7 - when and why matching – CEMB USA C75 (A) User Manual
Page 22
I 0202 - 22
GB
5.7 - WHEN AND WHY MATCHING
The C75 software associated with eccentricity measurement is a powerful tool for determining the need
to perform relative rotation between the rim and tyre in order to reduce the eccentricity of the wheel down
to acceptable limits. The principle adopted is based on the consideration that a rim with acceptable
tolerance, mounted with an acceptable tyre, can statistically generate a total eccentricity which is not
acceptable but can be improved by matching.
Generally speaking, rim measurement is not necessary, accurate or useful because:
• To measure the rim it is necessary to remove the tyre. There can by coarse errors on the outside
(e.g.
aluminium
wheels!)
• The two rim sides can be eccentric in a very different way. Therefore to which one to make reference?
What is the effect on the tyre mounted?
• To improve the eccentricity of a wheel, the rim should be eccentric, to compensate the tyre. And
viceversa.
• If after a rotation by 180° of a wheel, the value is still out-of-tolerance, either the tyre or rim are too
eccentric: One of the two must be replaced!
SOLUTION:
Rotate the tyre on the rim by 180°
RESULT:
wheel eccentricity 0.3 - 0.4 mm
(in
tolerance)
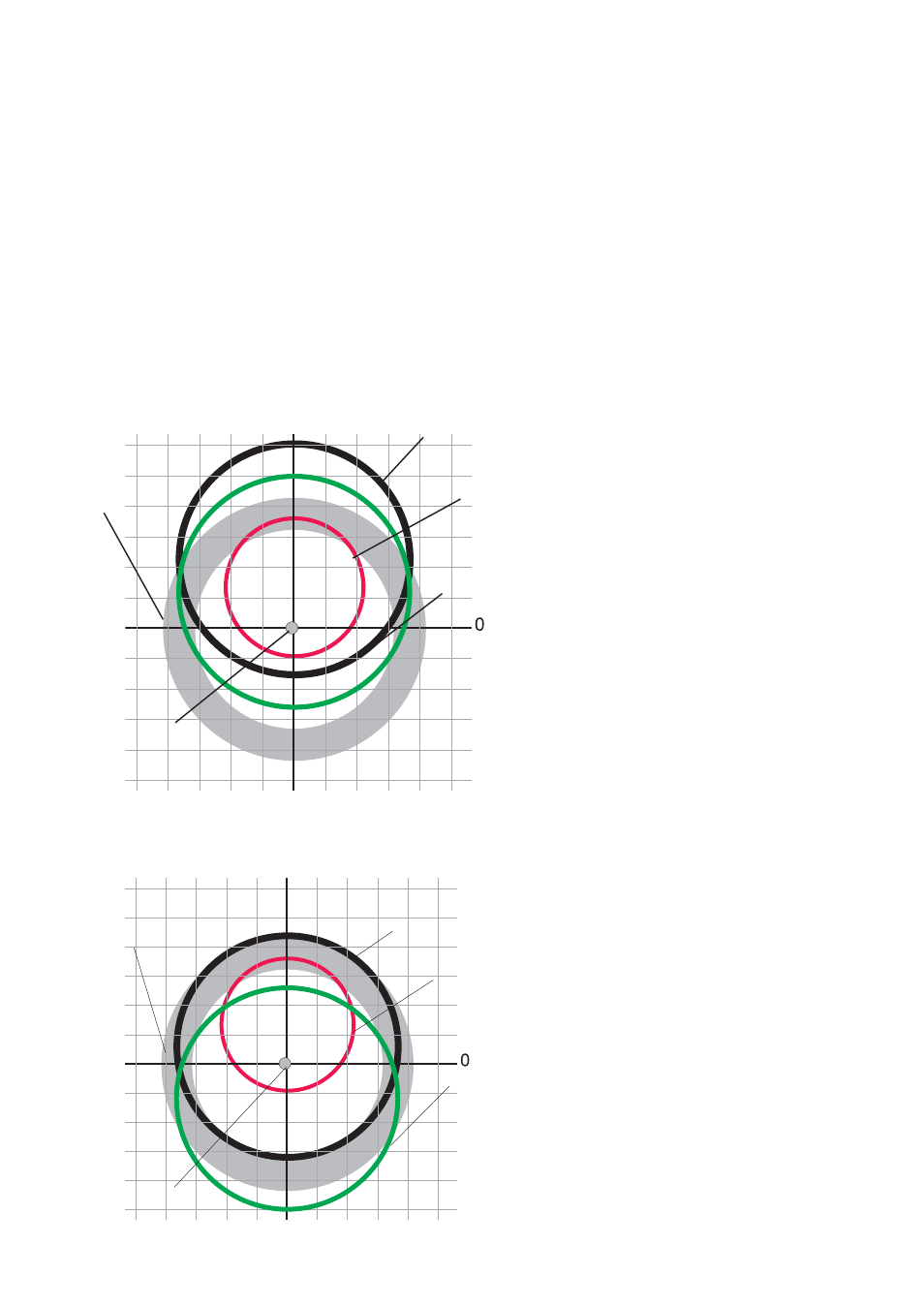
Example 1
Rim + 0.8 mm
Tyre + 0.6 mm
Wheel + 1.3 mm
Eccentricity of the wheel is
excessive, due to an acceptable
rim or tyre but randomly placed in
an “unfortunate” relative position.
wheel
rim
tyre
rotation axle
Ideal wheel
Example 2
Rim + 0.8 mm
Tyre - 0.6 mm
Wheel + 0.3 mm
Eccentricity of the single items
has been compensated.
The wheel is acceptable.
wheel
rim
tyre
rotation axle
Ideal wheel
