A.2.1 ipsec security components, A.2.1.1 authentication header (ah), A.2.1.2 encapsulating security payload (esp) – PLANET MH-1000 User Manual
Page 95
Multi-Homing Security Gateway User’s Manual
A.2.1 IPSec Security Components
IPSec contains three major components:
- Authentication Header (AH): Provides authentication and integrity.
- Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP): Provides confidentiality, authentication, and integrity.
- Internet Key Exchange (IKE): Provides key management and Security Association (SA) management.
These components are discussed below.
A.2.1.1 Authentication Header (AH)
The Authentication Header (AH) is a protocol that provides authentication and integrity, protecting data
from tampering. It provides authentication of either all or part of the contents of a datagram through the
addition of a header that is calculated based on the values in the datagram.
The AH can also protect packets from unauthorized re-transmission with anti-replay functionality. The
presence of the AH header allows us to verify the integrity of the message, but doesn't encrypt it. Thus, AH
provides authentication but not privacy. ESP protects data confidentiality. Both AH and ESP can be used
together for added protection.
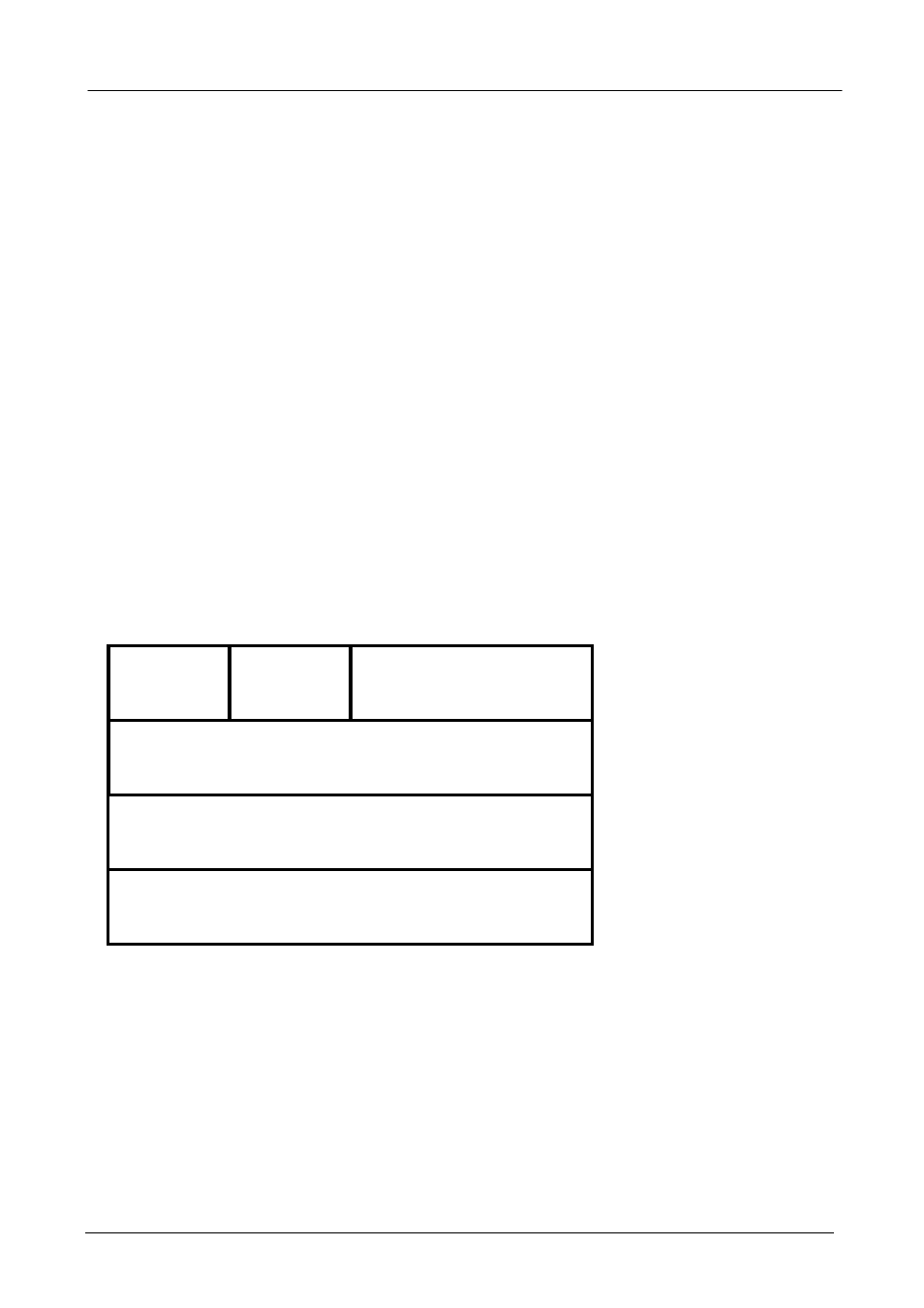
A typical AH packet looks like this:
Reserved
Payload
Length
Next
Header
SPI
Authentication Data
Sequence Number
A.2.1.2 Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP)
Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) provides privacy for data through encryption. An encryption
algorithm combines the data with a key to encrypt it. It then repackages the data using a special format,
and transmits it to the destination. The receiver then decrypts the data using the same algorithm. ESP is
usually used with AH to provide added data security.
ESP divides its fields into three components…
ESP Header: Placed before encrypted data, the ESP Header contains the SPI and Sequence Number. Its
- 91 -
