Return air duct sampling method – Edwards Signaling ReadySet User Manual
Page 25
Chapter 3: Installation and configuration
ReadySET Aspirating Smoke Detection System Installers Handbook
17
Return air duct sampling method
Duct sampling generally is the most cost-effective method of air sampling because the
pipe runs are minimal and a single detector may be used to cover a larger area. The
speed of response of the detector to smoke is given by the exchange rate in the rooms
ventilated by the duct ventilation system. This tends to be rapid, giving early warning of
any smoke present. This type of sampling is particularly suited to aspirated smoke
detection, since the smoke content in the air will tend to be diluted to a level below that
of point type detectors. Also, the relatively high airflow in the duct reduces the
effectiveness of point-detection devices.
The duct sampling method does have one major disadvantage. If the ventilation
becomes inoperative, the air-flow through the duct system ceases and the smoke-
detection system becomes ineffective.
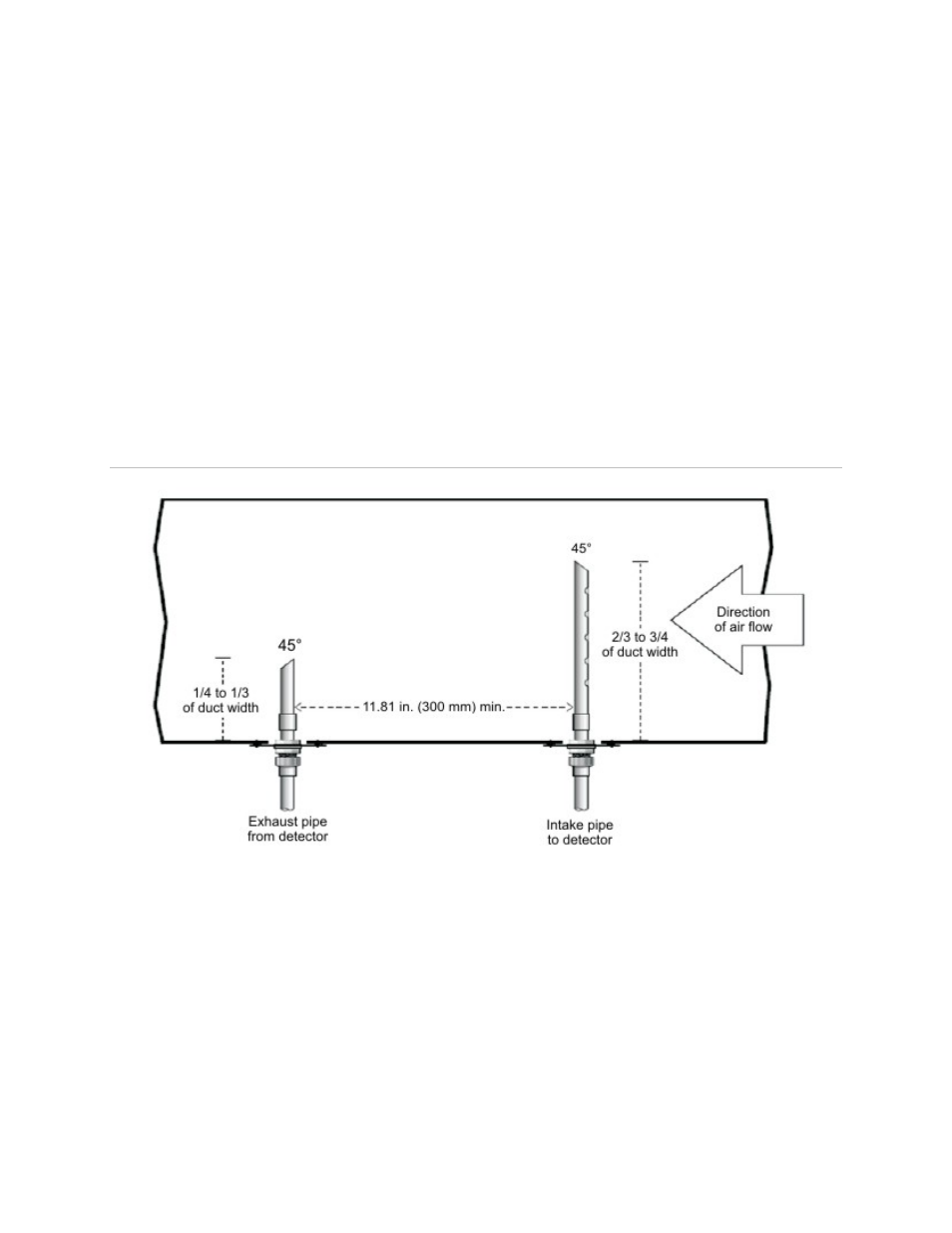
Figure 7: Return air duct sampling
Figure 7 above shows a typical sampling pipe arrangement for an air duct. The right
pipe is the sampling pipe and the holes on it are drilled 4 inches apart and face into the
oncoming air stream. The left pipe exhausts air from the detector.
The detector is UL 268A and ULC approved for duct applications with an operating air
velocity range of 300 to 4,000 ft/min (1.52 - 20.32 m/sec). The following guidelines
apply.
• Only one duct can be monitored per detector.
