Proxy arp configuration, Proxy arp overview, Proxy arp – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 13
1
Proxy ARP Configuration
This chapter includes these sections:
•
•
•
Displaying and Maintaining Proxy ARP
•
Proxy ARP Configuration Examples
Proxy ARP Overview
If a host sends an ARP request for the MAC address of another host that actually resides on another
network (but the sending host considers the requested host is on the same network) or that is isolated from
the sending host at Layer 2, the device in between must be able to respond to the request with the MAC
address of the receiving interface to allow Layer 3 communication between the two hosts. This is
achieved by proxy ARP. Proxy ARP hides the physical details of the network.
Proxy ARP involves common proxy ARP and local proxy ARP, which are described in the following
sections.
NOTE:
The term proxy ARP in the following sections of this chapter refers to common proxy ARP unless otherwise
specified.
Proxy ARP
A proxy ARP enabled device allows hosts that reside on different subnets to communicate.
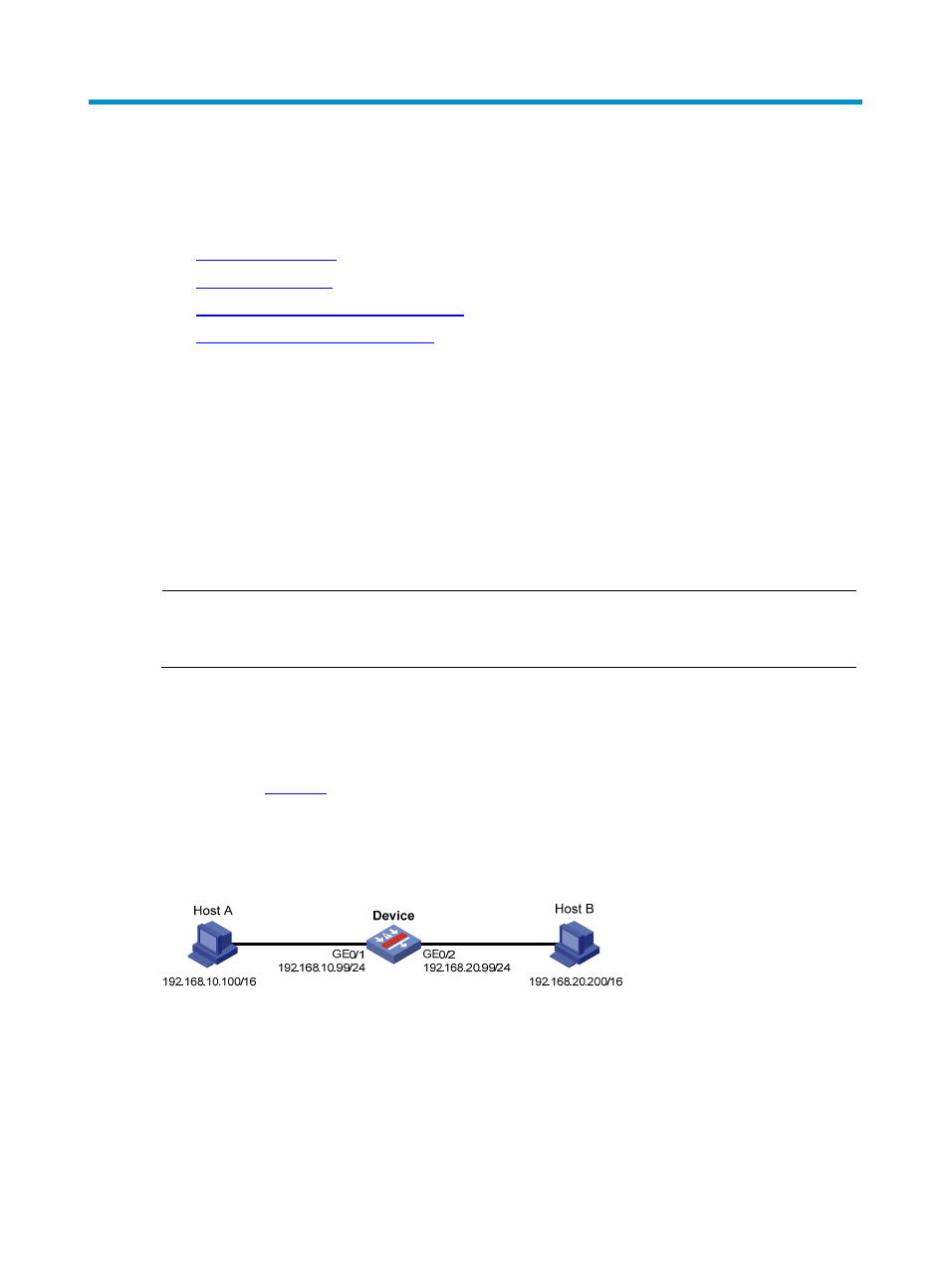
As shown in
, the device connects to two subnets through GigabitEthernet 0/1 and
GigabitEthernet 0/2. The IP addresses of the two interfaces are 192.168.10.99/24 and
192.168.20.99/24. Host A and Host B have the same prefix 192.168.0.0 assigned and connect to
GigabitEthernet 0/1 and GigabitEthernet 0/2, respectively.
Figure 4 Application environment of proxy ARP
Because Host A considers that Host B is on the same network, it broadcasts an ARP request for the MAC
address of Host B. Host B, however, cannot receive this request because it locates in a different broadcast
domain.
You can solve the problem by enabling proxy ARP on GigabitEthernet 0/1 of the device. After that, the
device can reply to the ARP request from Host A with the MAC address of GigabitEthernet 0/1, and
forward packets sent from Host A to Host B. In this case, the device acts like a proxy of Host B.
