Adc noise-canceling techniques, Adc characteristics, Attiny15l – Rainbow Electronics ATtiny15L User Manual
Page 50
50
ATtiny15L
1187E–AVR–06/02
ADC Noise-canceling
Techniques
Digital circuitry inside and outside the ATtiny15L generates EMI, which might affect the
accuracy of analog measurements. If conversion accuracy is critical, the noise level can
be reduced by applying the following techniques:
1.
The analog part of the ATtiny15L and all analog components in the application
should have a separate analog ground plane on the PCB. This ground plane is
connected to the digital ground plane via a single point on the PCB.
2.
Keep analog signal paths as short as possible. Make sure analog tracks run over
the analog ground plane, and keep them well away from high-speed switching
digital tracks.
3.
Use the ADC noise canceler function to reduce induced noise from the CPU.
4.
If some Port B pins are used as digital outputs, it is essential that these do not
switch while a conversion is in progress.
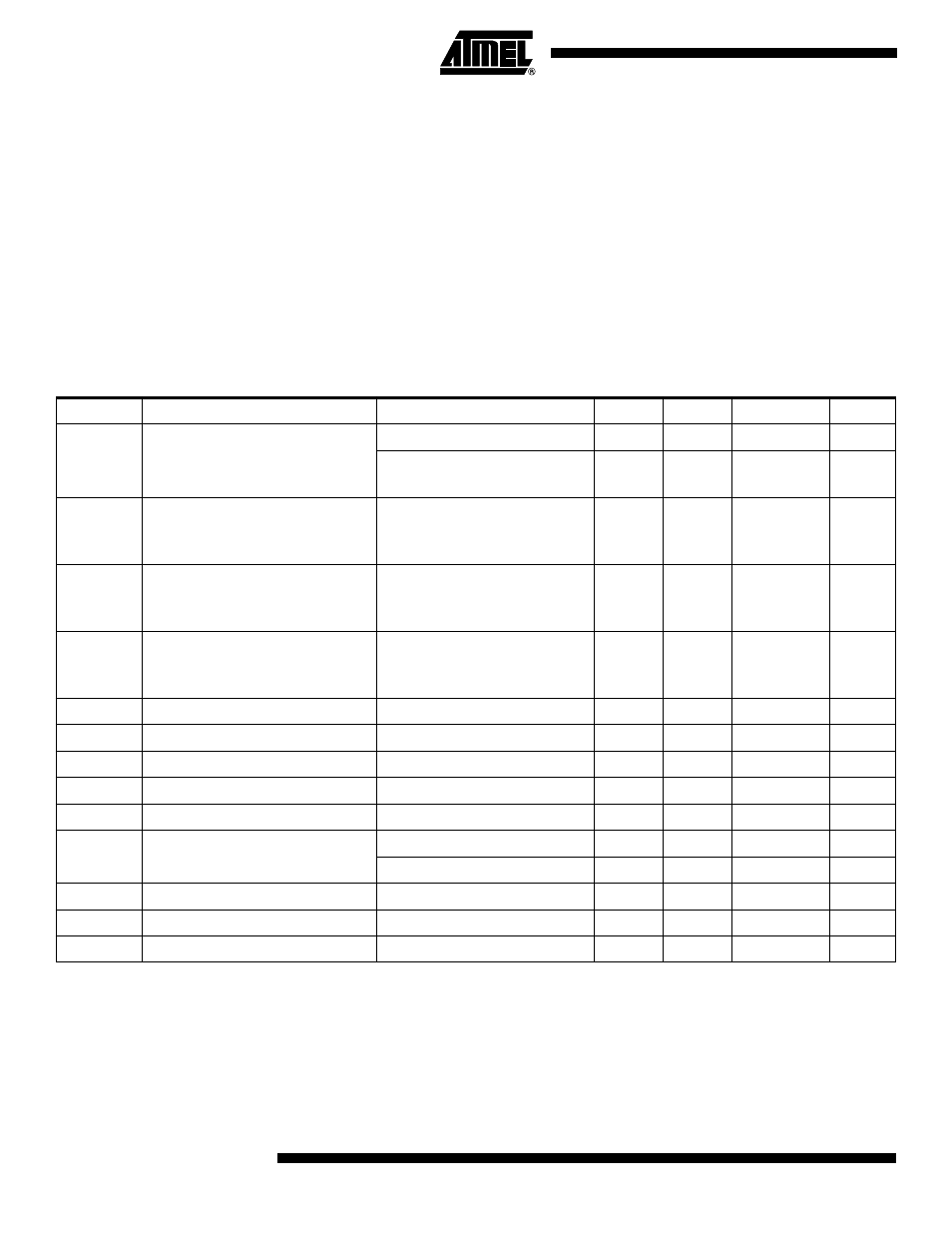
ADC Characteristics
Symbol
Parameter
Condition
Min
Typ
Max
Units
Resolution
Single-ended Conversion
10.0
Bits
Differential Conversion
Gain = 1x or 20x
8.0
Bits
Absolute Accuracy
Single-ended Conversion
V
REF
= 4V
ADC Clock = 200 kHz
1.0
2.0
LSB
Single-ended Conversion
V
REF
= 4V
ADC Clock = 1 MHz
4.0
LSB
Single-ended Conversion
V
REF
= 4V
ADC Clock = 2 MHz
16.0
LSB
Integral Non-linearity
V
REF
> 2V
0.5
LSB
Differential Non-linearity
V
REF
> 2V
0.5
LSB
Zero Error (Offset)
V
REF
> 2V
1.0
LSB
Conversion Time
Free Running Conversion
65.0
260.0
µs
Clock Frequency
50.0
200.0
kHz
V
REF
Reference Voltage
Single-ended Conversion
2.0
V
CC
V
Differential Conversion
2.0
V
CC
- 0.2
V
V
INT
Internal Voltage Reference
2.4
2.56
2.7
V
R
REF
Reference Input Resistance
6.0
10.0
13.0
k
Ω
R
AIN
Analog Input Resistance
100.0
M
Ω
