HT instruments FULLTEST3 User Manual
Page 43
FULLTEST
3
EN - 42
5.8. RESIDUAL VOLTAGE (URES)
•
What are residual voltages? Residual voltages are the voltages that remain present even after
switching off a machine or device. This can be caused e.g. by built in capacitors or subsequent
generators. This measurement is performed by using the U
RES
function.
• According to
EN 60204-1, accessible live parts connected to dangerous voltage must discharge
within 5 seconds (permanently connected machines) or within 1 second (plugged-in machines) down
to 60 V. Proof of this must be given through tests.
•
In the event of non-compliance, additional measures (discharge devices, warning information, covers
etc.) according to EN 60204-1 must be taken.
• With FULLTEST 3 tester the residual voltage can be measured 1 s or 5 s after switching off tested
machine. Measurement of residual
voltage can be carried out in linear or non-linear mode, see the
section "EXPLANATION OF LINEAR MODE" or section "EXPLANATION OF NONLINEAR MODE".
5.8.1. EXPLANATION OF LINEAR MODE
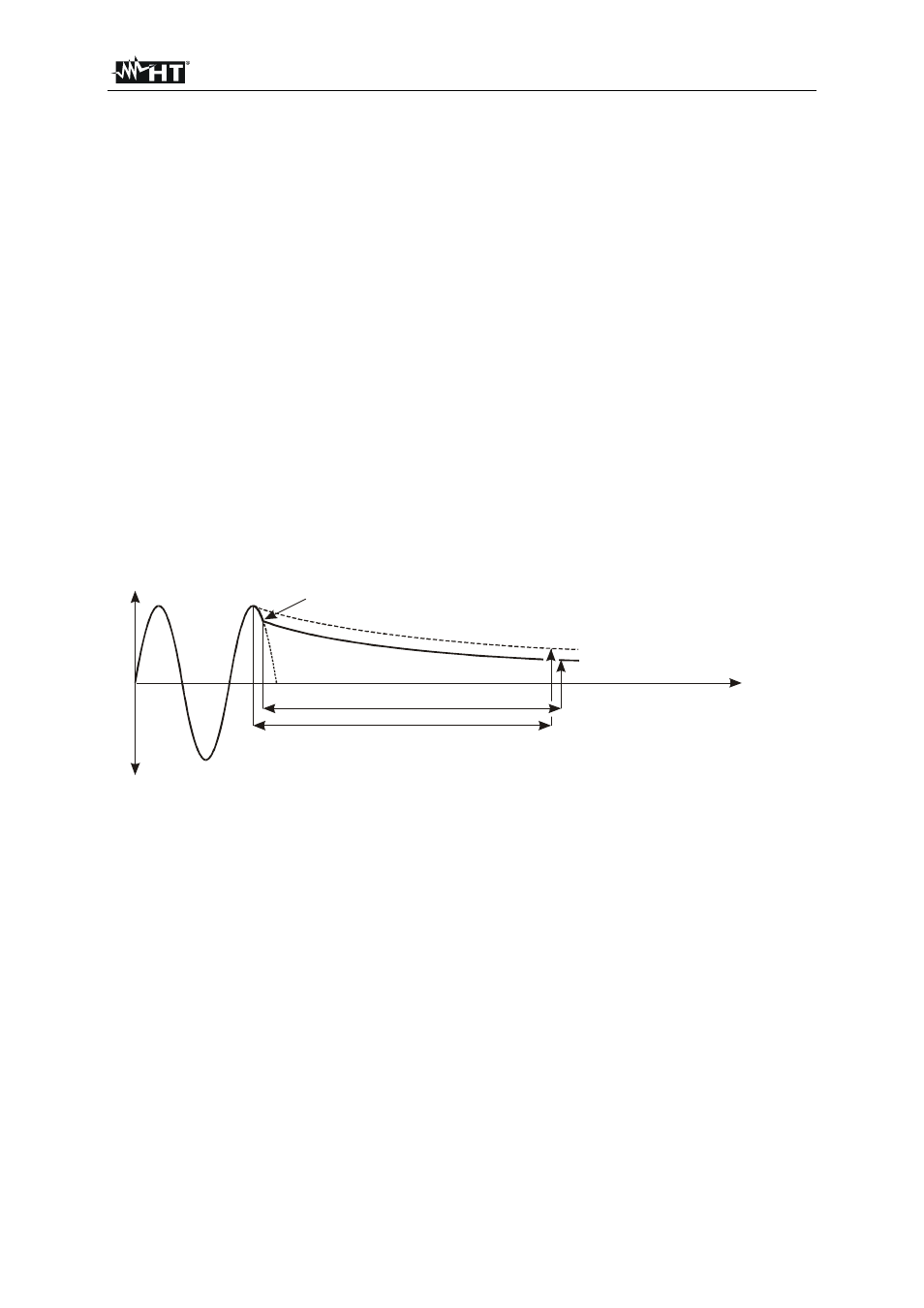
In linear mode it is assumed there are only
"
linear
"
components involved in discharging process
(capacitors, resistors, inductors etc.) and therefore discharge characteristic is exponential, see the
diagram below.
In linear mode displayed result is scaled to peak value of input voltage in order to evaluate most critical
situation, see the figure below.
U
(measured)
RES
t
1s / 5s
1s / 5s
U
U
(correct value)
RES
Coincidential switch off
at any mains voltage
Figure 30
: Discharge diagram in linear circumstances
For scaling of measured U
RES
voltage Un of mains installation is needed, so it must be selected in prior
to the measurements.
How to select the nominal voltage Un:
Press the MENU
SETUP NOMINAL VOL. touch-screen keys and select 230 V or 240 V. S
ee the
chapter “6.5.4. NOMINAL VOLTAGE menu”.
In linear mode the FULLTEST 3 detects automatically two standard system voltages:
a) Selected nominal voltage Un = 230 V
230 V ............................ U
IN
= 230 V
10%
400 V ............................ U
IN
= 400 V
10%
b) Selected nominal voltage Un = 240 V:
240 V ............................ U
IN
= 240 V
10%
415 V ............................ U
IN
= 415 V
10%
