Instantiation mode, Instantiating an forwarding group – H3C Technologies H3C SR8800 User Manual
Page 91
82
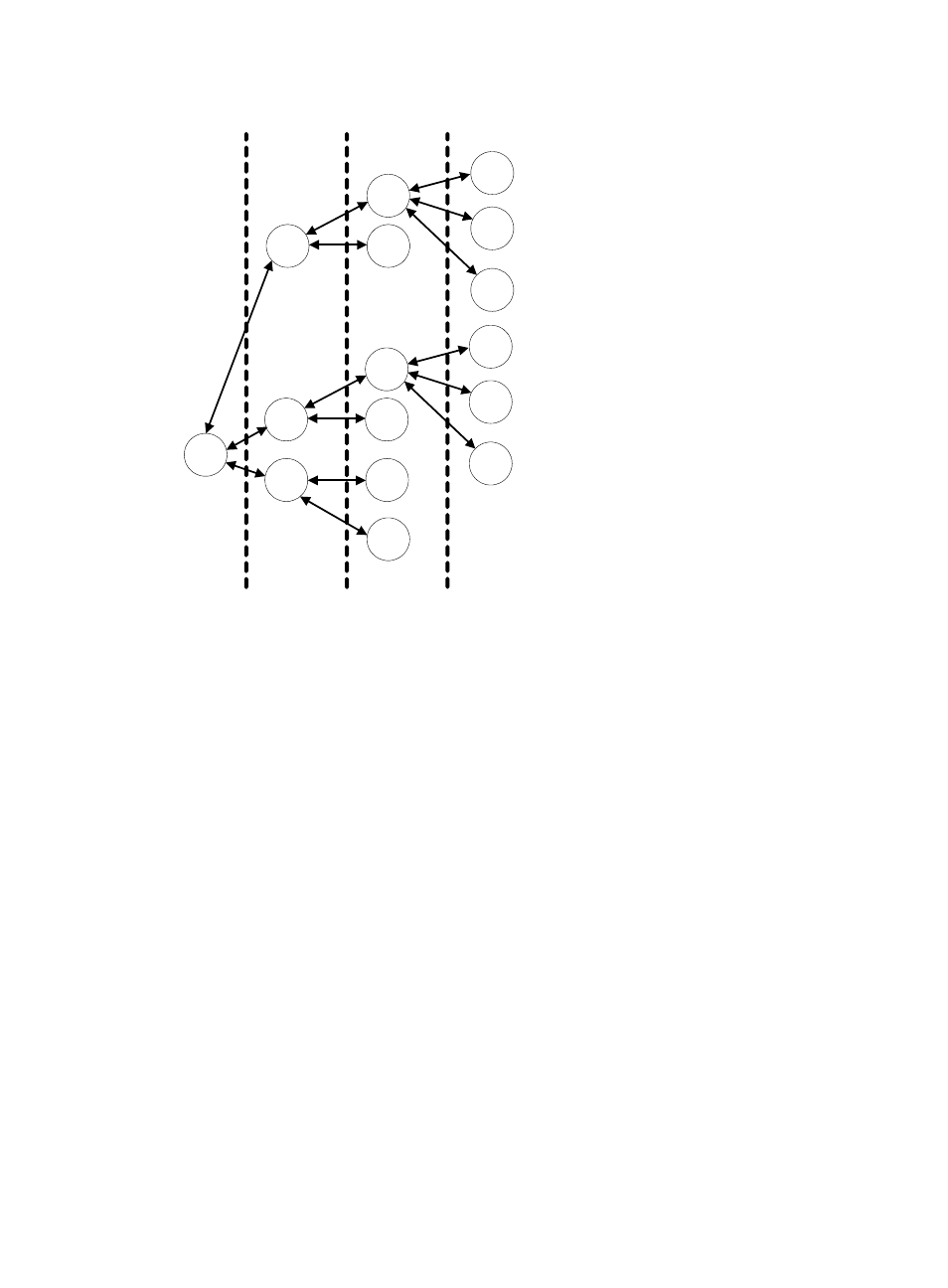
Figure 27 Instantiated forwarding groups in an scheduler policy
shows the results of a sample instantiation: forwarding group A at Layer 1 is instantiated by
QoS-local-ID into two instances with the same internal structure.
Instantiation mode
Instantiation can be performed in one of the following modes:
•
Match mode—Instances created from the same forwarding group in this mode are differentiated by
their match criteria. Traffic satisfying the match criteria configured for a forwarding group enters the
scheduler of the forwarding group. Match criteria can be QoS-local IDs. You can mark a packet
with a QoS-local ID as needed, for example, based on its source IP address. Packets from different
IP address segments can be marked with different QoS-local IDs.
•
Group mode—An instance created in this mode is only a set of child forwarding groups nested in
the source forwarding group. No match criteria are configured for the source forwarding group.
However, the child forwarding groups nested in the source forwarding group must be configured
with match criteria.
Because forwarding classes cannot be instantiated, you cannot instantiate a forwarding group with
nested forwarding classes in the group mode.
Instantiating an forwarding group
When instantiating a forwarding group, you must specify the scheduler policy layer of the forwarding
group. The forwarding groups nested in a scheduler policy are at Layer 1, and the forwarding groups
nested in a forwarding group at Layer 1 are at Layer 2. Instantiation of a forwarding group must be
performed in the corresponding layer view in the specified scheduler policy.
To instantiate a forwarding group:
0
2-C
1-B
PORT layer
Layer 1
Layer 2
FC layer
1- A
2-B
2-A
FC-A
(User 1)
QoS-local-ID 10
2- B
FC-B
FC …
…
1-A
2-B
2-A
FC-A
(User 2)
QoS-local-ID 20
FC-B
FC …
…
