To configure static vlans – Sun Microsystems Gigabit Ethernet MMF/UTP Adapter User Manual
Page 94
60
Sun PCI-Express Dual Gigabit Ethernet MMF/UTP Adapter Installation and User’s Guide • June 2006
IP subnets when setting up a VLAN network interface. This means that each VID
assigned to a VLAN interface of a physical network interface will belong to different
subnets.
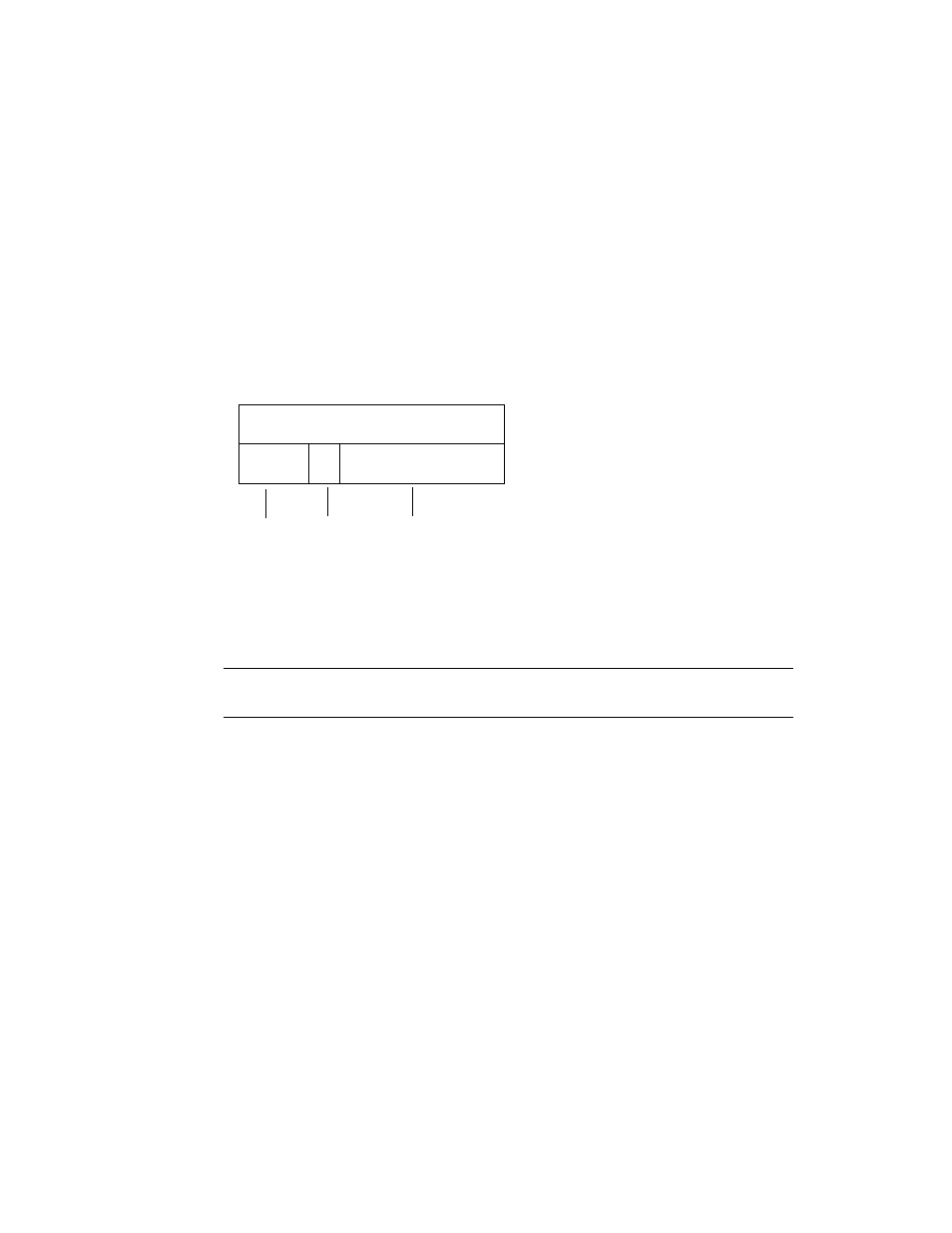
Tagging an Ethernet frame requires the addition of a tag header to the frame. The
header is inserted immediately following the destination MAC address and the
source MAC address. The tag header consists of two bytes of Ethernet Tag Protocol
identifier (TPID, 0x8100) and two bytes of tag control information (TCI).
shows the Ethernet tag header format.
FIGURE 5-2
Ethernet Tag Header Format
By default a single VLAN is configured for every port, which groups all ports into
the same broadcast domain, just as if there were no VLANs at all. This means that
VLAN tagging for the switch port is turned off.
Note –
If you configure a VLAN virtual device for an adapter, all traffic sent or
received by that adapter must be in VLAN-tagged format.
▼
To Configure Static VLANs
1. Create one hostname6.ipge
number file for each VLAN that will be configured for
each adapter on the server.
Use the following naming format, which includes both the VID and the physical
point of attachment (PPA):
VLAN logical PPA = 1000 * VID + Device PPA
ipge123000 = 1000*123 + ipge
This format limits the maximum number of PPAs (instances) you can configure to
1000 in the /etc/path_to_inst file.
For example, on a server with the Sun 10-Gigabit Ethernet adapter having an
instance of 0, belonging to a member of two VLANs, with VID 123 and 224, you
would use ipge123000 and ipge224000, respectively, as the two VLAN PPAs.
TPID (0x8100
3 bits
1
bit
12 bytes
User_priority CFI
VID
Octet
1
2
3
4
