A1.2.6 repair and replacement, A1.2.7 startup time, A1.2.8 firmware update – Yokogawa EJA440E User Manual
Page 89: A1.2.9 reliability data, A1.2.10 lifetime limits, A1.2.11 environmental limits, A1.2.12 application limits, A1.2.6, A1.2.7, A1.2.8
A1-2
IM 01C25T01-06EN
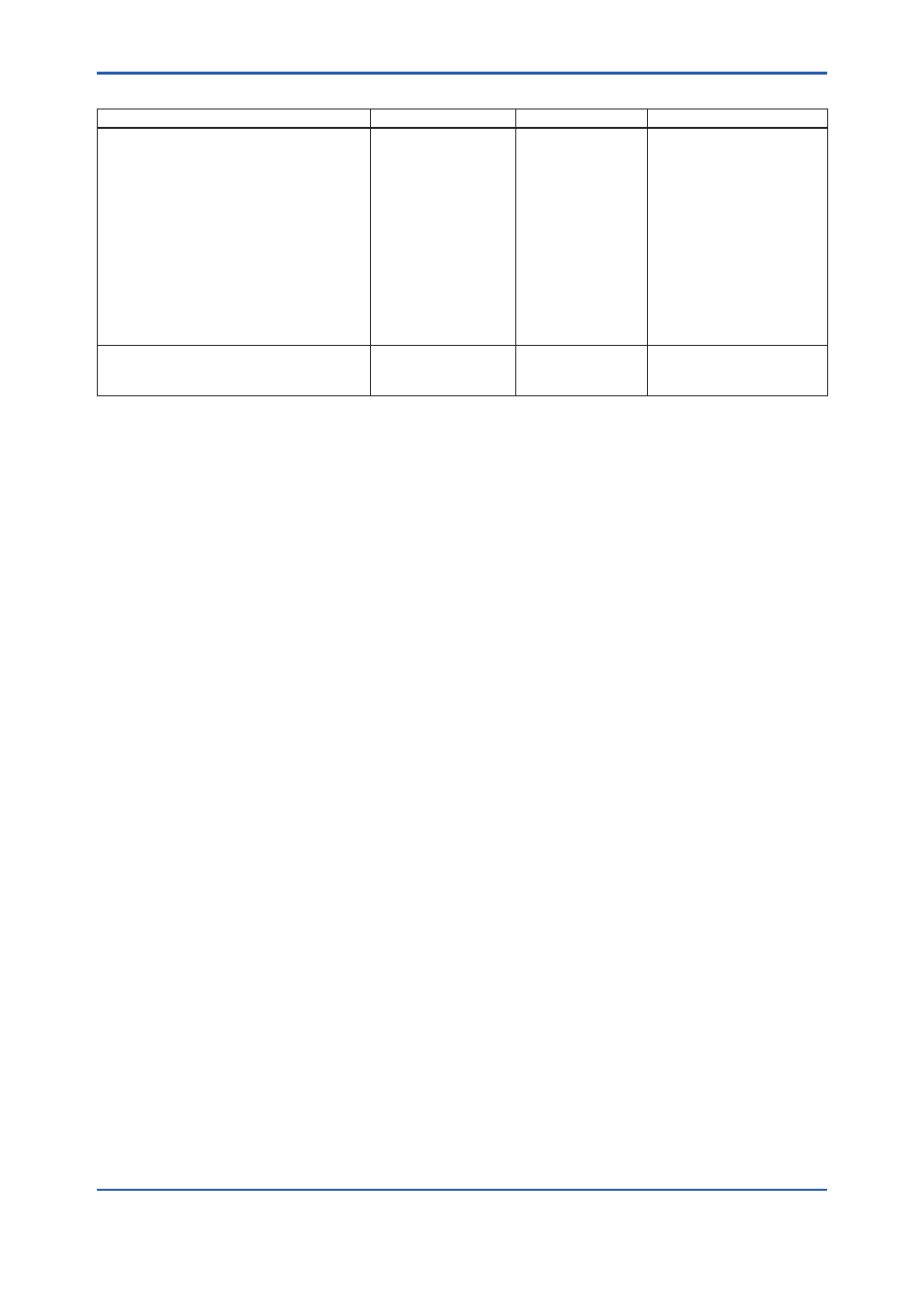
Table A1.2 Proof Testing
Testing method
Tools required
Expected outcome
Remarks
Functional test:
1. Follow all Management of Change
procedures to bypass logic solvers if
necessary.
2. Execute HART/BRAIN command to
send value to high alarm (21.5 mA) and
verify that current has reached this level.
3. Execute HART/BRAIN command to
send value to low alarm (3.6 mA) and
verify that current has reached this level.
4. Restore logic solvers operation and
verify.
• Handheld terminal
Proof Test Coverage
=52%
The output needs to be
monitored to assure that the
transmitter communicates
the correct signal.
Perform three point calibration along with
the functional test listed above.
• Handheld terminal
• Calibrated pressure
source
Proof Test Coverage
=99%
A1.2.6 Repair and Replacement
If repair is to be performed with the process online
the transmitter will need to be bypassed during the
repair. The user should setup appropriate bypass
procedures.
In the unlikely event that the transmitter has a
failure, the failures that are detected should be
reported to Yokogawa.
When replacing the transmitter, the procedure in the
installation manual should be followed.
The personnel performing the repair or replacement
of the transmitter should have a sufficient skill level.
A1.2.7 Startup Time
The transmitter generates a valid signal within 1
second of power-on startup.
A1.2.8 Firmware Update
In case firmware updates are required, they
will be performed at factory. The replacement
responsibilities are then in place. The user will not
be required to perform any firmware updates.
A1.2.9 Reliability Data
A detailed Failure Mode, Effects, and Diagnostics
Analysis (FMEDA) report is available from
Yokogawa with all failure rates and failure modes.
The transmitter is certified up to SIL2 for use
in a simplex (1oo1) configuration, depending
on the PFDavg calculation of the entire Safety
Instrumented Function.
The development process of the transmitter is
certified up to SIL3, allowing redundant use of
the transmitter up to this Safety Integrity Level,
depending the PFDavg calculation of the entire
Safety Instrumented Function.
When using the transmitter in a redundant
configuration, the use of a common cause factor
(β-factor) of 2% is suggested. (However, if the
redundant transmitters share an impulse line or if
clogging of the separate impulse lines is likely, a
common cause factor of 10% is suggested.)
Note that the failure rates of the impulse lines need
to be accounted for in the PFDavg calculation.
A1.2.10 Lifetime Limits
The expected lifetime of the transmitter is 50
years. The reliability data listed the FMEDA report
is only valid for this period. The failure rates of the
transmitter may increase sometime after this period.
Reliability calculations based on the data listed in
the FMEDA report for transmitter lifetimes beyond
50 years may yield results that are too optimistic,
i.e. the calculated Safety Integrity Level will not be
achieved.
A1.2.11 Environmental Limits
The environmental limits of the transmitter are
specified in the user’s manual IM 01C25.
A1.2.12 Application Limits
The application limits of the transmitter are specified
in the user’s manual IM 01C25. If the transmitter is
used outside of the application limits, the reliability
data listed in A1.2.9 becomes invalid.
