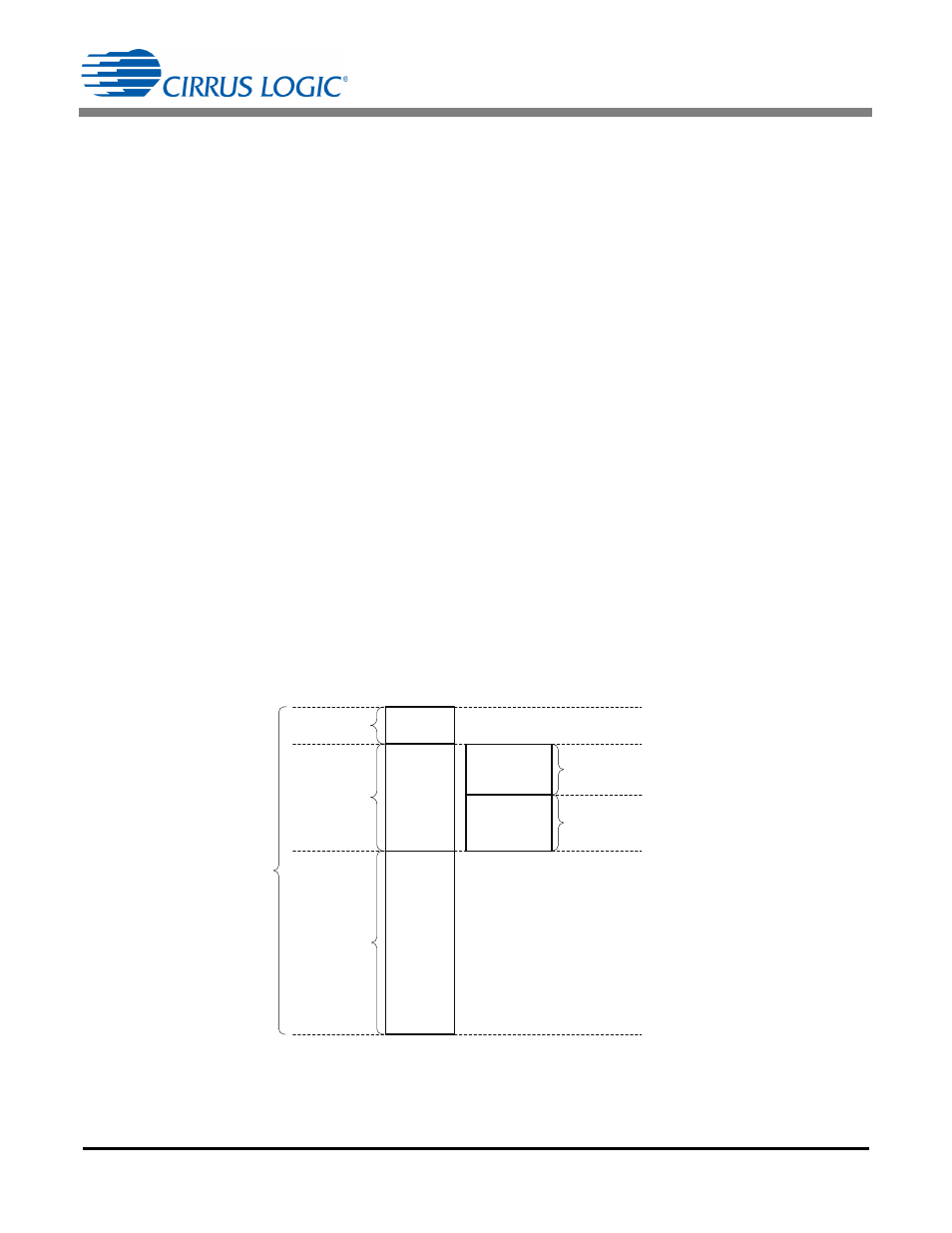
V
Margin
V
CLAMP
V
BST
V
Overshoot
V
Reflected
FET Breakdown
Voltage Rating
Clamp
Voltage
Boost Output
Voltage
Margin
Reflected
Voltage
Overshoot
Voltage
Overshoot is a brief condition
above V
Reflected
, required to
quickly dissipate the energy
stored in the inductor leakage,
L
K
.
During this time, the primary
current is kept from
transferring to the secondary,
siphoning energy from the load
to the clamp zener (snubber).
Figure 5. FET Breakdown Voltage
