High current, High current 59, On 4.4.3 – Campbell Scientific TGA100 Trace Gas Analyzer Manual User Manual
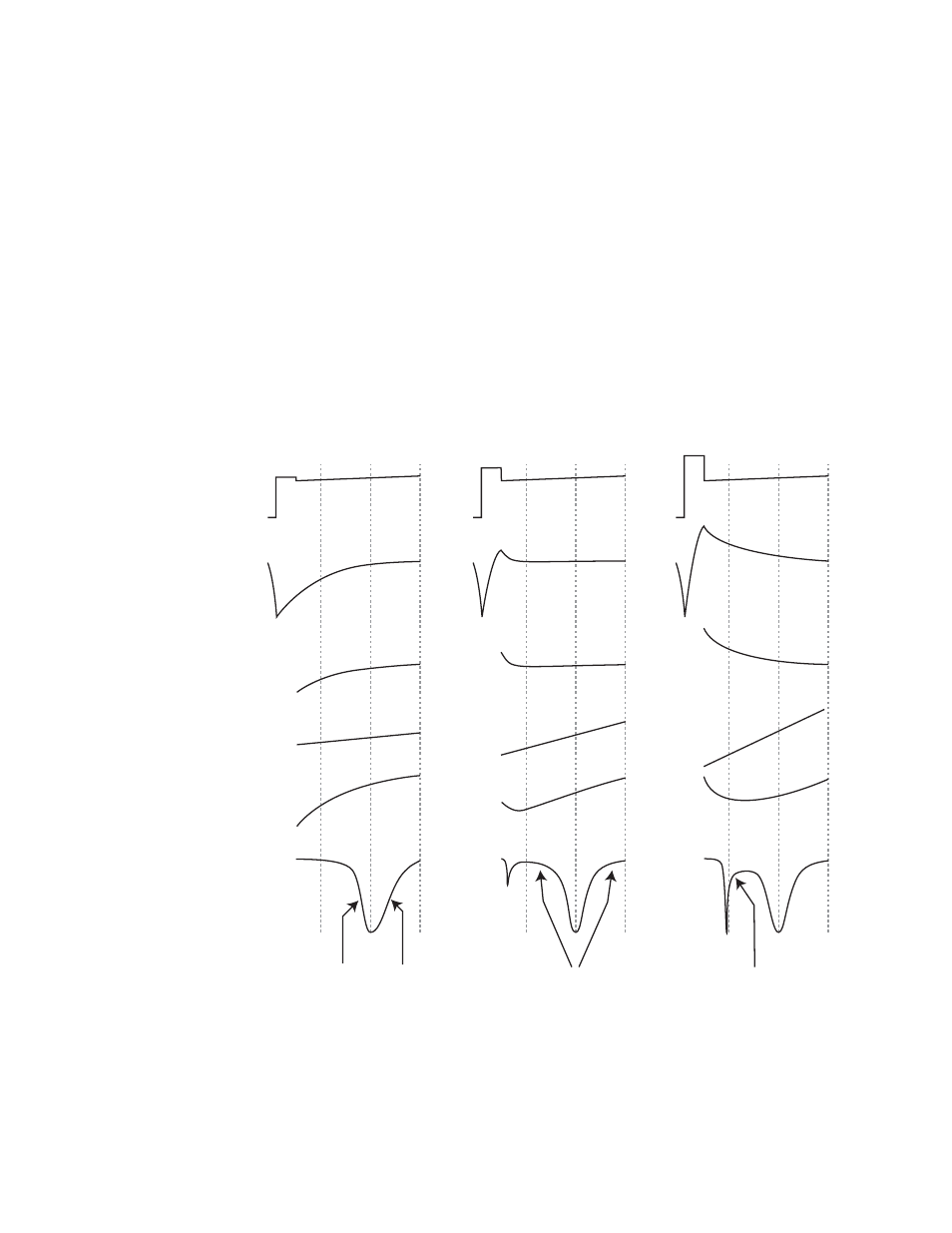
Page 59: Ssed in section 4.4.3, can help to stabilize, Figure 4-10. effects of temperature perturbation
response again increases, the algorithm reduces the zero current to just below the threshold current. After the algorithm
terminates, reenable automatic control of detector offset and gain, and restart line lock.
For dual ramp mode, the same value of the zero current is used at the start of ramp A and ramp B. The process
described above should set the zero current to a value that is acceptable for both ramps.
4.4.3
High Current
The laser cools slightly at the start of the spectral scan when it is turned off by reducing its current to the zero current
value, as discussed in section 4.4.2. If the actual spectral scan started immediately thereafter, the laser temperature
would rise during the entire spectral scan. The rise in temperature would be more rapid at first, and slower near the end
of the scan as the temperature approached equilibrium. The change in temperature would change the laser’s emission
frequency, adding an undesired spectral modulation, as illustrated in
. To minimize this problem, the laser
current is increased above the DC current by an amount specified in the high current offset parameter. The duration of
this high current pulse is determined by the laser high current count parameter. When these parameters are properly set,
the heat from the increased current compensates for the heat lost when the current is reduced, stabilizing the laser
temperature more quickly.
Figure 4-10. Effects of Temperature Perturbation
Laser
Current
Detector
Response
Laser
Temperature
Wavenumber
(temperature)
Wavenumber
(current)
Wavenumber
(combined)
High current
too low
High current
correct
High current
too high
Equilibrates slowly
Constant during ramp
Overshoots
Positive slope
Nearly Flat
Negative slope
Reduced
Normal
Increased
Steep slope
Shallow slope
Symmetrical
about center
Falls of
f at
left edge
59
