How autorouting works, Identifying images to be autorouted – Vista Imaging Vista Routing User Manual
Page 12
Routing Overview
Routing User Guide
How Autorouting Works
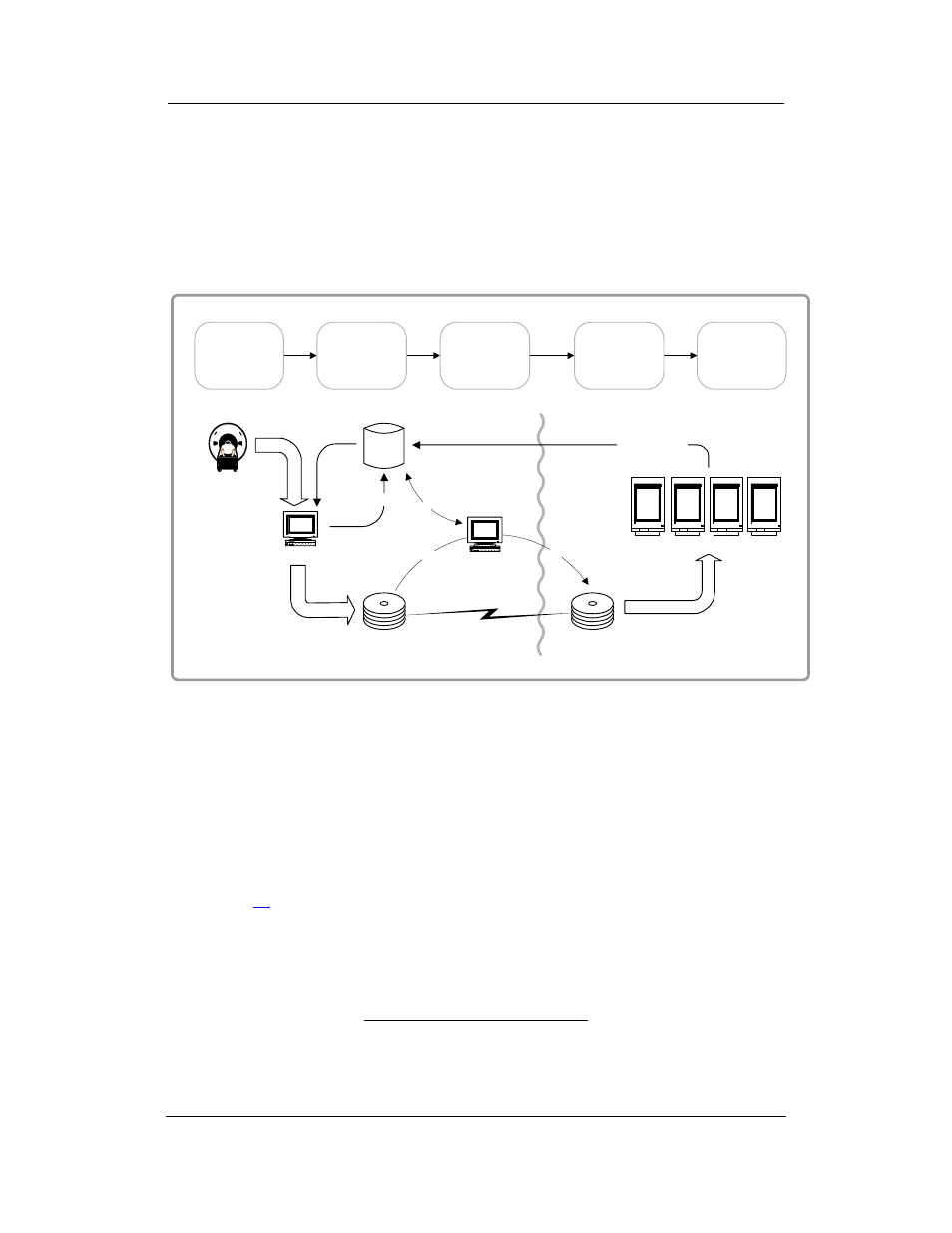
The following figure illustrates the transfer of automatically routed images to a
VistARad workstation for remote reading. The processes outlined in this figure are
explained in more detail below. (Apart from the destination, the same processes are used
when autorouting images to a DICOM Storage SCP).
Image Gateway
Patient
data
Image Archive
Images
VistA
HIS
Routing Gateway
Remote Storage
Destination
Local image copies
VistARad
Image links
1) Eval. Processor
2) Trans. Processor
1
2
2
Sending Site
Destination Site
Modality
Images
VistARad login
Routing G/W
compares
image data
to routing rules (1)
Images
acquired
Image G/W
processes
images, then
archives images
Images
reviewed
at destination
Routing G/W
copies
routable images
to destination (2)
Identifying Images to be Autorouted
Autorouting begins with an Image Gateway. As it is processing newly acquired images, a
properly configured Image Gateway will add routing-specific entries to the rule
evaluation queue.
This queue is continually checked by the evaluation processor (which
resides on the VistA Host and is started from the Routing Gateway).
 If the Image Gateway is not configured to add entries to the rule evaluation queue, the
images being processed by the gateway cannot be autorouted. For more information,
see page
Each image referenced in the rule evaluation queue is checked against a set of
site-specific routing rules. If the rules indicate that the image should be routed, the
evaluation processor creates an entry in the transmission queue.
Entries in the rule
evaluation queue are deleted after they are checked.
1
The rule evaluation queue is a subset of the
IMAGE BACKGROUND QUEUE
file (#2006.03).
2
The transmission queue is stored in the
SEND QUEUE
file (#2006.035).
VistA Imaging V. 3.0, Patch 18
April 2006
4
