Example: configuring ethernet lfm for ccc, Figure 20: ethernet lfm for ccc – Juniper Networks JUNOS OS 10.4 User Manual
Page 165
link-fault-management {
interface ge-1/1/0 {
pdu-interval 1000;
pdu-threshold 5;
}
}
}
}
}
Related
Documentation
Ethernet OAM
•
•
Ethernet OAM Link Fault Management on page 143
•
Example: Configuring Ethernet LFM for CCC on page 145
•
Example: Configuring Ethernet LFM for Aggregated Ethernet on page 146
•
Example: Configuring Ethernet LFM with Loopback Support on page 148
Example: Configuring Ethernet LFM for CCC
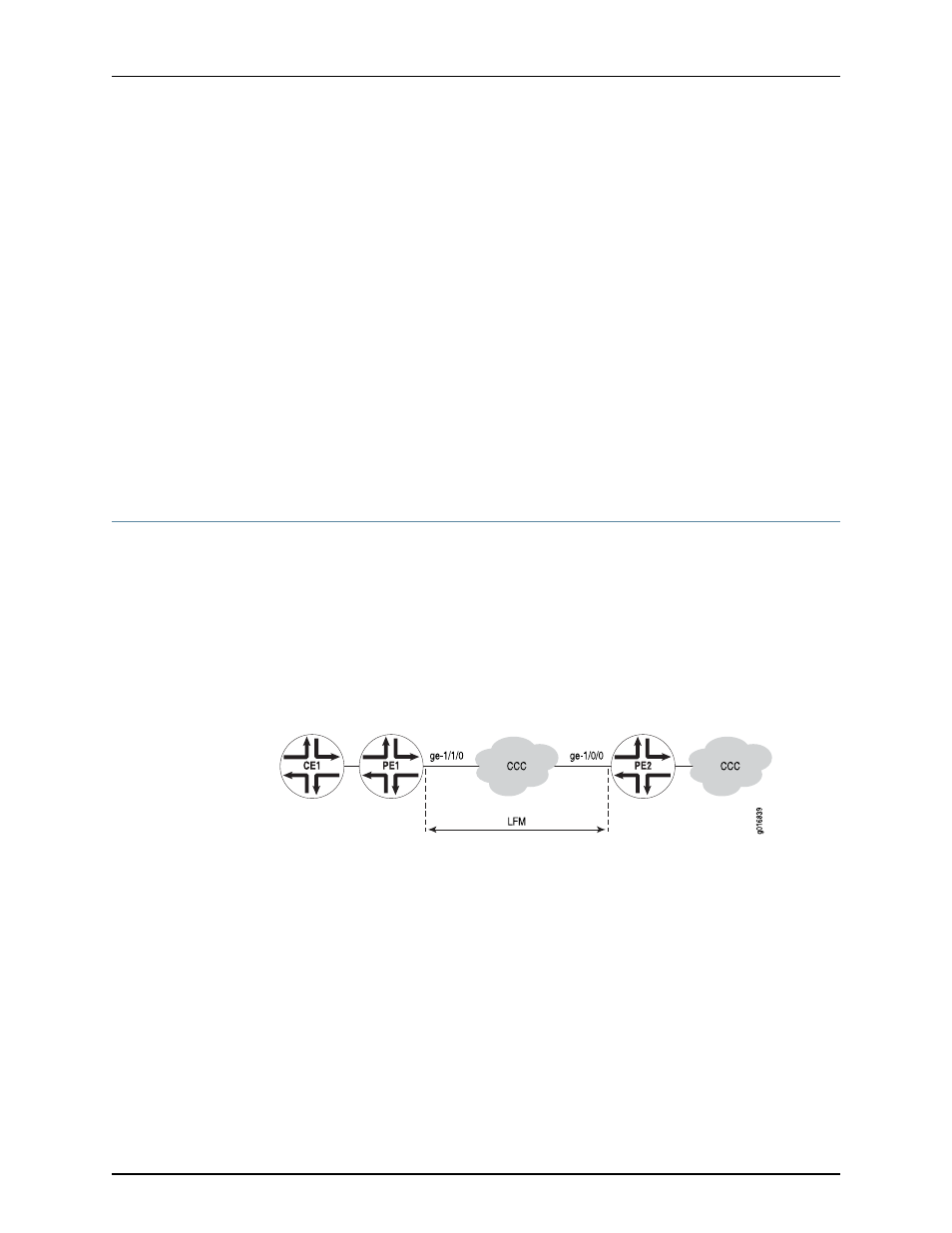
In this example, LFM is configured between two PEs (PE1 and PE2) connected using CCC.
With LFM in place, a link fault will be detected immediately, instead of depending on
routing protocols to find the fault on end-to-end CCC connection. This also helps in
detecting the exact failed link instead of only finding that the end-to-end CCC connectivity
has failed. Also, because LFM runs at the link-layer level, it does not need a IP address
to operate and so can be used where bidirectional fault detection (BFD) cannot.
The links running LFM are shown in
Figure 20: Ethernet LFM for CCC
To configure Ethernet LFM between two PEs connected using CCC:
1.
Configure LFM on the PE1 router with CCC:
[edit]
interfaces ge-1/1/0 {
encapsulation ethernet-ccc;
unit 0;
}
protocols {
oam {
ethernet {
link-fault-management {
interface ge-1/1/0 {
pdu-interval 1000;
145
Copyright © 2013, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Chapter 12: IEEE 802.3ah OAM Link-Fault Management
