Un-mounting an hpss filesystem, Linux ‘proc’ filesystem statistics – IBM RELEASE 7.3 User Manual
Page 354
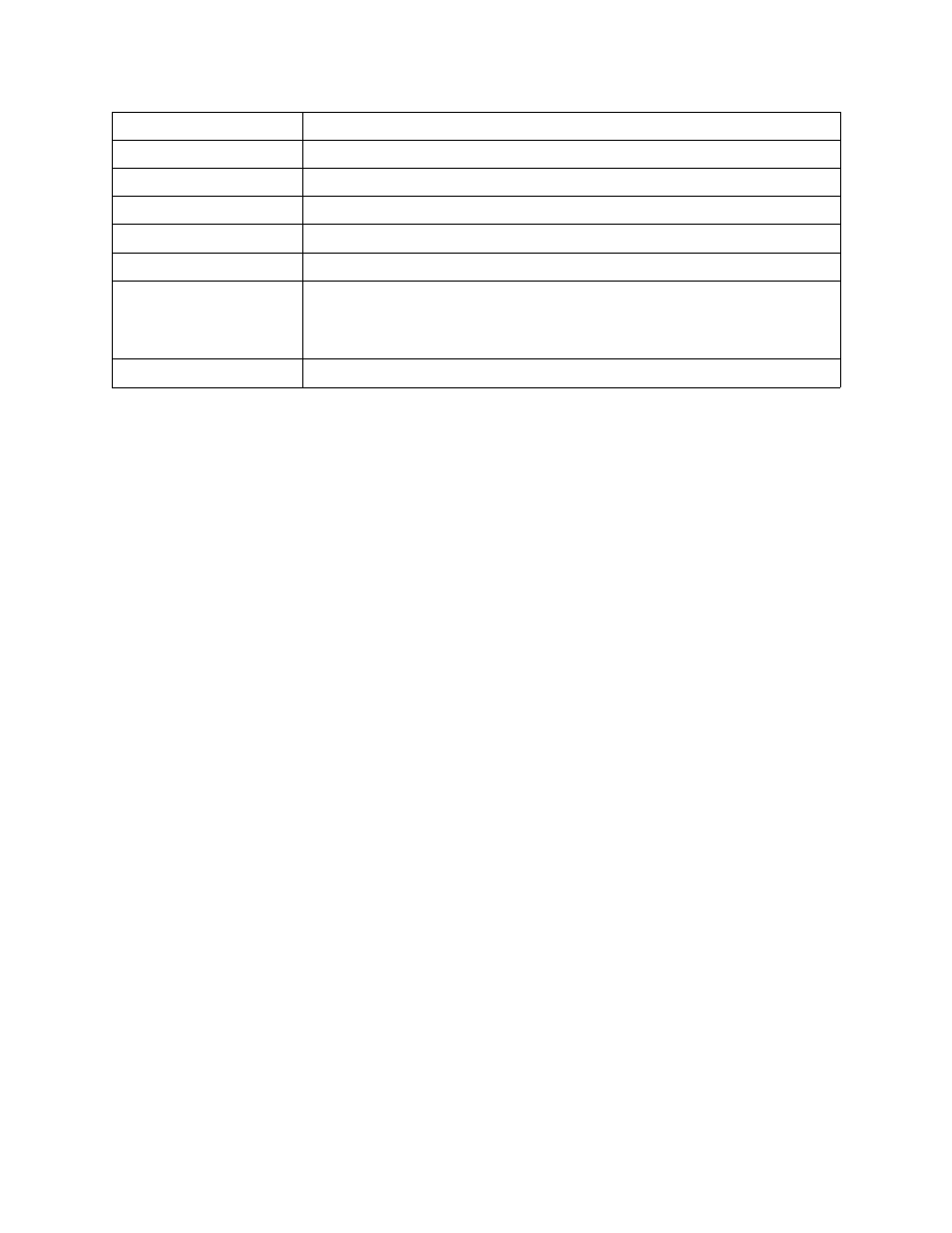
Mount Option
Mount Description
maxiowidth
maxiowidth
princ
Override for principal
auth
Override for authorization type
key
Override keytab type
keytab
Override for keytab file
stage / nostage
Default is stage. This overrides the COS
setting. Application can override this by
specifying O_NONBLOCK on the open() system call. An application cannot override
the nostage setting. Most standard Linux commands / library functions do not
specify O_NONBLOCK so this mount point option will determine what happens.
nfs
Only specify this if nfs is using this mount point.
14.4.4. Un-mounting an HPSS Filesystem
The mount(8) command (without command line parameters) can be used to view the list of hpssfs
mounted entries. An example of a mounted hpssfs entry is as follows:
hpssfs(2553:2554):/ on /tmnt type
hpssfs(rw,noauto,san,dio,ip=eth2,cos=96)
where:
•
2553 is the HPSS VFS Daemon process ID
•
2554 is the HPSS VFS Mount Helper group ID
The umount(8) command is used to unmount the above mounted file system. For example:
# su -
# umount /tmnt
14.4.5. Linux ‘proc’ Filesystem Statistics
The VFS Interface provides a Linux proc filesystem that contains run-time statistic. The statistics can be
viewed by running the 'cat' utility on various proc filesystem files.
•
Show kernel module version:
# cat /proc/fs/hpssfs/version
•
List all active SAN3P LUNs and their associated path:
# cat /proc/fs/san
•
Show or update current trace level for a mounted file system. Valid trace levels are 1 to 5 from
least to most.
# cat /proc/fs/hpssfs/
HPSS Management Guide
November 2009
Release 7.3 (Revision 1.0)
354
