20 bit device processing method, 1 1-bit processing, 2 digit designation processing – MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC 700 Series User Manual
Page 104
99
Bit Device Processing Method
3
3.20 Bit Device Processing Method
As the processing method when the bit device (X, Y, M) is specified, 1-bit processing
and 16-bit processing using digit designation processing are available.
3.20.1 1-bit processing
When a PLC instruction is used, the device used as the target of operation processing
is one bit (one point) of bit device, and multiple bits cannot be specified.
3.20.2 Digit designation processing
When a basic or application instruction is used, the bit device used as the target of
operation processing may have to be specified by digit designation. When the
instruction whose processing unit is 16 bits is specified by this digit designation, up to
16 points can be specified in units of four points.
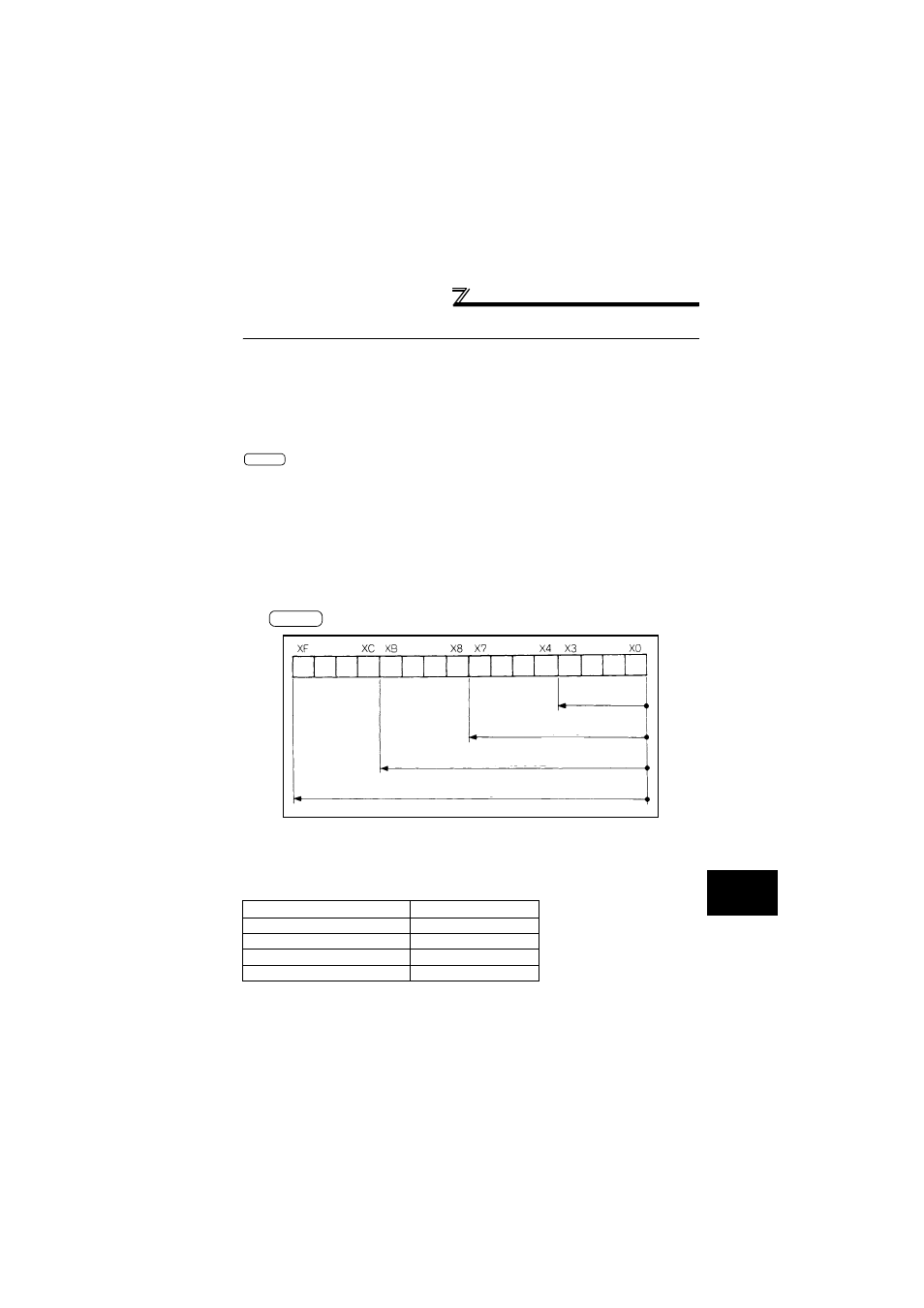
(1) 16-bit instruction: K1 to 4 (4 to 16 points)
Setting ranges of 16-bit data, X0 to F, by digit designation
Fig 3.25 Digit Designation Setting Range for 16-bit Instruction
(a) When there is digit designation on the source (S) side, the numerical values
that can be handled as the source data are as indicated in Table 3.6.
Table 3.6 List of Designated Digits and Numerical
Values That Can Be Handled
Number of Designated Digits
16-bit Instruction
K1 (4 points)
0 to 15
K2 (8 points)
0 to 255
K3 (12 points)
0 to 4095
K4 (16 points)
-32768 to 32767
LD XO,OUT
Example
Example
Designation range
of K1
(8 points)
(12 points)
(16 points)
(4 points)
Designation range of K2
Designation range of K3
Designation range of K4
