Logical server operations, Example logical server node information – HP Matrix Operating Environment Software User Manual
Page 41
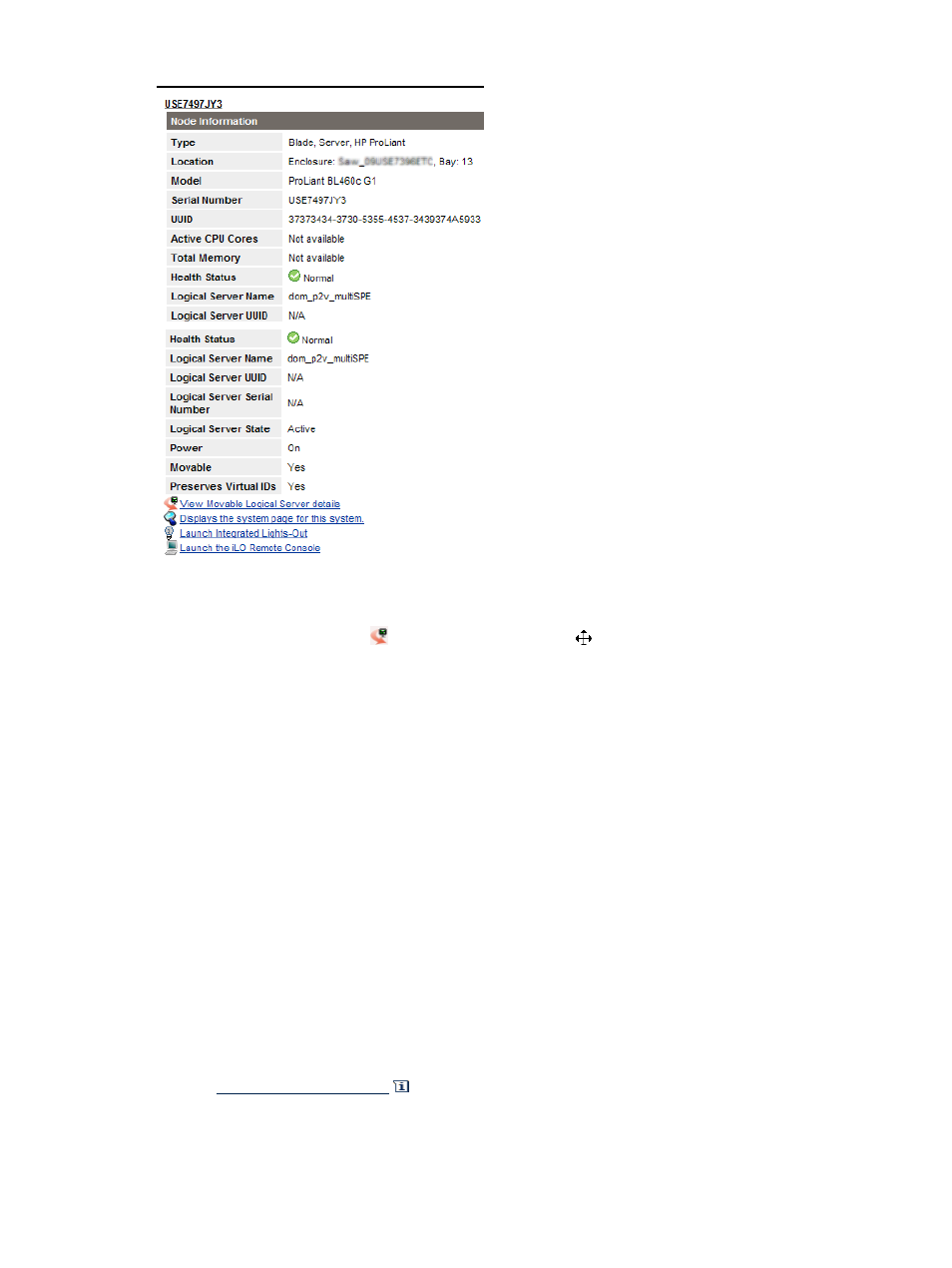
Figure 3-2 Example logical server node information
In the Physical and Virtual, Blades, and Virtual Machines perspectives, you can drag and drop
an active logical server onto another host. Move your mouse over the logical server (marked
with the logical server icon
) to see the move cursor
, which signifies that you can drag the
logical server. The hosts available for you to drop the logical server onto are highlighted with a
star rating. Unavailable hosts are grayed out. Before the move is complete, you have the
opportunity to confirm or cancel the drag and drop move operation.
The available target host can be a server with Virtual Connect or a hypervisor.
Using the drag and drop function is equivalent to using the Tools
→Logical Servers→Move...
menu selection.
Logical server operations
You can perform several actions on logical servers from Virtualization Manager. For a description
of the Virtualization Manager menu options that perform these tasks, see
.
A logical server can be active or inactive.
An active logical server has been bound to both an HP SIM node and a workload, and is bound
to specific storage. Active logical servers can be in one of two states: powered on or powered
off.
An inactive logical server has been defined but is not currently bound to a specific physical
server or system. Inactive logical servers that have never been activated might or might not be
bound to storage.
See the
node information icon
in the Logical Server perspective to see the attributes of the
logical server, including the logical server state.
The Activate and Deactivate operations change the state of the logical server.
Logical server operations
41
