Ssi peripheral configuration, Figure 64 – Rainbow Electronics T48C862-R4 User Manual
Page 67
67
T48C862-R4
4551B–4BMCU–02/03
SSI Peripheral Configuration
The synchronous serial interface (SSI) can be used either for serial communication with
external devices such as EEPROMs, shift registers, display drivers, other microcontrol-
lers, or as a means for generating and capturing on-chip serial streams of data. External
data communication takes place via the Port 4 (BP4),a multi-functional port which can
be software configured by writing the appropriate control word into the P4CR register.
The SSI can be configured in any of the following ways:
1.
2-wire external interface for bi-directional data communication with one data ter-
minal and one shift clock. The SSI uses the Port BP43 as a bi-directional serial
data line (SD) and BP40 as shift clock line (SC).
2.
3-wire external interface for simultaneous input and output of serial data, with a
serial input data terminal (SI), a serial output data terminal (SO) and a shift clock
(SC). The SSI uses BP40 as shift clock (SC), while the serial data input (SI) is
applied to BP43 (configured in P4CR as input!). Serial output data (SO) in this
case is passed through to BP42 (configured in P4CR to T2O) via the Timer 2
output stage (T2M2 configured in mode 6).
3.
Timer/SSI combined modes – the SSI used together with Timer 2 or Timer 3 is
capable of performing a variety of data modulation and demodulation functions
(see Timer Section). The modulating data is converted by the SSI into a continu-
ous serial stream of data which is in turn modulated in one of the timer functional
blocks. Serial demodulated data can be serially captured in the SSI and read by
the controller. In the Timer 3 modes 10 and 11 (demodulation modes) the SSI
can only be used as demodulator.
4.
Multi-chip link (MCL) – the SSI can also be used as an interchip data interface for
use in single package multi-chip modules or hybrids. For such applications, the
SSI is provided with two dedicated pads (MCL_SD and MCL_SC) which act as a
two-wire chip-to-chip link. The MCL can be activated by the MCL control bit.
Should these MCL pads be used by the SSI, the standard SD and SC pins are
not required and the corresponding Port 4 ports are available as conventional
data ports.
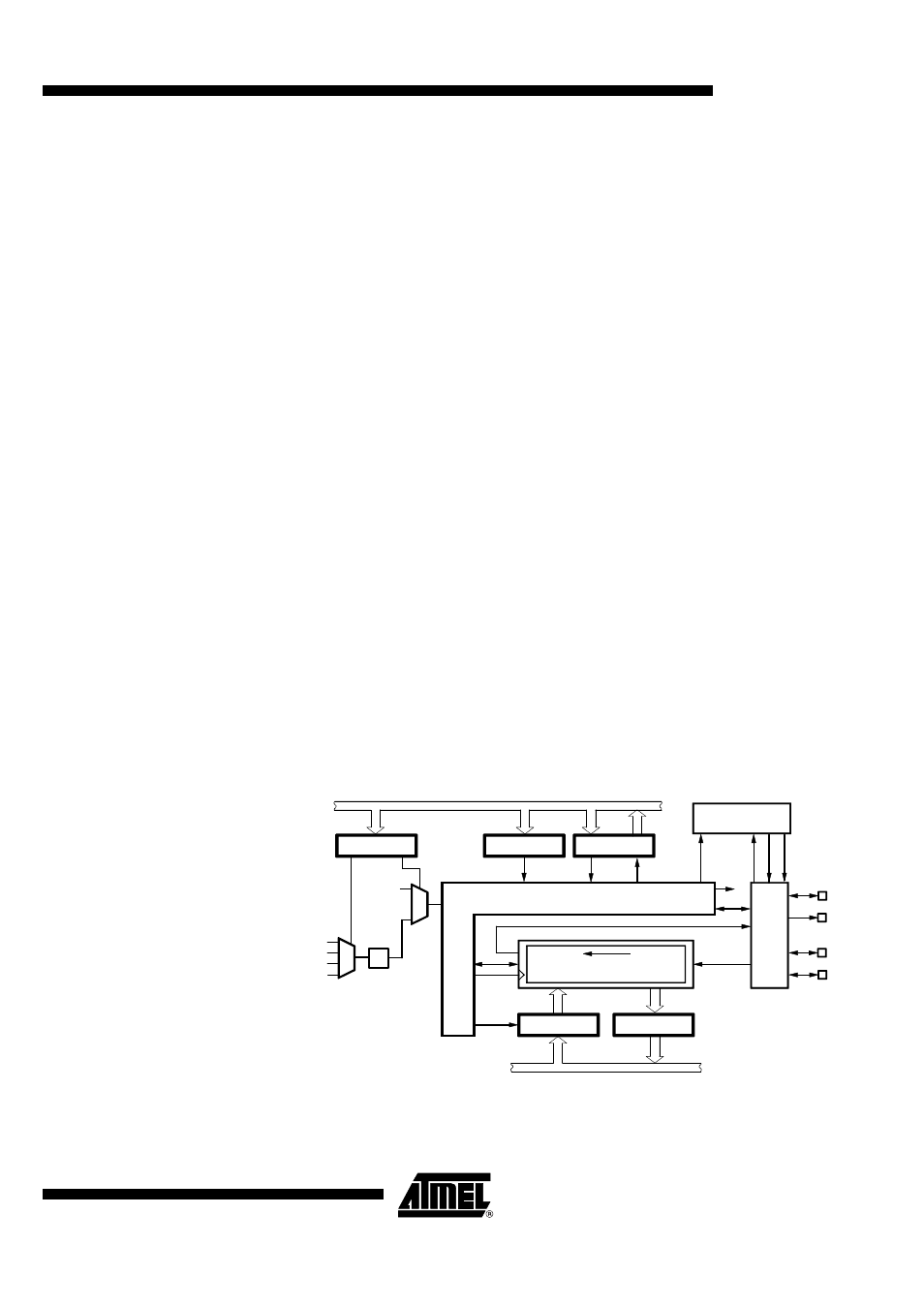
Figure 64.
Block Diagram of the Synchronous Serial Interface
8-bit Shift Register
MSB
LSB
Shift_CL
SO
SIC1
SIC2
SISC
SC
Control
STB
SRB
SI
Timer 2 / Timer 3
Output
INT3
SC
I/O-bus
I/O-bus
SSI-Control
TOG2
POUT
T1OUT
SYSCL
SO
SI
MCL_SC
SD
MCL_SD
Transmit
Buffer
Receive
Buffer
SCI
/2
