Power sink (option) – Powersolve HSEUIreg07201 Series User Manual
Page 7
Powersolve Electronics Ltd., Unit 8A Arnhem Road, Newbury RG14 5RU, United Kingdom
Tel 0044 (0)1635 521858 Fax 0044 (0)1635 523771
www.powersolve.co.uk
p.7/9 05.12D
(Subject to alterations. This product is not designed to be used in applications such as life support systems wherein a failure or malfunction could result in injury or death)
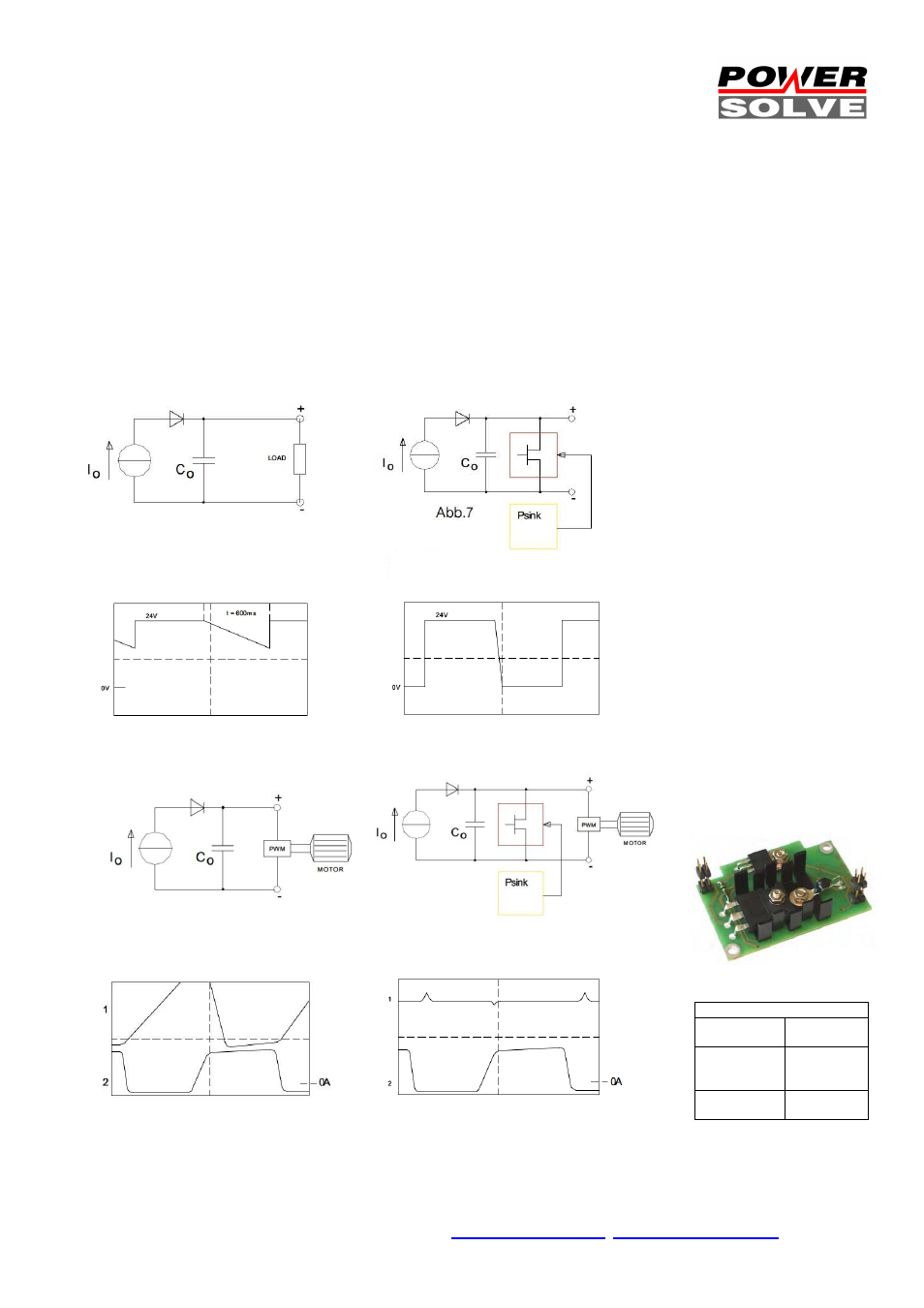
Power Sink (Option)
The power sink option features returned power to be terminated very quickly. The power sink records the output power status and guarantees
a constant output voltage. The power sink also provides quicker response time on setting down the output voltage.
Applications sample: DC-drives & ATE test systems
Most of modern dc-drives are controlled by a PWM (pulse wide modulation) controller. Such controllers feature a very flexible speed control
and high efficiency. A disadvantage of PWM controlled drives is the returned power into the system while decelerating the motor. The
dragging of the motor inverts the drive into a generator. The returned power may cause trouble or serious defects to the dc-system, but
definitely slows down the decelerating process of a drive. The returned energy is not terminated quickly enough and results in rising system
voltage. An integrated load, called power sink, terminates the returned power very quickly and enables the drive to small dynamic latency
(see figure).
ATE test-systems require quick down programming of the output voltage. Most ATE applications need to drag down the output voltage to 0V
as a new testee is put into the system. A power supply without a power sink is simply not quick enough to terminate the energy at the output
capacitors. Therefore an electronic power sink manages the output voltage to reset very quickly. Overall test time is being reduced and the
testee is uncontrolled transient voltage protected.
Conventional power supply circuit
simplified, without power sink
Latency of conventional power supply
Latency of power sink
equipped power supply
Power sink equipped power supply
Conventional power supply:
breaking power charges output
capacitor Co
Power sink equipped power
supply: absorbs breaking energy
Dynamic reaction of conventional
power supply: uncontrolled voltage
rises with negative reverse current
Dynamic reaction of power sink
equipped power supply:
load current switches between
positive and negative
Dynamic response
A common power supply is
usually not designed to absorb
returned
power
from
its
connected load.
The negative load current will
recharge the capacitor Co. The
output voltage starts rising and
get out of control.
This
is
essential
to
the
mathematic formula dv/dt=i/C.
As an electronic power sink
module is equipped to the
power supply unit, the output
voltage will constantly being
kept at the desired level. The
power sink provides very quick
dynamic response. The output
voltage only rises to a minimal
notching ratio for a very short
spell.
Using a power supply unit
without equipped power sink in
such application may result into
serious
damage
or
un-
controlled OVP activity to the
power supply unit.
Technical Data
Outline
Factory
built in
Continuous
Power
Capability
5W
Peak Power
Capability
10W
(100ms)
