7 operation, 7operation – Festo Электроцилиндр ESBF User Manual
Page 21
ESBF-BS
Festo – ESBF-BS – 1201NH English
21
Check travel
Homing run
Test run
Determining the approach
direction of the motor
Comparing the real situation
with the image in the controller
Checking the overall behaviour
Tab. 3
Definitions
1. Start a
Check travel and limit it to low dynamic response.
Despite identical control, motors of the same design sometimes turn in the opposite direction due
to different wiring.
The spindle of the ESBF turns in a clockwise direction: when the drive shaft is turned in a clockwise
direction, the piston rod moves in the direction of the motor.
2. Start a
Homing run up to the reference switch, in accordance with the operating instructions for
your motor drive system and limited to low dynamics (e.g. with a max. speed of 10 mm/s).
Providing the permitted impact energy is not exceeded, the homing run in conjunction with the
servo motor may be made directly against the mechanical end position on the motor side.
Maximum impact energy (= ½ mass x speed
2
):
–
ESBF-63 : max. 0.15 x 10
-3
J
–
ESBF-80 : max. 0.38 x 10
-3
J
–
ESBF-100 : max. 0.60 x 10
-3
J
3. Start a
Test run and limit it to low dynamic response.
4. Check whether the ESBF fulfils the following requirements:
–
The piston rod must move through the complete intended positioning cycle.
–
The piston rod must stop as soon as it reaches a limit switch.
5. If the proximity sensors fail to respond:
(
11 Troubleshooting and Proximity sensor operating instructions).
7
Operation
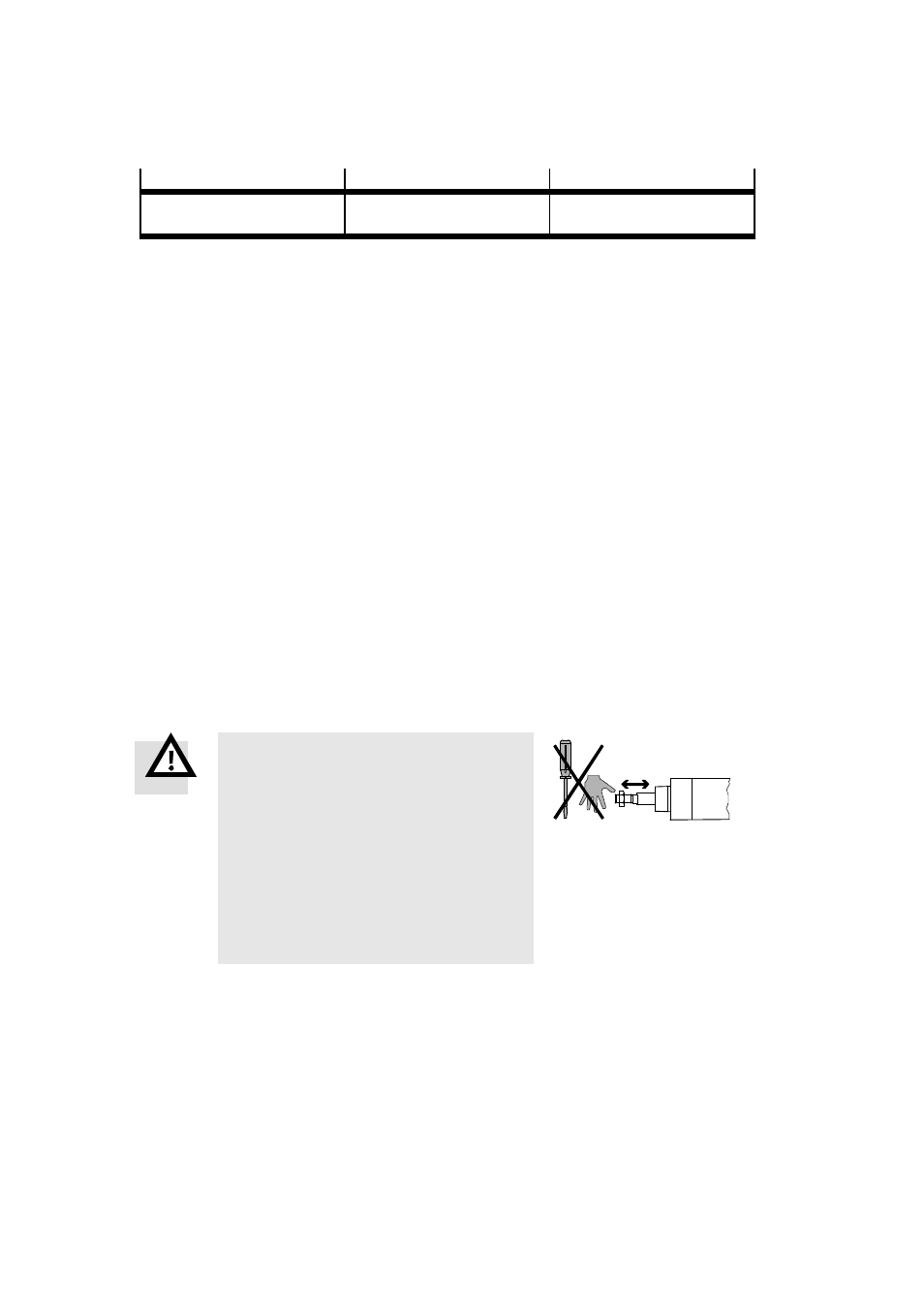
Warning
Moving masses can cause personal injury and ma-
terial damage (risk of crushing).
•
Make sure that, in the travel range,
–
nobody can place his/her hand in the path
of the moving components (e.g. through a
protective guard),
–
there are no foreign objects in the path of
the moving components.
It should not be possible to touch the ESBF un-
til the mass has come to a complete standstill.
Fig. 9
