Operation, Protocols and standards – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 83
4
With an IPv6 address obtained through stateless address autoconfiguration, a device automatically
enables the stateless DHCPv6 function after it receives an RA message with the managed address
configuration flag (M flag) set to 0 and with the other stateful configuration flag (O flag) set to 1.
NOTE:
Stateless address autoconfiguration means that a node automatically generates an IPv6 address based on
the information obtained through router/prefix discovery. For details, refer to
IPv6 Basics Configuration in
the
IP Services Volume.
Operation
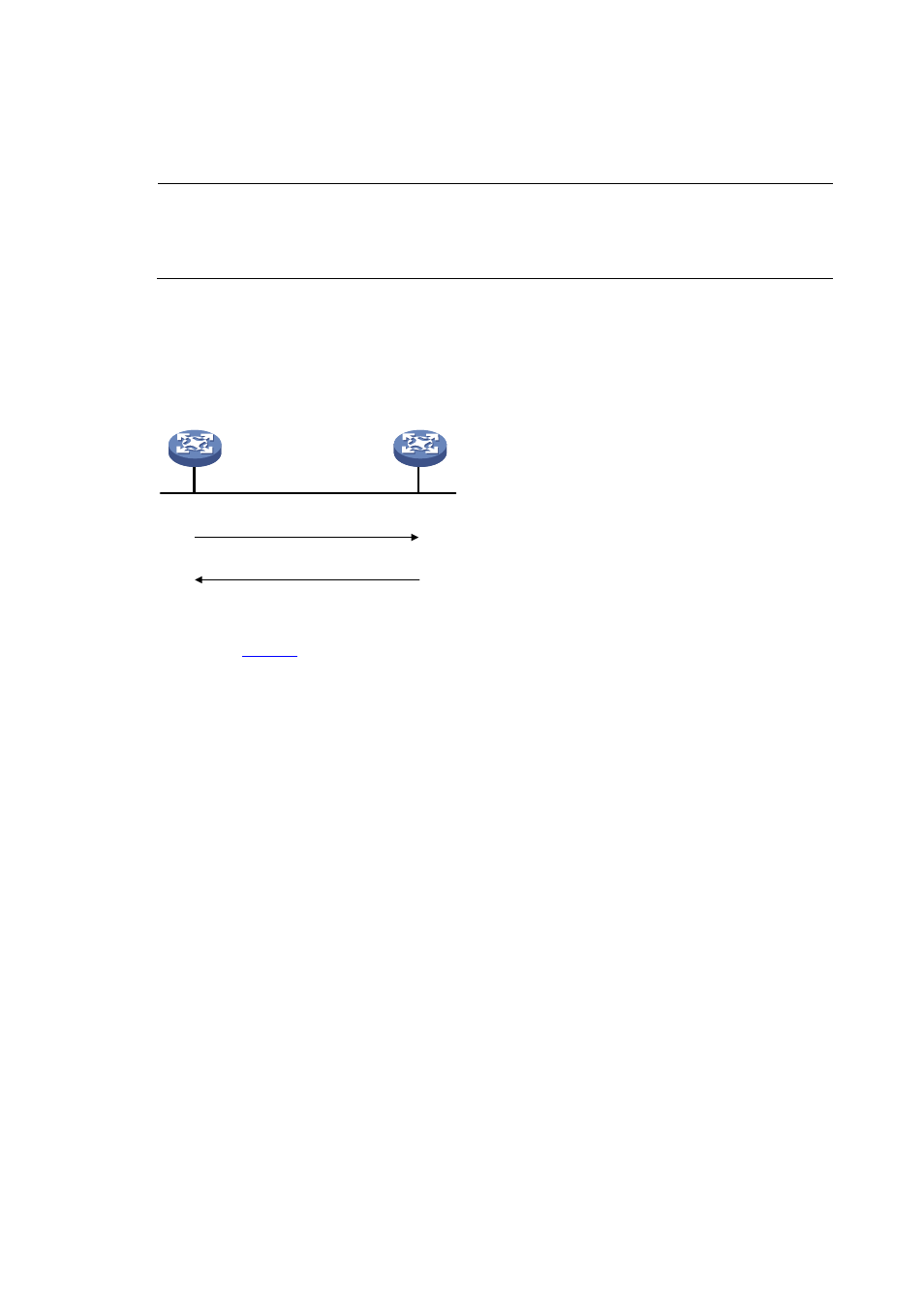
Figure 5 Operation of stateless DHCPv6
Information-request:
includes an Option Request option
Reply:
includes the requested options
DHCPv6 client
DHCPv6 server
As shown in
, stateless DHCPv6 operates as follows:
1.
The DHCPv6 client multicasts an Information-request message to the multicast address of all
DHCPv6 servers and DHCPv6 relay agents. The Information-request message contains an Option
Request option, specifying the configuration parameters that the client requests from the DHCPv6
server.
2.
After receiving the Information-request message, the DHCPv6 server returns the client a Reply
message containing the requested configuration parameters.
3.
The client checks the Reply message. If the obtained configuration parameters match those
requested in the Information-request message, the client performs network configuration with the
parameters. If not, the client ignores the configuration parameters. If multiple replies are received,
the first received reply will be used.
Protocols and Standards
•
RFC 3736, Stateless Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Service for IPv6
•
RFC 3315, Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6 (DHCPv6)
•
RFC 2462, IPv6 Stateless Address Autoconfiguration
•
RFC 3633, IPv6 Prefix Options for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) version 6
