Ipv6 over ipv4 tunnel, Implementation – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 148
2
processing, but may also lead to upper-layer application failures. Furthermore, they will still face the
problem that IPv4 addresses will eventually be used up. Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6) adopting the
128-bit addressing scheme completely solves the above problem. Since significant improvements have
been made in address space, security, network management, mobility, and QoS, IPv6 becomes one of
the core standards for the next generation Internet protocol. IPv6 is compatible with all protocols except
IPv4 in the TCP/IP suite. Therefore, IPv6 can completely take the place of IPv4.
Before IPv6 becomes the dominant protocol, networks using the IPv6 protocol stack are expected to
communicate with the Internet using IPv4. Therefore, an IPv6-IPv4 interworking technology must be
developed to ensure the smooth transition from IPv4 to IPv6. In addition, the interworking technology
should provide efficient, seamless information transfer. Currently, multiple transition technologies and
interworking solutions are available. With their own characteristics, they are used to solve
communication problems in different transition stages under different environments.
Currently, there are three major transition technologies: dual stack (RFC 2893), tunneling (RFC 2893),
and NAT-PT (RFC 2766).
NOTE:
•
For information about dual stack, see
IPv6 Basics Configuration in the IP Services Volume.
•
For information about NAT-PT, see
NAT-PT Configuration in the IP Services Volume.
•
The device supports IPv6 on the provider edge routers (6PE) – a transition technology.
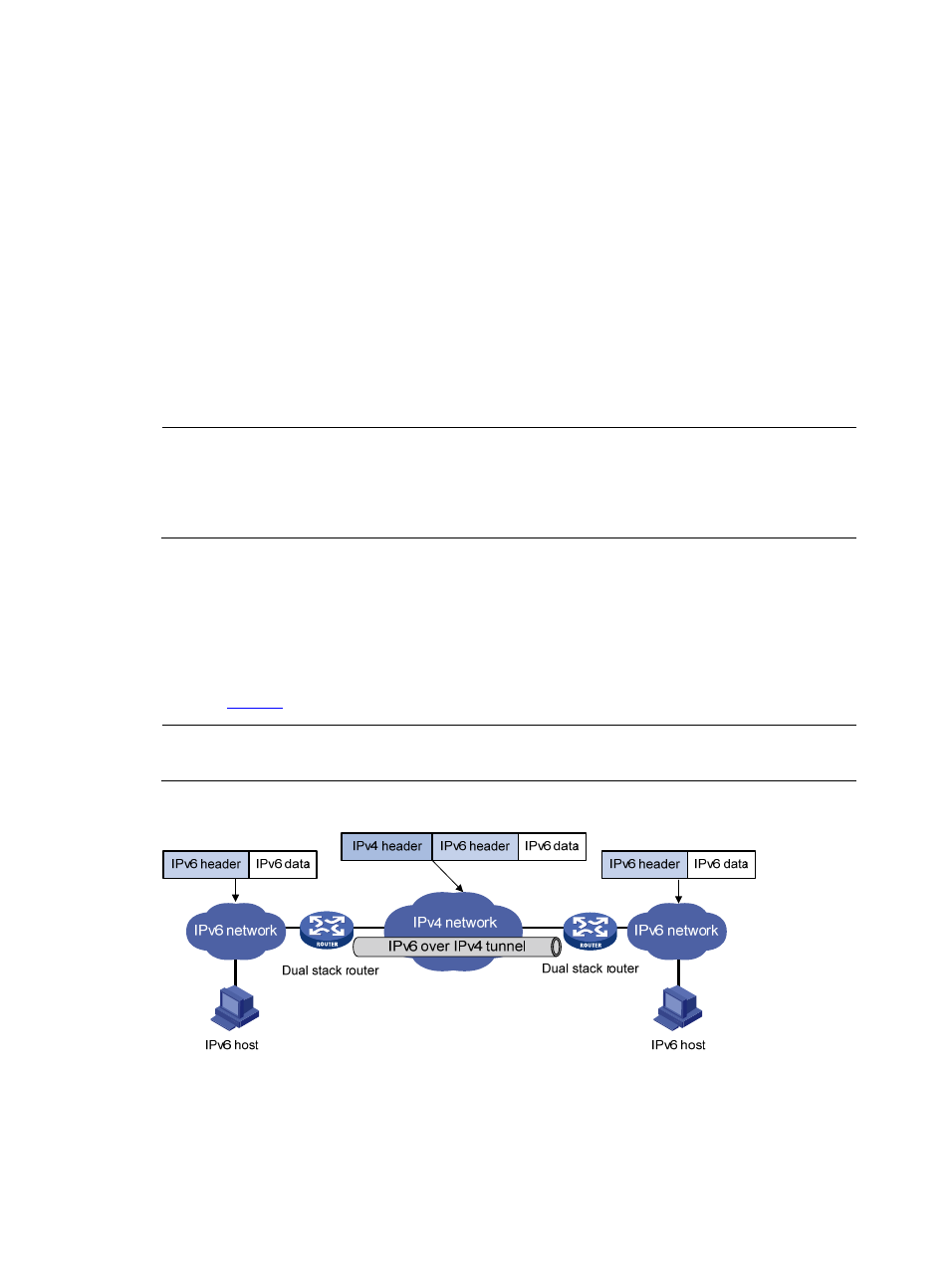
IPv6 over IPv4 Tunnel
Implementation
The IPv6 over IPv4 tunneling mechanism adds an IPv4 header to IPv6 data packets so that IPv6 packets
can pass an IPv4 network through a tunnel to realize interworking between isolated IPv6 networks, as
shown in
.
NOTE:
The devices at both ends of an IPv6 over IPv4 tunnel must support the IPv4/IPv6 dual stack.
Figure 1 IPv6 over IPv4 tunnel
The IPv6 over IPv4 tunnel processes packets in the following way:
1.
A host in the IPv6 network sends an IPv6 packet to the device at the source end of the tunnel.
